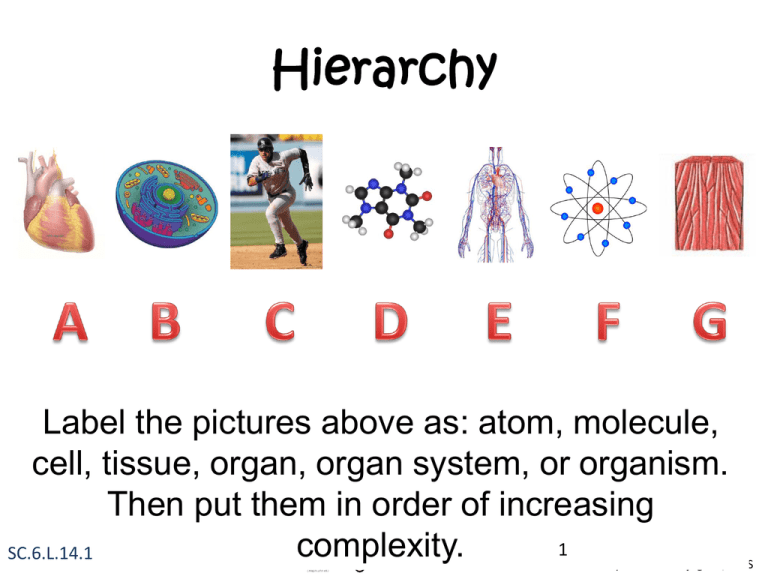
Hierarchy
Label the pictures above as: atom, molecule,
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, or organism.
Then put them in order of increasing
1
complexity.
SC.6.L.14.1
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Cell Theory
Which of the above statements is NOT part of
the Cell Theory? How do you know?
SC.6.L.14.2
2
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Homeostasis
What processes of cellular homeostasis are
represented by the images above? Explain
why those processes are important.
SC.6.L.14.3
3
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Parts of a Cell
What are some key differences between plant cells, animal cells, and bacteria cells?
SC.6.L.14.4
4
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Human Body Systems
How would a problem with your lungs effect your heart?
How are the systems inter-related?
SC.6.L.14.5
5
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Infectious Agents
Compare and contrast the infectious agents
above. Include information about how they are
transmitted and treated and if/how they can be
prevented
6
SC.6.L.14.6
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Classification of Life
What are the 3 Domains and how do the 6
Kingdoms fit within them?
SC.6.L.15.1
7
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Fossil Evidence
Relative Dating
(Law of Superposition)
SC.7.L.15.1
Carbon Dating
(Absolute dating)
8
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Adaptation or Extinction
Explain how polar bears would have to
adapt to their changing environment in order
to avoid extinction
SC.7.L.15.3
9
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
DNA
The diagram to the left shows
the structural hierarchy of
genetic material inside a cell
including: nucleus,
chromosome, gene, and DNA
Describe the hierarchy in your own words as it
applies to the transmission of genetic material
SC.7.L.16.1
10
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Punnett Squares
• What is the difference between organisms
that are heterozygous dominant and
homozygous dominant?
SC.7.L.16.2
11
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
• Mitosis is a process of cell duplication, or reproduction,
during which one cell gives rise to two genetically
identical daughter cells.
• Meiosis, on the other hand, is a division of a germ cell
involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to
four gametes, or sex cells, each possessing half the
number of chromosomes of the original cell.
• Mitosis is used by single celled organisms to reproduce;
it is also used for the organic growth of tissues, fibers,
and mibranes. Meiosis is useful for sexual reproduction
of organisms; The male and female sex cells, e.g. the
spermazoa and egg, fuse to create a new, singular
biological organism.
12
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Mitosis and Meiosis
Which of the cells above went through mitosis
and which went through meiosis? How do you
know?
13
SC.7.L.16.3
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Relationships between Organisms
Organism
Benefited
Organism
Harmed
Organism
Unaffected
Place the terms correctly in the Venn Diagram.
Give an example of each relationship.
SC.7.L.17.2
14
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Producers, Consumers, and
Decomposers
What role does each organism have in the
food chain/web?
SC.7.L.17.1
15
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Limiting Factors
Which limiting factors are represented by the images
above? What are examples of additional limiting
factors?
SC.7.L.17.3
16
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Conservation of Mass and Energy
• Energy: states that the total amount of energy in an isolated
system remains constant over time. This law means that
energy can change its location within the system, and that it
can change form within the system but not change in amount
of total energy.
• Mass: states that the mass of an isolated system will remain
constant over time. This law means that mass cannot be
created or destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space
and changed into different types of particles
Create a statement that combines both laws
into one concept. Give an example of how
these laws apply to living systems.
17
SC.8.L.18.4
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Photosynthesis and Respiration
• What is created during photosynthesis
that is used by the plant for energy?
What is created during photosynthesis
that is used by humans?
SC.8.L.18.1, SC.8.L.18.2
18
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS
Carbon Cycle
• All living things are made of carbon. Carbon is also a part of the ocean, air, and even rocks.
Because the Earth is a dynamic place, carbon does not stay still. It is on the move!
• In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to some oxygen in a gas called carbon dioxide.
• Plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make their own food and grow. The carbon
becomes part of the plant. Plants that die and are buried may turn into fossil fuels made of
carbon like coal and oil over millions of years. When humans burn fossil fuels, most of the
carbon quickly enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
• Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas and traps heat in the atmosphere. Without it and other
greenhouse gases, Earth would be a frozen world. But humans have burned so much fuel
that there is about 30% more carbon dioxide in the air today than there was about 150 years
ago, and Earth is becoming a warmer place. In fact, ice cores show us that there is now more
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere than there has been in the last 420,000 years.
• CARBON is STORED in the OCEANS and in
FORESTS because water and trees absorb it
SC.8.L.18.3
19
Created by: R. Hallett-Njuguna, SCPS