CLONING - Bioenviroclasswiki
advertisement

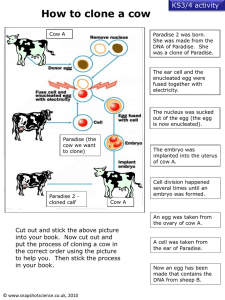
Things to Do • As you enter the class collect one laptop, make sure you write your name and also the number of the laptop in the book. • Complete your warm-up Quiz and get ready for the class. • There is a big difference between reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning. • Reproductive cloning involves creating an embryo and then actually implanting it into a uterus. It is highly unlikely this could work for humans, and for ethical and scientific reasons, all but a handful of radical scientists are strongly opposed to attempting it. Therapeutic cloning creates an embryo but never implants this in a uterus as it intends to only create patient specific stem cells, not a person. • Many countries and some US states already have legislation that permits therapeutic cloning while continuing to prohibit reproductive cloning. The vast majority of scientists support the prohibitions against reproductive cloning. GENETICS 4.4.11 CLONING “Big Question” • Humans have the technology to change the biology and chemistry of living organisms but should they? • Share your thoughts with your partner and list down what you both think. We can then share it with the class. • Time 2 minutes. Warm-up Video Be prepared to answer • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gPxH3O5C T-8 “Cloning could be considered one of the greatest discoveries of all time!” after watching the video, what are your thoughts on cloning? Can it be beneficial to society? I expect each one of you to give what you feel about cloning after watching the video and whether it will be beneficial to society. Enduring Understanding • • • • We have the technology to manipulate DNA: Clones Designer Babies -Some families have difficulties in conceiving that can be overcome. • GMO’s Learning Activities • • • • Warm-up quiz( On the Previous day Lesson) Quiz time –Online quiz on animation Case Study –analysis with a partner Venn diagram – Determine the similarities and differences between reproductive and therapeutic cloning. • Venn Diagram –Pros and cons of cloning Project presentation on • Just Because We Can, Does it Mean We Should? Choose any one of the topics given and present your findings before the class. EXPECTATIONS • Be an active participant, in fact I would like to learn from you today. • I would like you to watch all animations/video very carefully and be prepared to answer at the end of the animation. Be alert as the animations don’t have music but it is followed by questions. • You will be given a case study on cloning, an article on cloning, article on ethics and Human Cloning. Guess what? • You can have a laptop for use today to clone. How is Cloning Done? • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/c loning/whatiscloning/twinning.swf In nature, twins occur just after fertilization of an egg cell by a sperm cell. In rare cases, when the resulting fertilized egg, called a zygote, tries to divide into a two-celled embryo, the two cells separate. Each cell continues dividing on its own, ultimately developing into a separate individual within the mother. Since the two cells came from the same zygote, the resulting individuals are genetically identical. Artificial embryo twinning uses the same approach, but it occurs in a Petri dish instead of in the mother's body. This is accomplished by manually separating a very early embryo into individual cells, and then allowing each cell to divide and develop on its own. The resulting embryos are placed into a surrogate mother, where they are carried to term and delivered. Again, since all the embryos came from the same zygote, they are genetically identical. Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer • This was the method used to create Dolly the Sheep. • To make Dolly, researchers isolated a somatic cell from an adult female sheep. Next, they transferred the nucleus from that cell to an egg cell from which the nucleus had been removed. After a couple of chemical tweaks, the egg cell, with its new nucleus, was behaving just like a freshly fertilized zygote. It developed into an embryo, which was implanted into a surrogate mother and carried to term. • The lamb, Dolly, was an exact genetic replica of the adult female sheep that donated the somatic cell nucleus to the egg. She was the first-ever mammal to be cloned from an adult somatic cell. Video on cloning Dolly the sheep Biology: Nuclear Transfer http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hepoJgGJtNc Before you actually see an animation on SCNT I would like you to see a very short video on Nuclear Transfer and the sterile technique involved. Cloning 101 You Tube Dolly the Sheep Animation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q0B9Bn1WW_4 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hepoJgGJtNc Video on dolly the Sheep, one you need to watch later at home How does SCNT differ from the natural way of making an embryo? • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/c loning/whatiscloning/scnt.html • Natural Reproduction and Somatic cell Nuclear Transfer ( this link is good for review) • You can write an answer to this question in your note book. Do you want to Clone a mouse and have fun? • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/c loning/clickandclone/ • CLICK AND CLONE • Now that you know the steps involved in SCNT, you can have fun in cloning this mouse by making use of the above link and it is a good review as well. QUIZ TIME –NO STRESS • Now that you have a fair understanding of cloning be ready to take up a quiz. • It is based on just the concept of cloning. IS It Cloning or not? • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/clonin gornot/ • Test your cloning savvy with this interactive quiz. • Play Cloning • I would like each one of you to answer this questions. Those who know the answer Don’t have to get super excited. As usual I will call out the name of the person. Everyone will get a chance to play this game. • Have Fun. Cloning using undifferentiated cells Therapeutic cloning • Making copies of cells is known as therapeutic cloning and its aim is to develop cells which have not yet gone through the process of differentiation. • Since the first technique in this are involved using embryos, the cells are referred to as embryonic stem cells. Human embryos are produced and allowed to grow for a few days into a small ball of cells. These cells are not yet specialized and when SCNT is used, the cells can grow into any of a large number of different specialized tissues. • Other sources of stem cells are cells from the umbilical cord or cells from aborted fetuses. Therapeutic Cloning • Aims at cell therapy where diseased cells are replaced with healthy ones. • Cell therapy is used for people suffering from Parkinson’s disease, patient suffering from spinal cord injury. • Bone marrow transplants for patients with leukemia, new skin cells for burn victims and to grow new corneas for some forms of visual impairments are examples of therapeutic cloning 4.4.13 Discuss the ethical issues of therapeutic cloning in humans • Arguments in favor of cloning focus on: • The ability to cure serious diseases with cell therapy: currently leukemia and in the future possibly cancer and diabetes. • Growing skin to repair a serious burn • growing new heart muscle to repair an ailing heart • Growing new kidney tissue to rebuild a failing kidney 4.4.13 Discuss the ethical issues of therapeutic cloning in humans • Arguments in favor of cloning focus on: • The ability to cure serious diseases with cell therapy: currently leukemia and in the future possibly cancer and diabetes. • Growing skin to repair a serious burn • new heart muscle to repair an ailing heart • Growing new kidney tissue to rebuild a failing kidney Is it ethically acceptable to generate a new human embryo for the sole purpose of medical research? • Some of the concerns raised about therapeutic cloning relate to: • Fears of it leading to reproductive cloning • Use of embryonic stem cells involves the creation and destruction of human embryos (although it is possible to use embryos left over from IVF treatment which would be destroyed otherwise • Embryonic stem cells are capable of many divisions and may turn into tumors. Case study -Cloning • http://home.southernct.edu/~hotta2/Activities/cloning .html • Cloning Case Study • http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg19726493.00 0-therapeutic-cloning-cures-parkinsons-mice.html • Therapeutic cloning cures Parkinson's mice (Article) I would like you to read the case study and also the articles given to you and give your opinion when asked. Silent reading time – 3 minutes/4 minutes Venn Diagram Assignment • Links that can help you • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/c loning/cloningrisks/ • Draw Venn diagram to determine similarities and differences between reproductive and therapeutic cloning. • Draw Venn Diagram to illustrate pros and cons of cloning WHY CLONE? • • • • Cloning for medical purposes Cloning stem cells for research "Pharming" for drug production Reviving Endangered or Extinct Species Could we really clone dinosaurs? • What would you need to do this? • Do you think a closely related species which can serve as a surrogate mother is available? • Do you think DNA of the dinosaur can remain undamaged for such a long time? "Can we really clone endangered or extinct animals?" • Can we really clone endangered or extinct animals? To date, the most successful attempt to do so was the cloning of a gaur, a rare oxlike animal from southeast Asia. Scientists used a cow to bring the cloned baby gaur, named Noah, to term. Two days after birth, however, Noah died from a common bacterial infection. More interesting news on Cloning • Is Cloning Endangered Species the solution to Other endangered species that may be cloned conserve? include the African bongo antelope, the Sumatran tiger, the cheetah and the giant panda. Cloning extinct animals such as the wooly mammoth or Tasmanian tiger is much more difficult due to the lack of properly conserved DNA. Efforts are underway to clone the very recently extinct bucardo mountain goat, formerly of Spain. However, if this effort succeeds it will only produce female clones. Scientists speculate they may be able to remove one X chromosome and add a Y chromosome from a related goat species to make a male. Cloning Humans? • To clone or not to clone: that is the question. The prospect of cloning humans is highly controversial and raises a number of ethical, legal and social challenges that need to be considered. Why would anyone want to clone humans? Some reasons include: To help infertile couples have children • To replace a deceased child • From a technical standpoint, before humans are cloned, we need to have a good idea of the risks involved. How sure can we be that a cloned baby will be healthy? What might go wrong? When will stem cell research lead to new disease cures? • Limited stem cell-based therapies are already in widespread clinical use, in the form of bone marrow and cord blood transplants. These procedures, which save many lives every year, demonstrate the validity of stem cell transplantation as a therapeutic concept. Similar successes should be possible with unlimited stem cells for many other diseases, but it is impossible to predict how soon this will happen. Human Cloning? • Preliminary experiments have shown that it may be possible to clone humans, too. • In 2004, the UK’s human Fertilization and Embryology Authority (HFEA) gave a Newcastle biomedical team permission to create human embryos that are clones to patients. The team is licensed to use the embryos to make embryonic stem cells to investigate diabetes, though their work could be relevant to diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Points in favor of human Cloning • Parents at high risk of producing offspring with genetic disease would have the opportunity of healthy children • Infertile couples could have children of their own. • Cloning technologies are being developed to deliver organs for transplants that are entirely compatible and are not rejected by the recipients immune system. • Cloning techniques are as and reliable as other comparable medical procedures. • New treatments for genetic diseases are planned and may shortly be achieved. Points against human cloning • Human beings might be planned and produced with the sole intention of supplying ‘spare parts’ for a related human being with some passing health problem. • Cloning could facilitate ‘improving’ humans by designing and delivering a race of ‘superior’ people. • Cloning techniques are experimental and unreliable and unreliable, resulting in the death of many embryos and newborns, since there are still so many unknown factors operating. Points against human cloning • The traditional concept of ‘family’ is of a group of people with individuality, and with a clear sense of personal worth. • Clones might have diminished rights and a lessened sense of individuality. • Some aspects of human life should exist above the values and standards of the laboratory. • Many believers consider that cloning is against the will of the god. • Human inventiveness must not tamper with ‘nature’, regarding human life issues. Cloning Scientists create human brain cells • http://www.guardian.co.uk/science/2012/jan/ 29/brain-cloning-breakthrough-mentalillness?INTCMP=SRCH Primer on Ethics and Human Cloning • Glenn McGee • An ActionBioscience.org original article Articlehighlights • Before cloning is considered permissible medicine for human infertility, society needs to resolve many questions, including: • Is cloning unnatural self-engineering? • Will failures, such as deformed offspring, be acceptable? • Will cloning lead to designer babies who are denied an open future? • Who is socially responsible for cloned humans? • Do clones have rights and legal protection? http://www.actionbioscience.org/biotech/mcgee.html Just Because We Can, Does it Mean We Should? • • • Geneticists are finding ways to change information in genes and move these messages to new locations. These advances can have an impact in science on individuals and to society. As a member of society you should have a understanding of the benefits and potential harm this technology could lead to. You should also start to form an educated opinion around these topics. Choose one of these topic questions and follow the instructions to complete a presentation that will be shared with the rest of the class. The method of your presentation is up to you: Video, Poster, power point, , other. Your presentation must include an introduction with background information about your topic and positive and negative arguments with supporting evidence. You must also include your opinion, for or against, about your topic with supporting evidence (see the rubric). • Should we have the right to know the results of genetic testing? • Should we be able to select the traits to make a perfect baby? • Should we clone extinct species? • Should we be allowed to change our own DNA during our lives? • Should we be able to select against embryos carrying genetic diseases? • Should we clone humans? Rubric will be given Reference/Resource • http://i-biology.net/ibdpbio/04-genetics-and-geneticengineering/genetic-engineering-and-biotechnology/ Stephen Taylor click 4 Biology IB Biology By Heinemann IB Biology By C.J. Clegg, IB Biology By Minca Peters Biology By CampBell Reece http://www.tellmeaboutstemcells.org/impact-of-stemcells/index.php Questions and answers about stem cells (interesting) 4.4.11 Define Clone • A clone is a group of genetically identical organisms or a group of cells derived from a single parent cell. 4.4.12outline a technique for cloning using differentiated animal cell • The technique for cloning using differentiated cells is mostly somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) but the use made of the produced cell can be quite different. Generally reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning are discussed separately. • In 1996, a sheep by the name of Dolly was born. She was the first clone whose genetic material did not originate from an egg cell. Reproductive cloning of Dolly Reproductive Cloning • Reproductive cloning creates a new individual. The best known example is Dolly, the sheep. • The technique used to create Dolly is known as SCNT. • First you take the nucleus from a somatic (body cell). In the case of Dolly, it was the nucleus from cell in the udder of her “mother”. • An unfertilized egg was collected from another sheep and its nucleus was removed. • Using a small and brief electric shock, the egg cell and the nucleus from the cultured somatic cell were fused together. • The new cell developed invitro in a similar way to a zygote and started to form an embryo • The embryo was placed in the womb of a surrogate mother sheep. • The embryo developed normally. • Dolly was born, and was presented to the world as a clone of the original donor sheep. • And with reference to therapeutic cloning the notes are there in the previous slides.