EDVOTEK 225 DNA Fingerprinting
advertisement

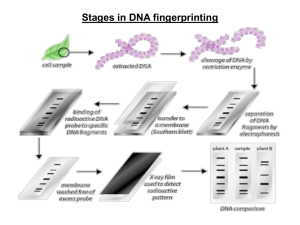
EDVOTEK 225 DNA Fingerprinting Spring 2010 Terry Kotrla, MS, MT(ASCP)BB DNA Fingerprinting • Also called – DNA profile analysis – DNA typing • Involves electrophoretic anlaysis of DNA fragment sizes generated by restriction enzymes • More accurate an unambiguous then blood typing Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes are endonucleases that catalyze cleavage of phosphate bonds • Require Mg-2 for activity • Generate 5’ phosphae and 3’ hydroxyl group • Endonuclease claves at specific sequence of bases. • Produce by bacteria Restriction Enzymes • Names after organism discovered in. – First 3 letters of genus – Strain or substrain – Roman numeral to designate one of the enzymes produced by the same organism. Restriction Enzymes • Require a specific double stranded sequence of nuceotide bases to cut DNA • Recognition sites usually 4-8 base pairs within or neat site • Frequently symmetrical, both DNA strands have same base sequence when read 5’ to 3’, ie, palindrome. • In forensics 2 most commonly used are Hae III and Hinf I. RFLP • Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms – http://tinyurl.com/2evjhfu Restriction Enzymes • Size of fragments depends on distances between recognition sites. • Long DNA molecule will have higher probability recognition site will be present. • Restriction enzyme with 6 bp recognition site expected to cut human DNA into approximately 750,000 different fragments Fragments • No 2 individuals have same pattern of recognition sites. – Alleles result in alternative expressions of genetic traits, dominant or recessive – Two copies of gene at given locus, mom & dad – Alleles have differences in base sequences – Mutations and deletions occur which eliminate palindromic site (figure 2) Repeats • • • • Repetitive base sequences occur Constitute large fraction of mammalian genome Have no known genetic function 10-15% of DNA consists of repeated short sequences. • Vary between individuals • When flanked by recognition sites the length of repeat will determine size of fragment generated. Electrophoresis • Used to analyze DNA fragments • DNA has negative charge. • Gel is a sieve which separate DNA fragments according to size, charge and shape. • Only size of DNA affects mobility. • Cleavage of large complex human DNA generates fragments which may exceed resolving capacity of gel. • Cleaved DNA will appear as a smear, no bands. Southern Blot • Electrophoresis is done. • Denature DNA fragments in alakali solution. • Double stranded fragments converted to single stranded form. • Trnafer DNA fragments to nitrocellulose (blotting) • Blotted DNA hybridized with labeled oligonucleotide DNA probe. Southern Blot • Probe – DNA fragment which is complementary to sequences found on human chromosomes – Labeled with a “reporter” to detect target – Probe incubated with blotted membrane and will hybridize to complementary sequences on membrane. – Allows only specific DNA fragments to be detected. Forensics • DNA samples collected at crime scene extracted from – – – – Skin Blood Semen Hair • Perform RFLP analysis • If pattern matches it will prove beyond a reasonable doubt that suspect was at crime scene. • Forensics uses different sets of probes to hybridize to different repetitious sequences to satisfy statistical probability for positive identification. DNA and PCR • PCR very sensitive, requires very little DNA • Allows increased speed for analyzing • Requires – DNA polymerase Taq polymerase – Four dinucleotides – Primers - two synthetic oligonuceotides 15-30 bp in length which correspond to start and end of DNA to be amplified (target) – Buffer with Mg2+ PCR • Three phases – Heat to 92-96C to denature DNA – Cool to 45-65 to allow primers to anneal to separated strands – Heat to 72C to all extension, nucleotides added to primers. DNA Fingerprinting • Significant in court cases such as: – Murder – Rape – Physical battery • Results in acquittal or conviction • Process is standardized Procedure • PCR has been done • Have crime scene DNA and 2 suspects • Will treat all 3 samples with 2 restriction enzymes. • After enzyme treatment will electrophorese and stain. • Analyze gels to determine guilty suspect, one whose DNA matches crime scene DNA