The History Of Astronomy
advertisement

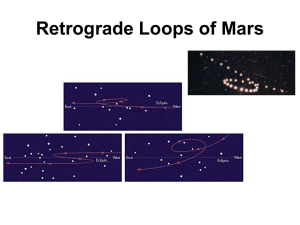
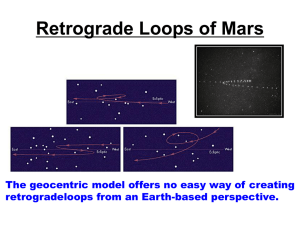
The History Of Astronomy History of Astronomy 1. Ancient times (Before 3000 B.C): a. Earth is Flat – astronomical bodies pass beneath Earth at night b. Astronomy is severe limited by the practical interests of the people and their still primitive outlook on the universe ** Some people still believe the world to be FLAT!!! www.flat-earth.org 2. Babylonians (3000 BC) a. 1st Evidence Earth is Round b. Basic Constellations and Astrology 3. Aristotle (384 BC – 322 BC) famous Greek writer, philosopher, physicist who was one of the 1st to attempt to develop a rational understanding of the universe. Aristotle History of Astronomy (Cont.) 3. Aristotle cont. (384 BC – 322 BC) a. Geocentric Theory – Earth is the Center of the Solar system (even universe) and planets, sun, and stars revolves around it - All stars are fixed points which rotate on a single sphere b. Believed there were only a few basic Substances 1. Earthly Realm – Air, Earth, Fire, and Water 2. Heavenly Realm – Quintessence (Not found on Earth) c. Also agreed Earth was round BUT obviously could not be moving 1. Rotation- NO sense of motion...no strong winds…..No displacement of thrown object. 2. Revolution – No stellar parallax - the shift of a nearby object with respect to more distant objects as seen from two different locations 5 Stellar Parallax – If the Earth revolved, the closer stars should shift among the background of further stars 7 History of Astronomy (Cont.) 4. Eratosthenes (276 - 195 B.C.) a. 1st person able to measure the circumference of the Earth (came within a couple thousand miles of actual value) - used geometry and ratios to determine the size of Earth 5. Ptolemy (90 – 168 AD) a. worked out a complex system of Epicycles and perfect circles for the orbits of planets, sun, and moon around Earth Geocentric Model History of Astronomy (Cont.) 6. Nicolas Copernicus (1473 –1543 AD) Problems with Geocentric Theory: 1. Model was becoming more and more inaccurate at making predictions as time passed 2. Orbits of planets had to become increasing comlpex in order to fit observations a. 1st to propose a Heliocentric Theory- Planets and moons revolve around the Sun. - Orbits still perfect circles with epicycles - Much better at predicting future planet locations but still not completely accurate b. Invented idea of Astronomical Unit (A.U.) – Distance of Earth from the Sun (About 93 million miles) NICOLAS COPERNICUS Copernicus Heliocentric Model Primitive Heliocentric Model Distances of Planets from the Sun Planets Copernicus Modern Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn 0.38 0.72 1.00 1.52 5.22 9.18 0.387 0.723 1.00 1.52 5.20 9.54 Distances Measured In Astronomical Units (A.U.) 14 History of Astronomy (Cont.) 7. Johannes Kepler (1571- 1630) a. Proposed that orbits of planets are not perfect circles but rather ellipses b. Developed 3 simple laws to explain thousands of years of planetary observations ** 1st law- Orbit of all planets are ellipses with the sun at one focus ** 2nd law – Law of Equal Areas ; which defines planetary speed as they go around the Sun ** 3rd law – As planet distance from the Sun increases, orbital period increases PROBLEM: What is force that locks the planets in space orbit?? How to Draw an Ellipse 16 KEPLER’S 1st LAW 17 KEPLER’S 2nd LAW 18 KEPLER’S 2nd LAW History of Astronomy (Cont.) 8. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642 A.D.) - Founder of Modern Mechanics and Astronomical use of the Telescope a. Proved Aristotle Wrong 1. Many more stars too faint to be seen with eye 2. Moon has mountains and craters like Earth…. Earth and Space made of same material 3. Discovered imperfection in Sun (SUNSPOTS)…Sun is not perfect b. Provided more evidence for a Heliocentric Solar System (Venus exhibits a full cycle of phases which is only possible in a Heliocentric system + Jupiter appears as a mini solar system which means that Kepler’s Laws apply for all planets) History of Astronomy (Cont.) 8. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642 A.D.) cont. c. Experimented with gravity and discovered that gravity is uniform on Earth d. Developed law of Inertia…an object at rest remains at rest. An object in motion will remain in motion in the absence of friction and gravity. Galileo Galilei Galileo’s Sketch of the Moon Using a Telescope SUNSPOTS Phases of Venus as Seen from Earth Phases of Venus….Evidence for a Heliocentric Solar system 27 History of Astronomy (Cont.) 9. Sir Isaac Newton (1642- 1727 A.D.) – mathematician and physicist who is considered the father of modern physics. He brought together the works of Kepler and Galileo with his basic physical laws and his laws of gravity. a. Gravity is a force in the whole universe, not just on Earth. b. Gravitational force between two object decreases as the distance between the objects increases More Mass = More Gravity c. Gravity is the force that keeps the planets in orbit around the Sun. d. Three basic laws of Physics 1st Law- Law of inertia – an object at rest will stay at rest an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an outside force History of Astronomy (Cont.) 9. Sir Isaac Newton (1642- 1727 A.D.) cont. d. Three basic laws of Physics (cont.) 2nd Law – More massive objects require more force to be accelerated (F= M x A) AN additional aspect of this law is that is provides for a way to calculate an objects weight. Weight equals the force of Earth’s gravity on the object times its mass (W=M x g) 3rd Law – For Force (Action) on one body there is an equal but opposite force (Reaction) acting on another body ex. - If an apple falls from a tree, not only does the apple fall to Earth but Earth falls towards the apple as well. F (Earth) = F (Apple) MA (Earth) = MA (Apple) Sir Isaac Newton Newton’s 1st Law of Inertia 31 Newton’s 1st law applied to Planets Newton’s 2nd Law 33 Newton’s 3rd Law 34 History of Astronomy (Cont.) 9. Sir Isaac Newton (1642- 1727 A.D.) cont. Aspects of Newton’s Laws of Motions 1. A force of gravity is present between any two masses regardless of size. Most objects are not massive enough to sense their force. 2. Using his laws of gravity Newton mathematically proved Kepler’s Laws to be correct 3. Calculated the existence of other planets due to orbital anomalies of outer known planets *** Although Newton is able to describe and calculate with great precision the forces of gravity he comes short in explaining the nature of gravity History of Astronomy (Cont.) 10. Albert Einstein (1879 – 1955 A.D.) American Physicist who came up with many theories which expanded our understanding of the universe a. Space and time are not separate units but rather one unit = space-time b. Gravity is the curvature of space-time. The more massive the object, the greater the curvature. (This is the basis of Einstein’s General Relativity Theory) *** Einstein explained the true nature of gravity. That’s it not a force but rather a course that mass takes around more massive objects. This theory was proven correct by the deflection of starlight observed during a 1919 eclipse. c. Most Famous for the Equation E=MC2 confirmed by the creation of the atomic bomb Lesser Known Einstein Equation Einstein’s Theory of Relativity 39 Less Massive Object More Massive Object Gravity as the Warping or Curving of Space Time…..The More Massive the Object the Greater the Curving Gravity as the Warping or Curving of Space-Time Final Thoughts on Einstein