Lesson 2: Magnetism
advertisement
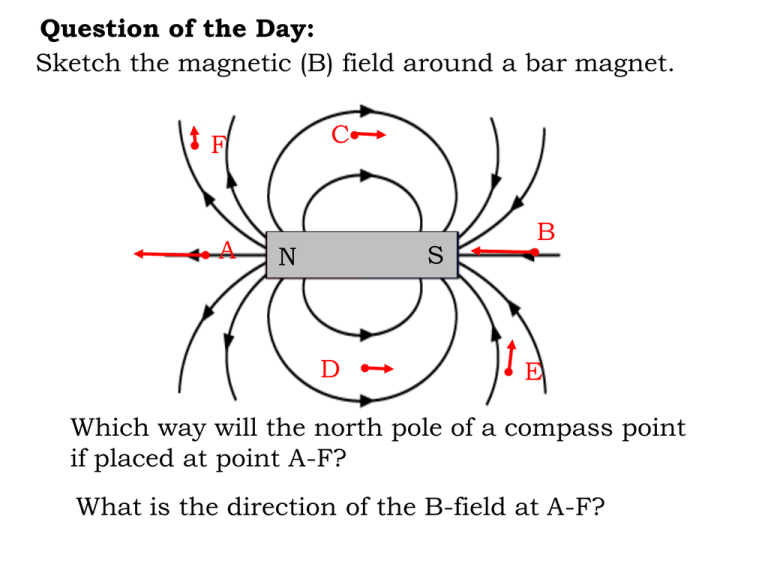
Question of the Day: Sketch the magnetic (B) field around a bar magnet. C F A S N D B E Which way will the north pole of a compass point if placed at point A-F? What is the direction of the B-field at A-F? A compass works just like iron filings: What do these have in common? north and south pole II. All magnets have a ___________________________. S N If you break a magnet… S N will become an entire magnet …each piece ________________________________: N S N S again have If you break it again, each piece will _____________ both a N- and S-pole A separate, single, N or S _____________________. magnetic pole (called a ________________ ) has monopole never been observed _____________________________ . Earth has a magnetic field that is __________________ similar to the field of ______________________. a bar magnet magnetic ______________ axis true axis ________ bar _________ magnet _________ S N Earth _________ Earth’s B field: --protects the planet from ______________________ cosmic rays borealis (northern) lights --produces the _________________________________ --at the surface is a result of the magnetic effects of: rotating currents in the outer core (90%) a/ __________________________________________ magnetic rocks in the crust b/ __________________________________________ electric currents in the ionosphere c/ __________________________________________ ocean currents d/ ___________________________________________ The magnetosphere—a magnetic “cocoon”: The Origin of the __________________________ : aurora borealis Charged particles from the Sun experience a ________________ magnetic perpendicular force that is _________________ velocity to their ______________ and to the magnetic field. This is a ____________ centripetal ________________ force Fc that spiral causes them to _____________ around the B field. As they spiral down to Earth, they knock electrons out of atmospheric ___________ atoms . When these electrons ________ re-combine _______________ with their atoms, emit light of different colors. they ___________________________ path of a charged _________ particle Fc due ____ to B field B_______ field line Earth's field makes an angle to its inclination surface called the _________________________. What is the angle at the poles? 900 What is the angle at the equator? 00 How to measure the inclination of Earth's B? magnetized steel needle 18 cm Compass and dip needles were used to find magnetite in Sweden in the Middle Ages, making the magnetic method the oldest of all applied geophysical techniques. This method of magnetic prospecting for ores was used extensively for iron mining up until the early decades of the twentieth century. However, the dip circle is not a sensitive enough instrument for most ore prospecting purposes and has been replaced with groundbased versions of magnetometers used in aeromagnetic surveys. The N- and S-poles of Earth’s B field: spin a/ are not the same as the __________ (true) poles slowly wander around b/ _____________________________ reverse c/ Sometimes ____________ polarity so that N becomes S ____________________ and vice versa. The last 750,000 time this occurred was about ____________ y ago Magnetic ___________________ is the angle that the declination true north. _______________ north makes with _________ magnetic 130 In Ilion, the declination is about ___________ 130 W magnetic __________ north true ________ north magnetic N pole The wandering _______________________ 130 New York _______________ Magnetic declination changes… …in space: …and in time. Neutron stars are large stars that have collapsed until they are planet sized. As they collapse, their magnetic fields intensify. As they rapidly rotate, their magnetic field sweeps around like a lighthouse. They were originally called pulsars. The Sun’s magnetic field… 1. produces sunspots 2. reverses itself every 11 y (next peak: 2012….) 3. affects climate on Earth. magnetograms of the sun: dark is one pole, light is the other In 2012: 1. A comet may strike Earth. 2. Yellowstone Caldera may erupt. 3. The Mayan Calendar predicts the End of the World. 4. The magnetic field of Earth may reverse 5. The sunspot cycle will reach its peak. Which one of these facts is an inference most likely to come true? Magnet therapy: Oersted’s __________________experiment (1819 in Copenhagen): wire S N compass battery switch deflected the compass An electric current ___________________________. Currents, I, _____________________________. cause magnetism, B Electricity ________________ and Magnetism are closely related. Each one can induce (give rise to) the other. This is electromagnetic the basis for the ______________________ generation of power . I. The Magnetic Fields of Current-Carrying wires: wire vertically. Support a piece Experiment: Hang a _______ current on of paper horizontally. Turn _____________. Sprinkle iron B field filings to see the ______________ pattern. nice animation right hand rule The _____________ tells you which one of the two possible ways that the B field points. The B field of a long straight wire has the shape of concentric circles _________________________ . View directly at wire with I towards I you: B B B side view: > I coil Ex: Twist a wire into coil the shape of a _______. I The B field of the coil is shaped like bar magnet a _______________: Side view: N N S S Electromagnets _______________________ are magnets made with coils. solenoids They are also called ____________________ . To strengthen its B field, use: more current 1. _______________________ more coils 2. ______________________ a ferromagnetic core 3. __________________________ Fe C o r e What are electromagnets used for? Plus electric motors and generators… The B field of the electromagnet turns its iron core into a magnet. The core will then be attracted into the coil's field. This is how solenoids work. Analog ammeters (and voltmeters) use coils, too: •Current is used in coils to create electromagnets. •The electromagnets repel/attract and move the needle. •The stronger the current, the more the force, and the more the needle moves. II. Magnetism in Solids. currents Magnetism in solids is caused by the ______________ electrons that result from the motion of ________________ as they "spin" on their axis 1/ _____________________________ , or "orbit" their nuclei 2/ _____________________________ within each atom. An atom: e- orbit Think of a spinning electron: nucleus as a tiny bar _______ magnet ___________: e- spins on axis Isn't it amazing that Earth's magnetic field is similar to that of an electron!!!! Types of magnetism: 1. ferromagnetism: strong --___________________ attraction Fe, Ni and Co --only in ______________________ unpaired --caused by ___________________electrons that act _______________________ cooperatively Why ferromagnetism only occurs in certain atoms: positions Electrons can only "fit" in certain _______________ around 2 orbitals the nucleus called _______________ . At most, only ___ electrons, spinning in ________________ directions, can fit opposite orbital in each _______________ . orbital = represents an electron ______________ in an atom one way = represents an e- spinning ______________ the other way = represents an e- spinning ______________ unique Each element has its own ______________ arrangement number of orbitals and ______________ of electrons. Whether an atom is ferromagnetic or not depends on whether filled up the ________________ are _______________ or not. orbitals not magnetic cancel _____________ filled orbital spins ________ = ________ unfilled orbital = _________ ferromagnetic because __________________________ spins act like magnets __________________________ 2. diamagnetism: repulsion --weak magnetic ________________ --occurs in water, glass, Cu, Pb, salt, wood, most gases, plastics, etc. 3. paramagnetism: attraction --weak magnetic _________________ --Al, O, Na In a ferromagnetic solid (iron, nickel or cobalt), atoms with unfilled electron orbitals organize themselves into domains -- area in which the electrons are lined up Ex. An unmagnetized ferromagnetic material has random domains: domains = spin of an electron Ex. A magnetized ferromagnetic material has domains that are aligned with each other external magnetic field 4. Human magnetism: Franz Mesmer (mesmerized…) Ex. Credit cards have a magnetic strip that records information: Don’t do this! What kind of field surrounds … 1. a neutron at rest? 2. a proton or an electron at rest? 3. a moving* proton or electron? Field caused by: gravitational g mass m gravitational g electric E gravitational g mass m charge q electric E mass m charge q magnetic B current I "relative" *The motion is _________________ . This means that at rest you will also measure a B if the charge is __________ past it and you _________________ . Uses of strong magnetic fields: 1. _______________________________________ medical - NMRs power transmission 2. ______________________________________ transportation – maglev trains 3. _______________________________________ computer memory 4. ______________________________________ research – contain fusion reactions 5. _____________________________________ To produce strong magnetic fields, high currents are needed. But this causes ___________________ I2R joule ______________ or ___________ heating. To reduce superconductors the heating, ____________________________ are used resistance because they have no __________________________.