投影片 1
advertisement

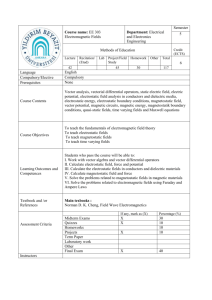
Electricity and Magnetism (I) 電磁學 (I) Electricity and Magnetism I 電磁學Ⅰ Professor: J.Y. Liu 劉正彥 E-mail: jyliu@jupiter.ss.ncu.edu.tw TEL: 03-4227151 ext. 65736 Textbook: Field and Wave Electromagnetics, 2nd Ed. 1989, David K. Cheng Class Hour: Thursday 08:00~09:00 & Friday 10:00~12:00 Classroom: S4-209 Office Hour: Week Date Content Chapter 1 The Electromagnetic Model 1 9/16-17 Teaching Assistant: 陳世平 976203025@cc.ncu.edu.tw Chapter 2 Vector Analysis Unit Test 1 (Chapter 1、Chapter 2) . 林其彥 986403005@cc.ncu.edu.tw 3-1 Introduction 2 9/23-24 3-4 Gauss’s Law and Applications 3-5 Electric Potential . 孫楊軼 986403008@cc.ncu.edu.tw 3 9/30-10/1 3-9 B.C. for Electrostatic Fields 3-10 Capacitance and Capacitors # attendance/quiz: 15% 4 10/7-8 3-11 Electrostatic Energy and Forces Unit Test 2 (Chapter 3) 100% = 15% + 15% × 5 × (4/5) + 25% 4-1 Introduction 5 10/14-15 6 10/21-22 7 10/28-29 8 11/4-5 9 11/11-12 10 11/18-19 11 11/25-26 12 12/2-3 13 12/9-10 14 12/16-17 15 12/23-24 16 17 18 12/30-31 1/6-7 1/13-14 4-3 Uniqueness of Electrostatic Solutions CSSSW9 (No Class) 4-4 Method of Images 4-7 BVP in Different Coordinates Unit Test 3 (Chapter 4) 5-1 Introduction 5-3 Electromotive Force & Kirchhoff’s Volt. Law 5-4 Equation of Continuity & Kirchhoff’s Curr. Law 5-7 Resistance Calculations Unit Test 4 (Chapter 5) 6-1 Introduction 6-4 The Biot-Savart Law and Applications 6-5 The Magnetic Dipole 6-9 Behavior of Magnetic Materials 6-10 Boundary Conditions for M Fields 6-13 Magnetic Forces and Torques Unit Test 5 (Chapter 6) 7-1 Introduction 7-2 Faraday’s Law of E-M Induction 7-3 Maxwell’s Equations 7-5 E-M Boundary Condition 7-6 Wave Equations and Their Solutions 7-7 Time-Harmonic Fields Final Exam (Chapter 1 ~ Chapter 7) No Class Remark 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 25% 1 The Electromagnetic Model • 1-1 Introduction • 1-2 The Electromagnetic Model • 1-3 SI Units and Universal Constants 1-1 Introduction • Electromangtics: the study of the effects of electric charges at rest and in motion. • A field is a spatial distribution of a quantity; action at a distance. • Wave: period/frequency, amplitude, phase; energy. • Time varying electric and magnetic fields are coupled, resulting in an electromagnetic field. • Time-dependent electromagnetic fields produce waves. 1-2 The Electromagnetic Model • Two approaches in development of a science subject: the inductive (歸納) approach and the deductive (演繹) approach. • Idealized model <> Real world • Three essential steps in building a theory on an idealized model: define quantities, specify operations, and postulate fundamental relations. Electric charge Conservation of electric charge • The principle of conservation of electric charge must be satisfied at all times and under any circumstances. The equation of continuity. • Charge density Current Fundamental EM Field quantities 1-3 SI Units and Universal Constants SI unit: International System Unit The universal constant • Velocity of EM wave in free space • Permittivity 電容率、介電常數 of free space • Permeability 磁導率、磁導係數 of free space 2 Vector Analysis 2 Vector Analysis • • • • • • • • • • • • 2-1 Introduction 2-2 Vector Addition and Subtraction 2-3 Product of Vectors 2-4 Orthogonal Coordinate Systems 2-5 Integrals Containing Vector Functions 2-6 Gradient of a Scalar Field 2-7 Divergence of a Vector Field 2-8 Divergence Theory 2-9 Curl of a Vector Field 2-10 Stokes’s Theory 2-11 Two Null Identity 2-12 Helmholtz’s Theory The law of cosines (length) Vector product (area) Scalar triple product (volume) Vector triple product (Back-cab rule) 2-4 Orthogonal Coordinate System 2-6 Gradient of a Scalar Field 2-7 Divergence of a Vector Field 2-8 Divergence Theory Flow Source 2-9 Curl of Vector Field 2-10 Stokes's Theory 2-11 Two Null Identities 2-12 Helmholtz’s Theory