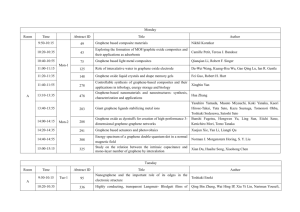
hn - PLMCN10
Ab-initio calculations of electronic and optical properties of graphane and related 2-D systems
Olivia Pulci
European Theoretical Spectroscopy Facilty (ETSF), and CNR-INFM,
Dipartimento di Fisica Università di Roma Tor Vergata http://www.fisica.uniroma2.it/~cmtheo-group http://www.etsf.eu
olivia.pulci@roma2.infn.it
Everything started with graphene
Novoselov et al. Science 2004
•
3D: stacked in graphite
•
2D: graphene
•
1D: rolled in nanotubes
•
0D: wrapped in fullerens
•
Unique physical properties:
H igh carrier mobility
Ambipolar field effect
RT quantum Hall
Single molecule detection
Special mechanical properties
…………………
For a review see for example:
Castro et al. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 109 (2009)
Allen et al. Chem. Rev. 110, 132 (2010)
Semi-metal
Functionalizing graphene
Graphene+H->Graphane
OUTLINE
Ab-initio: Theoretical Approaches
Functionalizing Graphene with H: graphane
Other exotic 2D systems (Si, Ge, SiC)
conclusions
OUTLINE
Ab-initio: Theoretical Approaches
Functionalizing Graphene with H: graphane
Other exotic 2D systems (Si, Ge, SiC)
conclusions
AB-INITIO methods
MBPT c h n c h n
EXC w cv c
W v
DFT v GW ground state
Band structure, I, A v
BSE
Optical properties
TDDFT
AB-INITIO methods c v
DFT
1) h n v GW
2)
MBPT c h n
EXC w cv v
BSE
3) c
W
TDDFT
(Step 2)
Lars Hedin 1965
iGW
G: single particle Green’s function
W: screened Coulomb interaction
W
1
V
For optical properties we need to go beyond:
Bethe Salpeter Equation c v
DFT
1) h n v GW
2)
MBPT c h n
EXC w cv v
BSE
3) c
W
TDDFT
h n
Step 3: calculation of optical spectra within the
Bethe Salpeter Equation c v
Absorption spectra
A photon excites an electron from an occupied state to a conduction state e
4
P
4
P
IQP
4
P
IQP
4 4
P h
Bethe Salpeter Equation ( BSE )
Kernel:
v
W e-h exchange bound excitons
Ab-initio applicable to:
Biological systems
0-D
Nanoclusters
• Generality, transferability 0D-3D
• Detailed physical informations
• Predictivity
• Complex theory+large comp.cost
1-D
2-D
3-D
Nanowires
Surfaces bulks
functionalizing graphene: graphene graphane
+ atomic H
Elias et al. Science 2009
Ryu et al. Nanolett. 2008 reversible!
Top view
Top view sp
2 sp
3
1.42 A-> 1.52 A (like C bulk)
Side view
Theoretically predicted in 2007 (Sofo et al PRB2007), synthesized in 2008
Electron affinity
E(vacuum)
A
I
E
(CBM)
A=electron affinity
A=E
(vacuum)
-E
(CBM)
I=Ionization potential
I= E
(vacuum)
-E
(TVB)
Especially interesting when A<0
Technological applications (cold cathod emitters,…..)
C(111):H NEA
E(vacuum)
A
E
(CBM)
(1x1) bulk-like
No states into the gap
A=E
(vacuum)
-E
(CBM)
=-1.4 eV (GW) (-0.6 eV in DFT)
Exp :-1.27 eV (J.B. Cui et al PRL1998)
Electronegativity plays a role!
graphane graphene
A(DFT)=4.21 eV metallic Egap DFT: 3.5eV metal---> insulator transition
GW: 6.1 eV!!
A(DFT)=1.27 eV; A(GW)=0.4 eV >0!!
WHY??
Side view compensating dipoles
+
_
_
+ d up d down
Graphane
NFES
Homo
Lumo
Nearly free electron states
Lumo+1
Graphane: optical properties
DFT-RPA without H with H
Dramatic changes in the optical absorption spectrum!
Graphane optical properties: excitonic effects
From Cudazzo et al. PRL 104 226804 (2010)
Other exotic 2-d materials?
H
Graphene graphane
H
Silicene(*) (?) polysilane
H
Germene (?) germane (?) polygermyne
……..?
22 toys models in Sahin et al. PRB2009
(*) Ag(110):Si Guy Le Lay and coworkers :
P. De Padova APL 2010
B. Aufray APL 2010
Silicon-based 2-D
+H
Polysilane top view
Silicene Top view
Silicene Side view
D
=0.44 Angstrom
Polysilane Side view
Not planar!!! Si larger atomic radii
D
=0.70 A
Si-based 2-D
Metallic!
Massless Dirac fermions at K
Wide gap semiconductor quasi-direct gap
DFT gap: 2.36 eV
GW gap: 4.6 eV
Ge-based 2-D
Germ e ne Top view
Germ e ne Side view
D
= 0.63
Å
+H
Germ a ne Top view
D
= 0.73
Å
Germ a ne Side view
Not planar!!!
Ge-sheets
Metallic!
Massless Dirac fermions at K semiconductor
Gap at
G:
DFT gap: 1.34 eV
GW gap: 3.55 eV
NFES
What can we learn?
gap
Buckl (Å) graphene Graphane no
No
(0) silicene Polysilane germene Germ a ne
(H) yes G no
(H) yes G
M no
(H) yes G
DFT:3.5 eV DFT:2.36 eV
GW:4.6 eV
DFT:1.34 eV
GW:3.5 eV GW: 6.1 eV yes
(0.46) yes
(0.44) yes
(0.70) yes
(0.63) yes
(0.73) sp2 sp3 sp3 sp3 sp3 sp3 d (Å) 1.42
1.54
2.28
2.39
2.35
2.39
NFES yes yes yes yes yes yes
Affinity >>0 ~0.4 eV >>0 >>0 >>0 >>0
OPTICAL PROPERTIES
Beyond single particle approach:
EXCITONIC EFFECTS c h n v
Excitonic effects
Large Exciton binding energies!!! 2-D confinement + expected trend
Further possible (?) 2D materials
Si+C!!!!
SILICONGRAPHeNE SiC
Side view
SILICONGRAPHaNE SiC:H
Topview
SiC based 2-D
With H
GAP EXISTS!
On one side the affinity is smaller!!!
SiC:H h n
2 eV e h n e -
Top and bottom semi-spaces have different ionization potential
Conclusions
H on graphene (graphane): metal->insulator transition; electron affinity decreases by factor 10
2-d systems (C, Si, Ge) show strong excitonic effects, with bound excitons
SiC:H presents 2 different ionization potentials!
(possible technological applications??)
Thanks to:
Paola Gori (CNR-ISM, Roma)
Margherita Marsili (Roma2)
Viviana Garbuio (Roma2)
Ari P. Seitsonen
(Zurich)
Friedhelm Bechstedt
(IFTO Jena, Germany)
Rodolfo Del Sole
(Roma2)
Antonio Cricenti
(CNR-ISM, Roma)
Development of theory training
Undergraduates
PhD Students
Post Docs
Other colleagues exp + Industry!
Development of codes
Distribution:
ABINIT
FHI
OCTOPUS
Yambo
DP+EXC
TOSCA
Research
Carrying on
Projects for users
BEAMLINES:
Optics
(O. Pulci)
EELS
(F. Sottile)
X-ray
(J. Rehr)
Transport
(P. Bokes)
Time-resolved excitations
(M.
Marques)
Photoemission (C. Verdozzi)
Raman
(G. Rignanese) new
Next call for projects: deadline 26 October
Thank you for your attention
http://www.etsf.eu
olivia.pulci@roma2.infn.it
From Dirac’s equation:
Si-C 1.79 Angstrom
BEAMLINES:
Optics
(O. Pulci)
EELS
(F. Sottile)
X-ray
(J. Rehr)
Transport
(P. Bokes)
Time-resolved excitations
(M.
Marques)
Photoemission (C. Verdozzi)
Raman
(G. Rignanese) new
(Step 2)
Lars Hedin 1965
iGW
G: single particle Green’s function
W: screened Coulomb interaction
W
1
V
Optical properties (DFT)
Optical properties
Comparison…
Large oscillators strength in Si and Ge-sheets!!!
Hamiltonian of N-electron system:
•
Biological systems
H
i
N
1 p i
2
2 m
I
M
1
P
I
2
2 M
I
• ...
1
2 i
j
| r i e
2 r j
|
i ,
j
| r
2 j
Z i
e
R i
|
1
2 i
j
|
Z i
Z
R i
j e
2
R j
|
•
0-D
• 1-D
•
Nanoclusters
•
Nanowires
•
2-D
•
Surfaces
• 3-D
• bulks
Silicongraphane sandwich geometry
NFE state C side
H
E
•
1964: Density Functional Theory
E=E
[ n
] n
1998 Nobel Prize to Kohn
•
Many Body Perturbation Theory
Green’s function method
GW + Bethe Salpeter Equation
(1965-->today)
G
•
Time Dependent DFT (TDDFT)
(Gross 1984) n(t)
GROUND-STATE
EXCITED STATES
C(001):H NEA
E(vacuum)
A
E
(CBM)
Negative electron affinity
A=E
(vacuum)
-E
(CBM)
=-1.5 eV
(-0.7 eV in DFT)
Exp: -1.3
eV (F. Maier et al PRB2001)
0
Hartree
iGV coul
Hartree Fock
V xc
DFT
iGW
'
DFT
GW'
Kohn Sham approx.
(Hedin 1964)
Vertex function
Polarization
iGW
Screened Coulomb interaction
Self-Energy
G: single particle Green’s function
W: screened Coulomb interaction
W
1
V
Optical properties…
Large oscillators strength in Si and Ge-sheets!!!