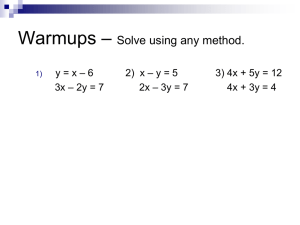
Open Course Library, WAMATH 2010
advertisement

Changing the world one course at a time… Melonie Rasmussen David Lippman Tyler Wallace Dale Hoffman Federico Marchetti What is the OCL Project? Design 42 high-enrollment courses for face-to-face, hybrid, or online delivery Reduce cost of course materials (< $30) New resources for faculty to use in their courses Creating ready-to-use course modules This is NOT Mandated curriculum Canned courses An effort to force classes to go online -----The courses will be digital and modular so faculty can take the pieces they want to use and ignore the rest What we will be doing Finding, compiling, or creating* a low-cost book or book alternative for under $30 And then… *writing a book is not what this grant is funding What we will be creating A syllabus with clear learning outcomes Course curriculum & instructional materials Formative and summative assessments Surveys Grading rubrics Cover letter describing tips and tricks of how to teach the course Cover letter for licensing Who’s doing what? Tyler Wallace, Big Bend CC Introductory and Intermediate Algebra Federico Marchetti, Shoreline CC Intro Statistics, Math& 146 Melonie Rasmussen & David Lippman, Pierce CC Precalculus 1 and 2, Math& 141/142 Dale Hoffman, Bellevue College Calculus 1, 2, and 3, Math& 151/152/153 Precalc 1 and 2 Planned approach: Contextual motivation Mix of plenty of drill with interesting applications that don’t exactly match examples A function exploration approach: With each new function we study: the graph, important features, domain/range, transformations, finding equations from sufficient data, solving equations, modeling, applications. Link graphical, verbal, numerical, and algebraic representations Precalc 1 and 2 Functions Functions and Function notation Basic Tool Kit functions Domain and Range and graphing and Piecewise Composition of functions Transformations Inverse functions Linear functions Linear functions (finding equations, rates of change, domain/range) Graphs (intercepts, parallel/perpendicular, relating words & tables to graphs) Solving equations and inequalities *maybe distribute to 1 & 4 Linear models (applications, extensions) Fitting lines to data Absolute value functions (transformations, graphs) Solving absolute value equations and inequalities Precalc 1 and 2 Polynomial and Rational functions Polynomial functions (power functions, form, domain/range, turning points, long run behavior) Quadratic graphs (vertex, intercepts, transformations) Solving quadratic equations and inequalities Polynomial graphs (intercepts, graph to/from equation) Rational functions (asymptotes, intercepts, domain/range) Solving polynomial and rational equations and inequalities Applications of polynomial and rational functions Exponential and Logarithmic functions Exponential functions (form, finding equations) Graphs (asymptotes, intercepts, transformations, domain/range) Exponential models (applications, continuous growth) Fitting exponentials to data Logarithms (def as inverse, use to solve basic exponentials) Log properties (properties, use to solve more difficult exponentials) Graphs (asymptotes, intercepts, transformations, domain/range) Solving exponential and log models (solving applications) Precalc 1 and 2 Trig functions Angles (degrees / radians / reference angle) Right triangles (define sin/cos/tan as right triangle proportions) Unit circle (relate triangles to unit circle, special angles to memorize, pythagorean identity) Trig graphs (transforms, domain/ranges) Reciprocal functions (graphs of sec/csc/cot, domain range, defs) Solving trig equations (basic solving using unit circle values. define inverse functions, domain/range, simple solves) Applications of trig equations (modeling) Changing Amplitude & Midline Non-right triangles (law of sines/cosines with applications) Simplifying trig expressions (use identities) Proving trig identities Solving equations using identities Applications of trig Polar coordinates Vectors Applications of vectors Polar form of complex numbers Parametric equations Intro and Intermediate Algebra Statistics Planning on working with Carnegie Mellon’s Open Learning Initiative http://oli.web.cmu.edu/openlearning/ Calculus 1, 2, and 3 How to Succeed in Calculus 0.1 Preview 0.2 Lines 0.3 Functions 0.4 Combinations of Functions 0.5 Mathematical Language 1.0 Slopes & Velocities 1.1 Limit of a Function 1.2 Limit Properties 1.3 Continuous Functions 1.4 Formal Definition of Limit 2.0 Slope of a Tangent Line 2.1 Definition of Derivative 2.2 Differentiation Formulas 2.3 More Differentiation Patterns 2.4 Chain Rule (!!!) 2.5 Using the Chain Rule 2.6 Related Rates 2.7 Newton's Method 2.8 Linear Approximation 2.9 Implicit Differentiation Calculus 1, 2, and 3 3.1 Introduction to Maximums & Minimums 3.2 Mean Value Theorem 3.3 f' and the Shape of f 3.4 f'' and the Shape of a f 3.5 Applied Maximums & Minimums 3.6 Asymptotes 3.7 L'Hospital's Rule 4.0 Introduction to Integration 4.1 Sigma Notation & Riemann Sums 4.2 The Definite Integral 4.3 Properties of the Definite Integral 4.4 Areas, Integrals and Antiderivatives 4.5 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.6 Finding Antiderivatives 4.7 First Applications of Definite Integrals 4.8 Using Tables to find Antiderivatives 4.9 Approximating Definite Integrals Calculus 1, 2, and 3 5.0 Introduction to Applications 5.1 Volumes 5.2 Length of a Curve 5.3 Work 5.4 Moments and Centers of Mass 5.5 Additional Applications 6.0 Introduction to Differential Equations 6.1 Differential Equation y'=f(x) 6.2 Separable Differential Equations 6.3 Growth, Decay and Cooling 7.0 Introduction 7.1 Inverse Functions 7.2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions 7.3 Calculus with Inverse Trigonometric Functions Calculus 1, 2, and 3 8.0 Introduction 8.1 Improper Integrals 8.2 Finding Antiderivatives: A Review 8.3 Integration by Parts 8.4 Partial Fraction Decomposition 8.5 Trigonometric Substitution 9.1 Polar Coordinates 9.2 Calculus with Polar Coordinates 9.3 Parametric Equations 9.4 Calculus with Parametric Equations 9.5 Conic Sections 9.6 Properties of the Conic Sections Calculus 1, 2, and 3 10.0 Introduction 10.1 Sequences 10.2 Infinite Series 10.3 Geometric Series & the Harmonic Series 10.4 Positive Term Series: Integral Test & P-Test 10.5 Positive Term Series: Comparison Tests 10.6 Alternating Sign Series 10.7 Absolute Convergence & Ratio Test 10.8 Power Series 10.9 Representing Functions as Power Series 10.10 Taylor and Maclaurin Series 10.11 Approximation Using Taylor Polynomials 11.0 Introduction: Moving Beyond Two Dimensions 11.1 Vectors in the Plane 11.2 Rectangular Coordinates in Three Dimensions 11.3 Vectors in Three Dimensions 11.4 Dot Product 11.5 Cross Product 11.6 Lines and Planes in Three Dimensions Calculus 1, 2, and 3 12.0 Introduction to Vector-Valued Functions 12.1 Vector-Valued Functions and Curves in Space 12.2 Derivatives & Antiderivatives of Vector-Valued Functions 12.3 Arc Length and Curvature of Space Curves 12.4 Cylindrical & Spherical Coordinate Systems in 3D 13.0 Introduction to Functions of Several Variables 13.1 Functions of Two or More Variables 13.2 Limits and Continuity 13.3 Partial Derivatives 13.4 Tangent Planes and Differentials 13.5 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient 13.6 Maximums and Minimums 13.7 Lagrange Multiplier Method 14.1 Double Integrals over Rectangular Domains 14.2 Double Integrals over General Domains Questions / Discussion What would make you want to use one of these OCL courses? What kind of course supplement materials are important to you? How important is the book itself? Could videos, Powerpoints / lecture notes, worked out examples, exercise sets suffice?