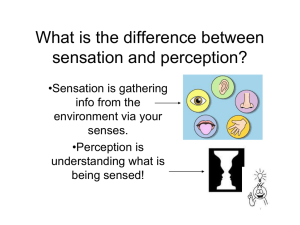
Sensation and Perception
Sense organs
See, hear, taste, smell, touch, balance, and
experience the world
Sensory receptor cells transmit sensation
Perception – interpreting information and
forming images
Stimulus
Sensation and Perception
Transduction – translates one form of
energy (incoming stimuli) into another
(sensory information)
Receptor cells to neural impulses
Sensation and Perception
Threshold – lower limits
Absolute threshold – smallest to be detected
Difference threshold – smallest difference
between 2 stimuli to be detected 50% of time
Sensory adaptation – one’s sensitivity to a
stimulus varies from time to time
Fatigue, inattention, repeated exposure
Vision
A candle flame seen at 30
mi. on a clear, dark night
Hearing The tick of a watch under
quiet conditions at 20 ft.
Taste
One teaspoon of sugar in
2 gallons of water
Smell
1 drop of perfume diffused
into the entire volume of a
3 room apartment
Touch
The wing of a bee falling on
your cheek from a height of
1 cm
Sensation and Perception
Psychophysics – studies sensory-related
matters
Weber’s law – amount of change needed for
detection 50% of time is always in direct
proportion to intensity of original stimulus
Sensation and Perception
Light
Electromagnetic radiation
Waves - frequency
Wavelength – determines hues seen
Intensity – brightness
The more wavelengths in light, the less saturated
or pure its hue is
Sensation and Perception
Light passes through cornea
Iris regulates light through pupil into lens
Lens held in place by ciliary muscle
Retina has rods and cones for receptors
Fovea – center of retina
Visual acuity – clarity and sharpness
Retina
Lens
Cornea
Fovea
Iris
Pupil
Optic nerve
Ciliary muscle
Rods
Cones
Sensation and Perception
Rods
Not located in fovea
Responsible for peripheral vision
Hundreds of times more sensitive to light
than cones
Produce images perceived with less visual
acuity than cones
Do not detect color
Sensation and Perception
Cones
Give brain more precise information
Code information about color
Respond only in bright light
Optic nerve – has no cones or rods
Blind spot – no visual reception in
optic nerve
Optic chiasm
Optic
nerve
Optic
chiasm
Blind spot
Sensation and Perception
Dark adaptation
Receptors receive new supply of chemicals
After 30 minutes in the dark - level of
sensitivity about 100,000 times greater than in
bright light
Light adaptation
Rods and cones highly responsive – overload
Bleaching out of receptor chemicals occurs
Sensation and Perception
Night blindness – vitamin A deficiency
Color vision
Wavelengths determine colors seen
Any color can be created from combinations of
red, blue, and green
Trichromatic theory – 3 kinds of cones in
eye responding mostly to light in either red,
blue, or green range of wavelengths
Trichromtic theory (Young-Helmholtz)
Sensation and Perception
Color afterimages
Complementary colors – yellow and blue, red
and green
Prolonged staring causes ghostly afterimage in
complementary colors
Occurs in all for complementary colors
Sensation and Perception
Opponent-process theory
Two kinds of color-processing mechanisms receiving
messages from three kinds of cones
Each mechanism responds in opposite ways
corresponding to two pairs of complementary colors
Opponent-Process Theory (Hering)
Fast
Slow
Slow
Fast
Sensation and Perception
Affects about 8% of males, 1% of females
Partial color blindness – difficulty
distinguishing between two colors
Red-green blindness due to genetic defect
Yellow-blue blindness due to absence of blue
pigment in cones
Color Blindness
Sensation and Perception
Audition - detection of sound waves
Frequency of cycles
Compression – increased density of waves
Rarefaction – reduced density of waves
Determines pitch of sound
Intensity measured in decibel (db) units
Prolonged exposure to over 85 db causes
hearing loss
Timbre – quality of sound
Characteristics of Sound Waves
Maximum level of industrial
noise considered safe
Pain
Threshold
0
db
20
Whisper
Absolute
threshold
of human
hearing
40
60
80
Normal
conversation
Quiet
office
100
City
bus
Noisy
automobile
Subway
120
Loud
thunder
or rock
concert
140
160
180
Rocket
launch
Sensation and Perception
Outer ear
Pinna – external part of ear that collects sound
External auditory canal – connects outer and
middle ear
Middle ear
Cardum – tympanic membrane; 1st structure
Eardrum - outermost structure of middle ear
Passes vibration to interconnected bones (hammer,
anvil, and stirrup)
Outer ear
Middle ear
Inner ear
Semicircular
canals
Hammer
Anvil
Nerve to
brain
Cochlea
Eustachian
tube
Pinna
Stirrup
External
auditory
canal
Eardrum
Oval
window
Round
window
Cochlea
Oval
window
Round
window
Hair cells
Basilar
membrane
Sensation and Perception
Inner ear
Oval window – eardrumlike structure at end of
cochlea
Round window – eardrumlike structure at other
end of cochlea
Basilar membrane – forms floor for ear’s sensory
receptors
Organ of Corti – contains hairlike receptor cells
Sensation and Perception
Orientation and movement
Vestibular organ – 2 sets of sensory structures
Semicircular canals
Saccule and utricle
Kinesthetic receptors – throughout body
Skin senses
Pressure sensitivity
Temperature sensitivity
The Skin Senses
Pressure
Free nerve
endings
Temperature
Tactile
discs
Specialized
end bulbs
basket cell
around
hair
hair
Braille Alphabet
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Sensation and Perception
Nerve endings in body act as nocioceptors
Neural messages transmitted along two distinct
pathways
Rapid – detects first pain sensation
Slow – detects second long-lasting pain
Endorphins and endogenous morphine
Sensation and Perception
Nerve endings in body act as nocioceptors
Pain gates regulate pain signals in 3 areas
Brain stem – gate-control theory of pain
Spinal cord
Peripheral regulation of pain
Phantom limbs
Up tp 70% of amputees experience this
Gate-control theory of pain
Stimulation of endorphin
receptors inhibits firing of
axon of slow-pain neuron
Somatosensory
area of cortex
neurotransmitter
molecules in
axon of slowpain neuron
Limbric
system
Area of
pain gates
Pathway of
fast-pain fibers
Endorphin
receptor
Direction of
pain message
Neuron in
slow-pain
fiber
endorphin
Axon of
inhibitory pain
gate neuron
Close-up view
of inhibitory
pain gates
Pathway of
slow-pain fibers
Inhibitory pain
gate neuron
Sensation and Perception
Bariba society – cultural emphasis on pain
Tolerate pain easily
Calm response to pain is part of Bariba pride
Pregnant women don’t show labor pain reaction,
experience labor pain and birth alone
Medical professionals can overestimate or
underestimate effects of pain if impact of
culture is not considered
Sensation and Perception
Senses of gustation (taste) and olfaction
(smell) differ from all other senses
Taste cells and papillae on tongue
Taste buds detect
Sweetness - mostly sugars
Sourness - mostly acids
Saltiness - mostly salts
Bitterness - toxins, chemicals
Fattiness - fats
Receptor
cells
Pore
Surface
of tongue
Taste
Bitter
Sour
Salty
Sweet
and fatty
Sensory nerve fiber
Sensation and Perception
Olfaction
Olfactory epithelium – top of nasal cavity
Pheromone detection of sweat and urine
Vomeronasal organ
Influence human female reproductive cycles
Inhalation of male sex hormone and mood changes
Males may respond to sex hormones
Olfactory nerve
to brain
Olfactory
epithelium
Nasal cavity
Sensation and Perception
Perception
Some unique aspects in different cultures
There is some common reality in shared world
Visual perception
Perceptual organization
Figure-ground
Continuity
Proximity
• Similarity
• Closure
Figure-Ground
Law of Proximity
Law of Continuity
Law of
Similarity
Law of
Closure
Sensation and Perception
Perceptual Constancy
Brightness constancy
Color constancy
Size constancy
Shape constancy
Sensation and Perception
Retina has two-dimensional surface
Monocular cues – perception of one eye
Texture gradient
Linear perspective
Superposition
Shadowing
– Speed of movement
– Aerial perspective
– Accommodation
– Vertical position
Sensation and Perception
Binocular cues – perception with two eyes
Visual Illusions
Convergence
Retinal disparity
Ponzo illusion
Vertical-horizontal
illusion
Color perception
– Zollner illusion
– Moon illusion
– Poggendorf illusion
The Ponzo Illusion
The Müller - Lyer Illusion
Visual Illusions
RED
Kanizsa square
Sensation and Perception
Integrate and interpret information from
multiple senses simultaneously
Motivation, Emotion, and Perception
Limited ability and accident occurrence
Motivation and emotions influence perception
Past experiences influence all perceptions
Sensation and Perception