1) The instruction cycle is also known as the ______.
advertisement
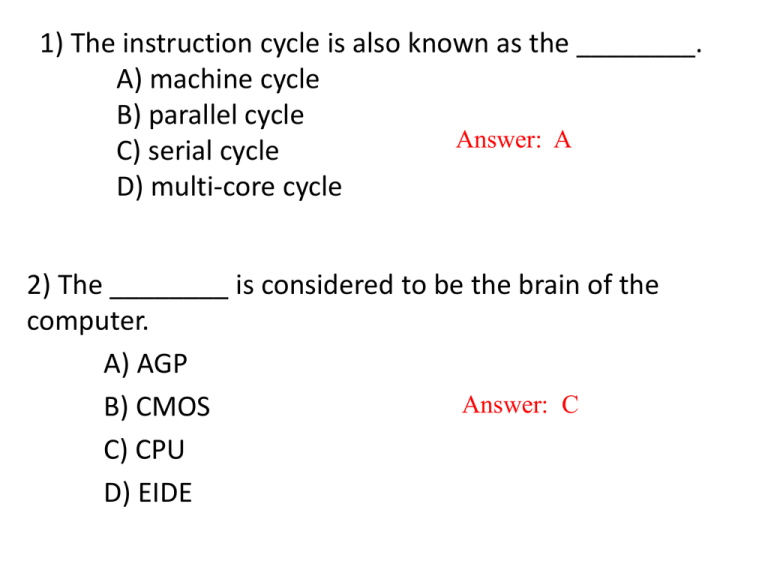
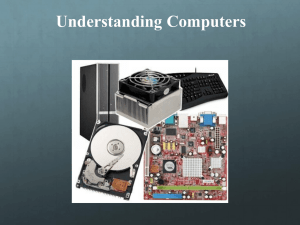
1) The instruction cycle is also known as the ________. A) machine cycle B) parallel cycle Answer: A C) serial cycle D) multi-core cycle 2) The ________ is considered to be the brain of the computer. A) AGP Answer: C B) CMOS C) CPU D) EIDE 3) The ________ component of the CPU performs arithmetic and logic calculations. A) control unit B) BIOS C) EIDE D) ALU Answer: D 4) The speed at which a processor executes machine cycles is called ________. A) clock speed B) resolution C) AGP D) SATA Answer: A Which of the following is NOT a step in the instruction cycle? A) Fetch B) Decode Answer: C C) Print D) Execute The main circuit board of of a computer is the ________. A) adaptive board B) peripheral board C) motherboard D) legacyboard Answer: C ________ data buses connect peripheral devices to the CPU and the computer's memory. A) Local B) External C) Expansion D) Bluetooth Answer: B The most common types of ports found on computers today are ________. A) serial and parallel B) PS/2 and parallel C) USB and FireWire D) BIOS and USB Answer: C A computer's ________ is a program stored on a chip on the motherboard used to start up the computer. A) EIDE B) AGP C) SATA D) BIOS Answer: D ________ is a short-range wireless technology used to connect many types of peripheral devices. A) Ethernet B) USB C) Bluetooth D) FireWire Answer: C Which of these items is NOT found inside the system unit? A) Processor B) Drive bays C) Power supply D) Flash drive Answer: D The ________ chip is volatile storage that stores settings used by the BIOS A) USB B) CMOS Answer: B C) RAM D) SATA A megabyte (MB) is equal to ________ bytes. A) 100 B) 1000 C) 1,000,000 D) 1,048,576 Answer: C The base of the binary numbering system is ________. A) 10 B) 12 C) 8 D) 2 Answer: D A MB of storage can hold about ________ pages of plain text. A) 500 B) 1000 C) 3000 D) 5000 Answer: A CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are examples of ________ discs where lasers are used to store data on the discs. A) flash B) magnetic C) solid-state D) optical Answer: D Computers convert data into information using ________. A) convergence B) ergonomics C) information processing cycle D) Moore's Law Answer: C Data that has been processed by the computer is called ________. A) bioinformatics B) information C) input D) raw data Answer: B First-generation computers used ________ and manual switches. A) integrated circuits B) transistors C) vacuum tubes D) microprocessors Answer: C Second-generation computers used ________, making the computers smaller, more powerful, and more reliable. A) vacuum tubes B) transistors C) integrated circuits D) microprocessors Answer: B First generation computers were built in the ________. A) 1910s and 1920s B) 1930s and 1940s C) 1940s and 1950s D) 1960s and 1970s Answer: B A(n) ________ is a type of notebook that allows the user to use a stylus or pen to write directly on the screen. A) netbook B) server C) client D) tablet PC Answer: D A small microprocessor-based computer is a(n) ________. A) supercomputer B) mainframe C) minicomputer D) personal computer Answer: D A compact desktop computer with an integrated monitor is called a(n) ________ computer. A) notebook B) netbook C) all-in-one D) tablet Answer: C A high-end desktop computer or one attached to a network can be called a(n) ________. A) netbook B) tablet PC C) workstation D) notebook Answer: C ________ are large computers that can perform millions of transactions in a day. A) PDAS B) All-in-ones C) Mainframes D) Netbooks Answer: C Today's personal computers are considered ________ -generation computers. A) first B) second C) third D) fourth Answer: D Which of the following is a high-end desktop computer in a business environment? A) Minicomputer B) All-in-one C) Mainframe D) Workstation Answer: D Which type of portable computer allows a user to write directly on the screen? A) Tablet PC B) Netbook C) Laptop D) Desktop replacement Answer: A Computers in traffic lights, at supermarket checkouts, and in appliances are examples of ________ computers. A) personal B) portable C) ubiquitous D) embedded Answer: D Which of these is NOT an input device? A) printer B) scanner C) keyboard D) mouse Answer: A The size of a monitor is measured: A) by adding length of the bottom of the screen to the length of one side of the screen. B) diagonally across the screen. C) from the top to the bottom of the screen. D) from the left edge to the right edge of the screen Answer: B The processor on a video card is called a(n) ________. A) GPU B) USB C) DLP D) OLED Answer: A The wires that transfer data across the motherboard are known as ________. A) system clock B) CPU C) CMOS D) data buses Answer: D Data after processing is 1.Metaware. 2.Hardware. 3.Information. 4.Manuals / procedures. Information. •What is the maximum capacity for floppy diskette? 1. 1.2 MB 2. 1.44 MB 3. 2.0 MB 4. 1.4 GB 1.44 MB •Each computer directly linked to the Internet must obtain a unique address. 1.URL 2.ISP 3.DNS 4.IP URL •An internet tool that enables you to quickly find information on the web is called: 1.A uniform resource locator 2.A search engine 3.A find wizard 4.Online help A search engine •The two main parts of the system unit are 1.A mouse and a keyboard. The CPU and memory. 2.The CPU and memory. 3.A printer and a monitor. 4.Primary storage and secondary storage. •Object copied through the 1.Ctrl+C 2.Ctrl+V 3.Ctrl+D 4.Ctrl+F Ctrl+C •The PC is an abbreviation of? 1.Protocol of Computer. 2.Pascal in Computer. 3.Private Computer. 4.Personal Computer. Personal Computer. •Printers and screens are: 1.Input 2.input/output. 3.Output 4.Memory Output •What is a URL? 1.An email address 2.The title of a web site 3.The address of a page on the World Wide Web 4.A communication method between computers and printers The address of a page on the World Wide Web •Servers are? a.High speed computers with huge memory. b.Some programs used in displaying pictures. c.Kind of computer games. d.None of the above. a.High speed computers with huge memory. A(n) ________ is a chip that contains the central processing unit of a computer. A) transistor B) server C) client D) microprocessor D) microprocessor Data is entered into a computer during the ________ step of the IPC. A) processing B) output C) input D) storage C) input A(n) ________ is a light, inexpensive computer designed primarily for Internet access. A) workstation B) netbook C) desktop computer D) all-in-one computer B) netbook A compact desktop computer with an integrated monitor is called a(n) ________ computer. A) notebook B) netbook C) all-in-one D) tablet C) all-in-one ________ are large computers that can perform millions of transactions in a day. A) PDAS B) All-in-ones C) Mainframes D) Netbooks Mainframes Complex mathematical calculations such as those used in weather forecasting are carried out by ________. A) servers B) minicomputers C) all-in-one computers D) supercomputers D) supercomputers Minicomputers have largely been replaced by ________. A) all-in-one computers B) tablet PCS C) midrange servers D) netbooks C) midrange servers The integration of technology on multifunction devices, such as smartphones is called ________. A) ergonomics B) convergence C) bioinformatics D) green computing B) convergence The main circuit board of of a computer is the ________. A) adaptive board B) peripheral board C) motherboard D) legacyboard C) motherboard ________ is a short-range wireless technology used to connect many types of peripheral devices. A) Ethernet B) USB C) Bluetooth D) FireWire C) Bluetooth In a computer, a(n) ________ code is used to represent digital data. A) parallel B) decimal C) binary D) solid-state C) binary Which of these is NOT an example of an optical drive? A) CD-ROM B) DVD C) Blu-ray D) Hard disk D) Hard disk Which of these is NOT an input device? A) printer B) scanner C) keyboard D) mouse A) printer The data signal and connection for a monitor or projector are provided by the ________. A) modem B) video card C) network adapter D) DLP B) video card