Lecture 10
advertisement

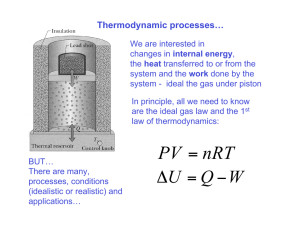
Paperwork • Today – Problems ch.20 – ?’s • Friday – Guest Lecture to Kick off Ch. 21 • What are on quizzes? – Seriously – Read chapter (Yellow!) Lab 3 Thoughts • Exemplified heat engine processes • Quantitative analysis of work done Entropy Question • A 740 g quantity of an ideal gas undergoes a reversible isothermal compression at a temperature of 330 K. The compression reduces the volume of the gas from 0.40 m3 initially, to 0.32 m3 finally. The molecular mass of the gas is 320 g/mol. The entropy change for the gas, in SI units, is ? • Entropy, Ideal Gas, Energy Tools: 2 dQ S T 1 pV nRT dQ dU dW First Thought • Entropy Change positive or negative? • Is it zero? • Why do we usually talk about S & not S? 2nd thought • Parameters • Initial • Final • Tools 2 dQ S T 1 pV nRT dQ dU dW What are constants? • Temperature? – Yes 330 K • Mass (Moles)? – Yes: Mass = 740 g & M.M. = 320 g/mol – # moles = – n = 2.31 moles • Volume? – No: Goes from 0.4 to 0.32 m3. • Pressure? – No: Increases • Heat? – No. dQ = dU + dW – dQ = dW, dW not likely zero with volume change • Fill in previous page, Follow main entropy Equation Next Fill in & Follow Thru • Parameters (SI UNITS): R=8.31 • Initial – V1 = 0.4 n1 = 2.31 – p1 = (nRT)/V = 15357 T1 =330 • Final – V2 = 0.32 n2 = 2.31 – p2 = (nRT)/V = 19161 T2 =330 • Tools 2 dQ S T 1 pV nRT dQ dU dW Equation Fun Isothermal Implications 2 dQ S T 1 pV nRT dQ dW [Isothermal] dQ pdV 2 S 1 pdV T dQ dU dW Equation Fun Insert Ideal Gas Constraint 2 S 1 dQ T dQ dW pV nRT dQ dU dW [Isothermal] dQ pdV 2 S 1 pdV T nRT V 2 2 2 p 1 nRT 1 S dV dV nR dV T T V V 1 1 1 p S nR ln V 2 ln V 1 nR ln V 2 / V 1 4.3 Entropy Units? Why not use: dQ = nCdT? Make Random Engine Make p-V Diagram Calculate Work Done, Entropy Constraints Ideal Gas cV = 3R/2, CP = 5R/2 (monotomic) For Each Cycle: Something Constant Tools 2 dQ S T 1 pV nRT dQ nCdT dU nCV dT dQ dU dW Friday • Guest Lecture Ch. 21