Map Reading 1 (Intro)
advertisement

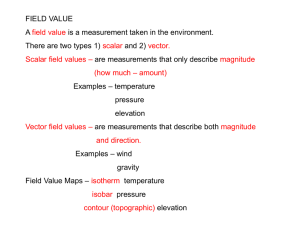
Introduction to Map Reading GRC JROTC COL(R) ALEXANDER Map Reading I Outline Purpose Marginal Information Colors Terrain Features Conclusion Map Reading I Purpose To lay the groundwork for successful map reading and land navigation by exposing the cadet to basic information, significant color coding, and terrain features used on maps. Map Reading I Marginal Information 1 of 4 Sheet Name Sheet Number Adjoining Map Sheets Diagram Map Reading I Marginal Information 2 of 4 Special Notes Declination Diagram Map Reading I Marginal Information 3 of 4 Scales Contour Interval Notes Grid Reference Box Map Reading I Marginal Information 4 of 4 Unit Imprint Legend Map Reading I Colors (x6) BLACK: Man-made features (Buildings, roads, grid-lines) RED-BROWN: cultural features (contour lines) BLUE: Water features (Lakes, swamps and rivers) BROWN: Relief features and elevation on older or red-light readable maps (contour lines and cultivated land) GREEN: Vegetation (forest, woods, brush, orchards) RED: Man-made features (populated areas, major highway roads, boundaries on older maps) Map Reading I Contour Lines & Interval 1. Check contour interval 2. Find given elevation 3. Determine direction of slope 4. Count contour intervals. Change in ELEVATION Map Reading I Contour Lines & Interval Lines that are farther apart (interval) = GENTLE SLOPE Map Reading I Contour Lines & Interval Lines that are close together (interval) = STEEP SLOPE Map Reading I 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Map Reading I Major Terrain Features (x 5) Hill. Valley. Ridge. Saddle. Depression. H idden V alley R anch S alad D ressing Major Terrain Features 1 of 5 Hill: An area of high ground - Concentric circles. The center of the smallest circle is the hilltop. Map Reading I Major Terrain Features 3 of 5 Valley: a stretched-out groove in the land, usually formed by streams or rivers. Valley - U or V shaped contour lines. High ground on 3 sides usually with water flowing in the middle. V or U points upstream. Map Reading I Major Terrain Features 4 of 5 Ridge: This is a sloping line of high ground. - low ground in three directions and high ground in one direction. Contour lines tend to be U-shaped or V-shaped. The closed end of the contour line points to lower ground Map Reading I Major Terrain Features 2 of 5 Saddle: Low point between 2 areas of high ground X - hour glass or figure eight contour lines. Map Reading I Major Terrain Features 5 of 5 Depression: This is a low point in the ground. - Low ground or sink hole. Closed contour lines that have tick marks pointing toward low ground. Map Reading I Minor Terrain Features (x 3) 1. 2. 3. Map Reading I Draw. Spur. Cliff. Minor Terrain Features 1 of 3 Draw: a less developed stream course than a valley. There is essentially no level ground . - contour lines depicting a draw are U-shaped or V-shaped, pointing toward high ground. Map Reading I Minor Terrain Features 2 of 3 Spur: a short, continuous sloping line of higher ground, normally jutting out from the side of a ridge. - Contour lines depict the U or V pointing away from high ground. Map Reading I Minor Terrain Features 3 of 3 Cliff: a vertical or near vertical feature. - Contour line converge together into one “Carrying” contour. The last contour has tick marks pointing towards low ground. Sometimes depicted by contours running very close or touching. Map Reading I Supplementary Terrain Features (x 2) 1. 2. Map Reading I Cut. Fill. Supplementary Terrain Features Cut or Fill: a man-made feature resulting from cutting through high ground or filling low ground. - Contour line extends the length of the cut (tick marks point to roadbed) and fill (tick marks point away from roadbed). Map Reading I Practical Exercise 8 9 6 6 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Map Reading I Practical Exercise Key 1. HILL 2. VALLEY 3. RIDGE 4. SADDLE 5. DEPRESSION 6. DRAW 7. SPUR 8. CLIFF 9. CUT 10. FILL Map Reading I Summary Purpose Marginal Information Colors (x6) Terrain Features Map Reading I Major Minor Supplementary Conclusion Knowing how to read and understand maps are valuable skills that can strengthen your awareness, credibility as a leader, and help you standout among your peers. Map Reading I Introduction to Map Reading GRC JROTC COL. ALEXANDER Map Reading I