BIO2093_DMS1_phylogeny

Phylogeny I
BIO2093 – Phylogenetics
Darren Soanes
Phylogenetics
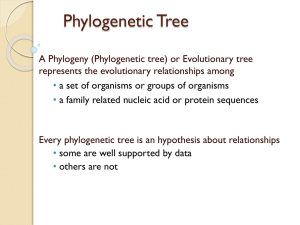
• The study of evolutionary relationships among groups of organisms.
• Phylogenetic tree : a hypothesis of the order in which evolutionary events are assumed to have occurred.
Phylogenetic tree
Parts of a tree plural of taxon = taxa
Phylogenetic tree: evolutionary family tree
Nodes in the tree represent speciation events, where an ancestral lineage gives rise to daughter lineages.
Relationships in trees
Rooting a tree outgroup
Root - most recent common ancestor of all the taxa in a tree outgroup — a taxon outside the group of interest. All the members of the group of interest are more closely related to each other than they are to the outgroup. Used to root the tree.
Outgroup
Rooted and unrooted trees rooted tree unrooted tree
Types of trees
• A cladogram is a phylogenetic tree formed using cladistic methods. It shows branching pattern only.
• A phylogram is a phylogenetic tree that has branch lengths proportional to the amount of character change.
• A chronogram is a phylogenetic tree that explicitly represents evolutionary time through its branch lengths.
Cladistics
Classification into clades based on shared derived characters
(synapomorphies).
A synapomorphy is a trait shared among species because the common ancestor of those species also had the trait.
Analogy
Homoplasy: homoplastic character state is a trait that is shared by two or more taxa because of convergence, parallelism or reversal e.g modified nostrils on top of head in cetaceans and dinosaur group
Macronaria .
Convergent evolution
Plant kingdom
Clades
A clade consists of an ancestor organism and all its descendants.
Clade = monophyletic group
Each monophyletic group can be identified by one or more synapomorphies.
Phylogenetic classification system
Phylogenetic groups are based on clades
(monophyletic groups)
Phylogenetic classification system
Reptile is not a legitimate phylogenetic grouping (unless we include birds as reptiles) – paraphyletic group
Birds are part of the clade
Dinosauria.
Phylogenetic classification system
Mono, poly and paraphyly
Polyphyletic group – ‘warm blooded’
Types of trees
• A cladogram is a phylogenetic tree formed using cladistic methods. It shows branching pattern only.
• A phylogram is a phylogenetic tree that has branch lengths proportional to the amount of character change.
• A chronogram is a phylogenetic tree that explicitly represents evolutionary time through its branch lengths.
Phylogram
Cladogram
Phylogram
Types of trees
• A cladogram is a phylogenetic tree formed using cladistic methods. It shows branching pattern only.
• A phylogram is a phylogenetic tree that has branch lengths proportional to the amount of character change.
• A chronogram is a phylogenetic tree that explicitly represents evolutionary time through its branch lengths.
Chronogram
Phylogram calibrated based on fossil record
Constructing phylogenetic trees
Constructing phylogenetic trees
From studying fossils and lineages closely related to the vertebrate clade, we hypothesise that the ancestor of vertebrates had none of these features
Constructing phylogenetic trees
Constructing phylogenetic trees
Parsimony
All other things being equal, the best hypothesis is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary changes
Reading
• Freeman and Herron – Evolutionary
Analysis (4 th Edition): Chapter 4
(Estimating Evolutionary Trees).
Summary
• Phylogenetic tree : a hypothesis of the order in which evolutionary events are assumed to have occurred.
• Constructed using shared derived characters (synapomorphies).
• Parsimony: All other things being equal, the best hypothesis is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary changes.