File - Biology with Ms. Murillo
advertisement
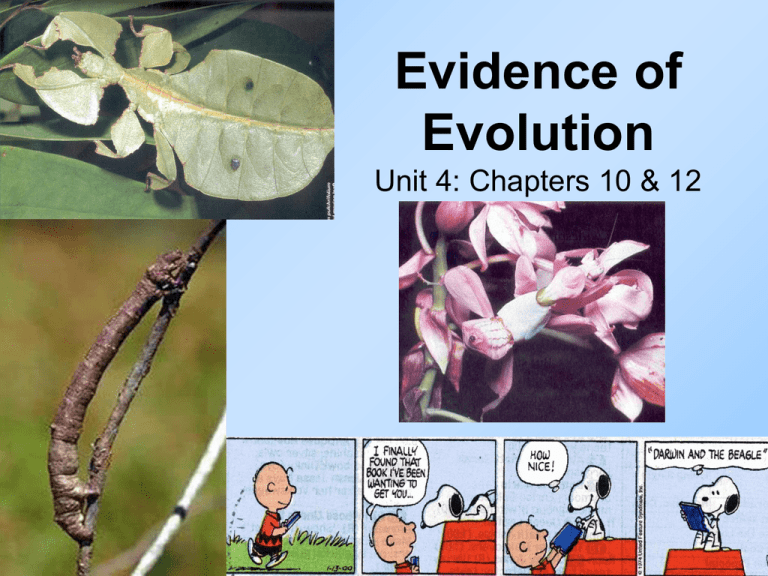
Evidence of Evolution Unit 4: Chapters 10 & 12 Important Vocabulary 1. Species: A group of organisms that can breed together to produce fertile offspring. 2. Population: A localized group of individuals belonging to the same species. 3. Evolution: A slow change in a population over time. Charles Darwin explained how Natural Selection could cause a population to adapt and change over time. (note he states- a “population” will change -not an “individual”) What is a theory vs. a hypothesis? Hypothesis Theory An educated guess that has to be testable by scientific methods Has to be wellsupported and has been tested over and over Is an explanation of a phenomenon that has occurred in the natural world. Who influenced Charles Darwin? The Work of Lyell Influenced Darwin’s Ideas 1. Charles Lyell – English geologist a. Earth’s geologic features formed as a result of gradual processes. b. Floods, earthquakes, and glaciers of the present do not cause great destruction (ex: Grand Canyon) of Earth’s surfaces c. Must take millions of years to change geography, thus the earth must be millions of years old. 2. Darwin read Lyell’s work while on his voyage & agreed with Lyell’s conclusions Charles Lyell The Work of Malthus Influenced Darwin’s Ideas 1. 1798: Thomas Malthus -- Englishman a. Essay on the Principle of Population b. Said that humans tend to have more offspring than nature can support c. Food production increases at a slower rate than population 2. Darwin read Malthus’s essay after he returned from his voyage 3. Darwin concluded that all organisms produce more offspring than the environment can support Thomas Malthus Darwin explained Evolution by Natural Selection 1. 1859: Darwin published On the Origin of Species a. Proposed that natural selection was the mechanism for evolution. • Individuals vary in one or more traits & there can be slight differences in their ability to survive & reproduce. b. Nature selects those individuals w/ favorable traits to leave more offspring that are better suited (FIT) for their environment. c. Descent with modification occurs over time • Each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time Published 25 years after Darwin wrote it! Evidence that Supports Evolution: Fossil Record 1. Fossil: preserved remains (bones, teeth, shells) or evidence (imprint or footprint) of ancient organisms. a. Fossils found in sedimentary rock b. Younger sediments deposited on top of older sediments c. Older sediments contain older, simpler fossils d. Younger sediments contain younger, more complex fossils 2. Fossils found in sediments of organisms that are extinct. Trilobites are extinct! Age of Fossils Paleontologists determine the age of fossils using two techniques: 1. Relative dating: age of a fossil is determined by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of rock. Paleontologists estimate the age based on the age of other fossils found near it. 1. Radioactive (absolute) dating: Scientists use radioactive decay to assign absolute ages to rocks. Evidence that Supports Evolution: Geographic Distribution of Living Species 1. Similar animals on each continent live in similar ecological conditions a. They were exposed to similar pressures of natural selection. b. Because of similar selection pressures, different animals ended up evolving similar characteristics Beaver Beaver NORTH AMERICA Muskrat Beaver and Muskrat Muskrat Coypu Capybara SOUTH AMERICA Coypu and Capybara Capybara Coypu Evidence that Supports Evolution: Homologous Structures 1. Homologous structures: similar structures but different functions a. Structures develop from same clump of embryonic cells b. Provides evidence that four-limbed vertebrates descended from a common ancestor. 2. Vestigial structures: structures or organs that are reduced in size; do not seem to serve a useful function 3. Homologous & vestigial structures imply that common genes are involved. Homologous structures: forelimbs of vertebrates Pelvis & femur bones are vestigial in whales Evidence that Supports Evolution: Similarities in Embryology 1. The embryos of vertebrates are very similar during early development. 2. The same groups of embryonic cells develop in the same order and in similar patterns to produce tissues & organs. 3. Common cells & tissues growing in similar ways produce homologous structures. 4. Implies that common genes are involved. Embryos of vertebrates develop gill slits and tails.