Fallswallppt
advertisement
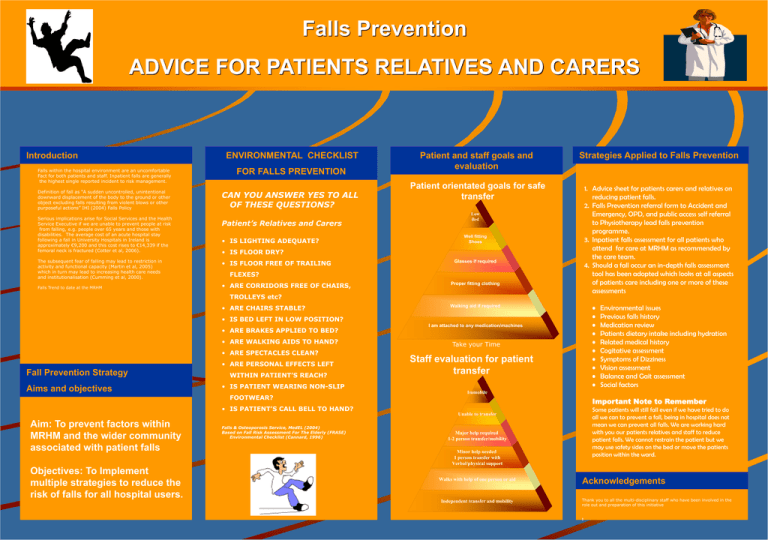
Falls Prevention ADVICE FOR PATIENTS RELATIVES AND CARERS Introduction Falls within the hospital environment are an uncomfortable Fact for both patients and staff. Inpatient falls are generally the highest single reported incident to risk management. Definition of fall as “A sudden uncontrolled, unintentional downward displacement of the body to the ground or other object excluding falls resulting from violent blows or other purposeful actions” IHI (2004) Falls Policy Serious implications arise for Social Services and the Health Service Executive if we are unable to prevent people at risk from falling, e.g. people over 65 years and those with disabilities. The average cost of an acute hospital stay following a fall in University Hospitals in Ireland is approximately €9,200 and this cost rises to €14,339 if the femoral neck is fractured (Cotter et al, 2006). The subsequent fear of falling may lead to restriction in activity and functional capacity (Martin et al, 2005) which in turn may lead to increasing health care needs and institutionalisation (Cumming et al, 2000). Falls Trend to date at the MRHM ENVIRONMENTAL CHECKLIST FOR FALLS PREVENTION CAN YOU ANSWER YES TO ALL OF THESE QUESTIONS? Patient and staff goals and evaluation Strategies Applied to Falls Prevention Patient orientated goals for safe transfer 1. Advice sheet for patients carers and relatives on reducing patient falls. 2. Falls Prevention referral form to Accident and Emergency, OPD, and public access self referral to Physiotherapy lead falls prevention programme. 3. Inpatient falls assessment for all patients who attend for care at MRHM as recommended by the care team. 4. Should a fall occur an in-depth falls assessment tool has been adopted which looks at all aspects of patients care including one or more of these assessments Patient’s Relatives and Carers • IS LIGHTING ADEQUATE? • IS FLOOR DRY? • IS FLOOR FREE OF TRAILING FLEXES? • ARE CORRIDORS FREE OF CHAIRS, TROLLEYS etc? • • • • • • • • • • • ARE CHAIRS STABLE? • IS BED LEFT IN LOW POSITION? • ARE BRAKES APPLIED TO BED? • ARE WALKING AIDS TO HAND? • ARE SPECTACLES CLEAN? • ARE PERSONAL EFFECTS LEFT . Fall Prevention Strategy Aims and objectives WITHIN PATIENT’S REACH? Take your Time Staff evaluation for patient transfer • IS PATIENT WEARING NON-SLIP FOOTWEAR? Important Note to Remember • IS PATIENT’S CALL BELL TO HAND? Aim: To prevent factors within MRHM and the wider community associated with patient falls Objectives: To Implement multiple strategies to reduce the risk of falls for all hospital users. Environmental issues Previous falls history Medication review Patients dietary intake including hydration Related medical history Cogitative assessment Symptoms of Dizziness Vision assessment Balance and Gait assessment Social factors Some patients will still fall even if we have tried to do all we can to prevent a fall, being in hospital does not mean we can prevent all falls. We are working hard with you our patients relatives and staff to reduce patient falls. We cannot restrain the patient but we may use safety sides on the bed or move the patients position within the ward. Falls & Osteoporosis Service, MedEL (2004) Based on Fall Risk Assessment For The Elderly (FRASE) Environmental Checklist (Cannard, 1996) Acknowledgements Thank you to all the multi-disciplinary staff who have been involved in the role out and preparation of this initiative t