Managed care is not only about containing costs
advertisement

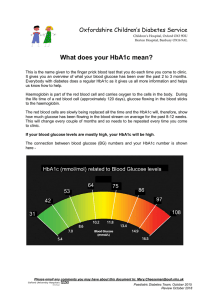
MANAGED CARE IS NOT ONLY ABOUT CONTAINING COSTS GERALDINE BARTLETT Medical Scheme FINANCIALS Medical Scheme Financials Health of member Financials Health Where does Managed CARE come in? What is Managed Care? hospital utilisation management pre-authorisations drug utilisation review (DUR) risk sharing and risk transfer arrangements fee arrangements with providers baskets of care disease management programmes co-payments case management preferred providers & DSPs formularies capitation provider profiling predictive modelling gate-keeping second opinions Managed Care • Broad and varied strategies and tools • Involves interventions by the MCO Managed care interventions Costs Care What should be happening in Managed Care? What do we do? What should we also be doing? Cost savings Care management Financial information Clinical information Provider interventions Involve patient (DM) Report on activities and costs Report on member health • What is your MCO doing to manage the health of your members? • What is your MCO measuring re the health of your members? • What do you know about the health of your members? • What types of reports should you be asking for? The Health Continuum Wellness Illness Do you know ? • • • • • How many members have chronic illnesses? What chronic illnesses? How many are receiving quality care? What is being done to improve care? What are the outcomes? Chronic condition prevalence Are these members receiving quality care? Measuring Care Donabedian Model Structure Process Outcome Diabetes - measuring care (process) Necessary monitoring % of patients at first measure HbA1c Lipogram Blood pressure Renal function 21 54 65 53 Eye examination Podiatrist 26 38 Case study : Diabetes Disease Management Programme Diabetes - measuring care Necessary monitoring % of patients At first measure At current measure % improvement HbA1c 21 75 257 Lipogram 54 87 61 Blood pressure 65 85 31 Renal function 53 85 60 Eye examination 26 56 115 Podiatrist 38 60 58 Case study : Diabetes Disease Management Programme % of diabetic patients having HbA1c test 80 70 60 50 % of diabetic 40 beneficiaries 30 20 10 0 Jan-13 Apr-13 Jul-13 Oct-13 Jan-14 Jan 2013 - July 2014 Case study: Diabetes Disease Management Programme Apr-14 Jul-14 But ….is their chronic condition well controlled? Benefits of Good Control Measures Benefit Blood sugar (including HbA1c) Per 1% reduction in HbA1c 37% reduction in complications e.g. amputations, blindness, kidney damage 16% reduction in heart attacks 21% reduction in diabetes-linked deaths Blood Pressure 51% reduction in major cardiovascular events e.g. heart attacks and strokes. 32% reduction in diabetes-linked deaths Lipids (LDL) 55% reduction in major cardiovascular events e.g. heart attacks and strokes 48% reduction in deaths Ref: SEMDSA Guidelines on Management of Type 2 Diabetes 2012 South African Dyslipidaemia Guidelines Consensus statement 2012 South African Hypertension Guideline 2011 Measures Targets HbA1c •Young, low risk, newly diagnosed <6.5% •Majority of patients < 7% •Elderly, frail, high risk, CVD < 7.5% Lipids- LDL •Low-med risk <3mmol/l •High risk <2.5mmol/l •Very high risk <1.8mmol/l Blood pressure •All stages < 140/90mmHg •High risk <130/80mmHg SEMDSA Guidelines on Management of Type 2 Diabetes 2012 Diabetes - measuring care Measure % of patients “controlled” (within target) At first At current measure measure % improvement HbA1c 41 79 93 Lipids 38 64 68 Blood pressure 67 89 33 Case study: Diabetes Disease Management Programme HbA1c within acceptable levels 90 80 70 60 % of diabetic 50 beneficiaries 40 30 20 10 0 Jan-13 Jul-13 Jan-14 Jan 2013 - July 2014 Jul-14 Diabetes- Improving Outcomes Hospital admissions Pre- DM programme Current % improvement 5.3%* 0.9% 83% * Per annum Asthma Number of patients using medicines correctly At first measure At current measure 59% 82% GINA: Update 2014 Asthma – Health status Asthma control At first measure At current measure Controlled 52% 79% Partially controlled 33% 15% Uncontrolled 15% 6% Ref: GINA Update 2014 Asthma- Improving Outcomes Hospital admissions Pre-DM programme Current % Improvement 5.1% 0.2% 88% Case study: Asthma Disease Management Programme HIV – Health status CD4 Ranges % of HIV patients Stage 1 >500-600 cells/ml 42 Stage 2 350-500 cells/ml 38 Stage 3 200-350 cells/ml 12 Stage 4 < 200 cells/ml 8 Stage (CD4) WHO Consolidated guidelines on use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection. June 2013 ? Are these patients having • Viral load tests • CD4 counts HIV – Health status Status 2nd Q 2014 Improved 43% Stable 49% Regressed / deteriorated 8% Ref: HIV Disease Management Programme What do you know about hospital admissions? How many hospital admissions are preventable? 4.5% 4.0% 3.5% 3.0% 2.5% % OF HOSPITAL ADMISSIONS 2.0% 1.5% 2012 1.0% 2013 0.5% 0.0% TYPES OF ADMISSIONS Prevention and Screening • Flu vaccines • Pneumococcal vaccines • Mammograms • Cervical cytology • HIV screening • Cholesterol screening • Glaucoma screening • Colorectal cancer screening • Managed Care is not only about cost savings • Managed Care is also about CARE - members’ health • MCO’s should be measuring costs and care • MCO’s should be reporting on members’ health/care Every Board of Trustees should have at least one person who has a medical background. THANK YOU