Drug Information Resources by Mr. Barcelona

Drug Information Resources:
An Overview
Rob Barcelona, PharmD, BCPS
Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, CICU
Objectives
Utilize drug information sources available at
University Hospitals Case Medical Center
Describe UHCare functionality as it relates to Pharmacy Services
List dosing and monitoring of specific patient populations and medications
Pharmacy Clinical Resources
Clinical on Call Pager 30558
–
Rotates among all clinical specialists
CICU: Rob Barcelona 30274
SICU: Wes Bush 30393
Infectious Diseases: Ron Cowan 31960
NSU: Jason Makii 37884
MICU: Andreea Popa 31503
Transplant: Raelene Trudeau 38643
Tertiary Resources
Condense, digest, and summarize information from primary and other resources
Provide rapid access to information
Limitations:
–
–
–
Currency of the resource (i.e., how long ago was that information published?)
Accuracy of information
Incompleteness (e.g., over the counter medications not contained)
Examples include MICROMEDEX ® , textbooks, UpToDate ® , review articles, and encyclopedias
UH Case Medical Center
Specific Resources
Anticoagulation Therapy and Anticoagulation
Reversal
Adult IV Medication Guidelines
Antimicrobial Usage
Restricted Medications
Drug Specific Guidelines (e.g., antibiotic locks,
IVIG, etc.)
Where can resources be found?
Lexi - Comp
®
Online™
> 4,000 monographs of medications and nearly 30 fields with each drug monograph
Both text and on-line in UpToDate®
Information includes:
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Dosing
Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Pregnancy/lactation considerations
Adverse reactions
Drug interactions
Nutrition/herb interactions
MICROMEDEX
®
Available from UH Pharmacy website: http://intranet.uhhs.com/pharmnet/
Facts on drugs, teratogenicity, toxicology, and alternative medicine
On-line version of the Physicians ’ Desk Reference
Very comprehensive and contains the following:
–
–
–
–
–
–
Dosing
Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Drug interactions, cautions
Clinical applications
References
Limitations: difficulty in finding information and frequency of updates
UHCMC Adult IV Guidelines
The Internet
Many resources available using the Internet
Should be utilized only if other databases or references fail to provide any valid information
Limitations include lack of quality control and imprecise searching that may lead to many undesired “ hits ”
Information found may not come from a verifiable source and potentially could be inaccurate, possibly leading to patient harm
If UHCMC has guidelines, protocols, or ordersets, use those developed by UHCMC staff
Conclusion
Variety of resources are available
Familiarize yourself with the on-line resources, databases, and textbook references in finding drug information
If all else fails, ask your pharmacist
More on Resources … and EMR stuff
Andreea Popa PharmD, BCPS
MICU Clinical Pharmacy Specialist
MICU and other resources
Why does the pharmacist call you???
Invalid order/need further clarification
Bad Orders
Non-formulary drug
Renal Dosing
Drug interactions
Drug on short supply
Restricted drug
Duplicate orders
What happens after you place an order?
Pharmacist actively looks for the orders on the different units (2-3 units per pharmacist; 60 -100 pts)
Looks at all medication orders for that patient, diagnosis and pertinent labs
User Schedule Ordering
Verification Screen
Order verification
If no questions order is verified and a label prints
technician prepares drug pharmacist checks drug again drug leaves for delivery to respective nursing units
Controlled substances, emergency meds
OMNICELL
If need something urgent: call area pharmacist
EMR issues…..
Standard administration times
– QD: 9:00
– BID: 09:00; 21:00 12 hours off drug
– TID: 09:00; 14:00; 21:00 12 hours off drug
– QID: 09:00; 13:00; 17:00; 21:00 12 hours off drug
– Q 24, Q 12, Q 8, Q 6: Timing of these is dependent on ordering/nursing administration; subsequent doses are automatically scheduled based on the first dose
Routine, now, stat and time critical….
Routine, now, stat and time critical….
Amlodipine 5 mg daily
– Routine : if passed 9 am, first dose schedule for RN to give next day at 9 am
– ( 99% of ALL medication orders defaulted to routine )
– Now : one dose will be sent now and than next day at 9 am
– STAT : generates a red flag for the pharmacist urgent order first dose now then next day at 9 am (regardless what time now, could be 9 PM)
– TIME CRITICAL : you select the time for the 1 st dose and the subsequent doses will be automatically scheduled q 24 hours from the time of first dose (if ordered Q24H)
Routine, now, stat and time critical….
Cipro 400 mg IVPB q 24 hours
–
–
–
Routine: scheduling of first dose related to ordering time
Now and Stat: create a yellow/red flag for verification
TIME CRITICAL : you select the time for the 1 st dose and the subsequent doses will be automatically scheduled q 24 hours from the time of first dose!
Ordering IV Heparin:
Loading dose, infusion, repeat bolus
Pearls:
1.
Most of lab work is pre-checked
2.
If running continuous infusion, ALWAYS order the repeat boluses
3.
Open Dosing: Never order the open dosing unless Heme/Onc or
Vascular Medicine involved
Electrolyte Ordering
Units, units…….
MMF grams vs. milligrams
Premixed antibiotics, customizing the dose
So, how do I order:
– 1,000 mg
– 500 mg or
– 2,000 mg of vancomycin
????
Restricted Ordersets and
REMS
Pulmonary
Hypertension
Hemodialysis/CVVH
Chemotherapy
Dofetilide (Tikosyn)
Non-formulary drugs
REMS (Risk
Evaluation and
Mitigation Strategy)
– > 200 REMS Drugs
– > 30 Drugs have
Elements to Assure
Safe Use
– > 20 REMS Drugs require informed consent
Other Ordersets…
Admission Ordersets
–
Most patients do not need an IV PPI…
Pneumonia Orderset
–
Antibiotics default to routine
–
Antibiotic selections in alphabetical order vs. preferred
Tylenol OD
Generic Questions
When calling pharmacy for drug info questions:
1.
Ask to talk to a pharmacist
2.
Tell them who you are/contact info
3.
Give them patient name and location
4.
Give them synopsis of case and relevant clinical information to get most appropriate answer (what you are treating,other drugs, renal function, etc.)
Drug Dosing in Special
Populations
Renal Failure
–
Intermittent vs Continuous Hemodialysis vs Ultrafiltration
Obese/Low weight
Geriatrics
Estimating Renal Function
Cockcroft and Gault equation:
CrCl = (140 - age) x IBW / (Scr x 72)
(x 0.85 for females)
IDMS-traceable MDRD Study Equation
Conventional units
GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) = 175 x (Scr)-1.154 x (Age)-0.203 x (0.742 if female) x (1.212 if
African American)
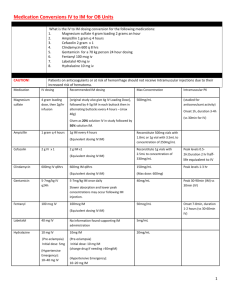
Vancomycin
Drug
Immunosuppressants
Phenytoin
Aminoglycosides
Digoxin
Heparin assay, Lovenox
Drug Levels
Timing Notes
Trough 30 minutes prior to 4 th dose Individualized dosing for patients with renal dysfunction
Trough levels within 1 hour of dose
(0600, 1800)
Contact Transplant Service for guidance
1.
2.
3.
Trough concentration
Within 2-3 days of initiation
Within 1 hour of load to determine maintenance or need to reload
Traditional: trough with 3 rd dose and peak 30 minutes after end of infusion
Extended: trough with 2 nd dose
Trough concentration
NO need for daily levels
Order free levels in patients with renal failure and/or low albumin
Depends on traditional vs. extended dosing
Must be drawn at least 6 hours post-dose
4 hours post-3 rd dose Use in extremes of body weight, pregnancy, renal dysfunction