ADHERENCE TO FBP BY HIV POSITIVE CHILDREN 6

F ACTORS INFLUENCING THE
NUTRITIONAL OUTCOME OF HIV
POSITIVE CHILDREN
ON
6-59 MONTHS
F OOD B Y P RESCRIPTION IN
DANDORA , NAIROBI KENYA
EDWINA MAKOKHA
A90/0307/2008
SUPERVISOR 1:Prof.S.K.Mbugua
SUPERVISOR 2: Mrs. A.A. Andago
I NTRODUCTION
FBP is a nutrient based intervention that provides fortified blended food and nutritional care at HIV care and treatment facilities in
Kenya.
The programme’s objective is to provide energy and nutrient-dense food products along with nutrition assessment, counselling and clean, safe water to PLHIV who are malnourished or at risk of malnutrition
Study was conducted in Dandora at Lea Toto program -provides support to most of the households of children infected with HIV through provision of medication, nutrition support and social support
RESEARCH PROBLEM
Despite the efforts by the government and various NGOs to offer nutrition and food to
PLHIA to improve well-being and treatment outcomes, support treatment adherence and protect household integrity and to encourage a productive recovery and sustained adherence through various interventions ,there are various factors that interfere with the effectiveness and positive outcomes of such food based interventions.
These factors are both external and internal.
JUSTIFICATION
Food by prescription aims at improving nutritional status of children living with
HIV/AIDS.
This is quite a challenge because of various factors e. g socio-economic factors, demographic factors, household food security and morbidity experience that negatively impact on the improvement of nutritional status.
This research will assist bring out the real issues beyond the service delivery which when addressed will improve the nutritional outcome and thus nutritional status of the HIV positive children.
AIM
To contribute towards improving the nutritional status of HIV positive children who are below five years of age in Kenya
PURPOSE
To identify factors affecting the effectiveness of feeding programme related to HIV/AIDS for children to ensure improvement of service delivery aimed at enhancing their nutritional status and their overall health
MAIN OBJECTIVE
To assess factors influencing the nutritional outcome of HIV positive children 6-59months on Food by
Prescription in Dandora
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVE
To determine the socio-economic and demographic factors that affect children who are on FBP
To determine adherence to prescribed treatment and feeding regimes
To determine the nutritional status of the children at their enrollement to the programme and subsequent visits to the clinic
To determine the morbidity experience of the study children.
METHODOLOGY AND TOOLS
STUDY SETTING
Study was based in Dandora at the Lea Toto program.
Dandora is a high density slum with high poverty, unemployment and crime rates and high prevalence of disease especially HIV/AIDS.
STUDY DESIGN
The study encompassed a crosssectional design with a descriptive and analytical component undertaken at Lea Toto program in
Dandora
Both qualitative and quantitative data was collected
The study tools used; semi structured questionnaire and
Dietary diversity score
SAMPLE SIZE DETERMINATION
Exhaustive sampling was done that generating a population size of 37 clients which met the rule of a minimum size of 30 for valid statistical analysis.
This is because only 37 clients were enrolled into the programme at the time of the study.
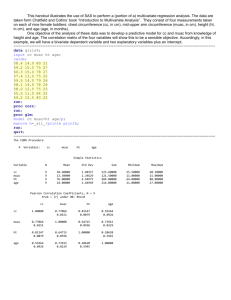
AGE (mo)
6-17
18-29
30-41
42-53
54-59
Total
D ISTRIBUTION BY AGE AND SEX
Boys no.
8
%
66.7
Girls no.
4
8 44.4
1 100.0
10
0
1 1
1
19
50.0
25.0
51.4
3
18
%
33.3
55.6
0.0
50.0
75.0
48.6
Total no.
12
18
1
2
4
37
%
32.4
48.6
2.7
5.4
Ratio
Boy:girl
2.0
0.8
10.8
100.0
1.0
0.3
1.1
E DUCATION LEVEL ATTAINED
A VERAGE FAMILY SIZE
P ROPORTION OF CLIENTS COLLECTING
FBP/M EDICINES AS SCHEDULED
Yes No
38%
62%
P ERCENT DISTRIBUTION OF CLIENTS WHO
FINISHED THE FEED GIVEN
No yes
34,1
Percent
56,1
NUMBER OF FOOD GROUPS
CONSUMED
60
50
40
80
70
30
20
10
0
4-7 >8
FOOD GROUPS
M ORBIDITY EXPERIENCE malaria pneumonia skin diseases others-RTI,TB,dehydration,diahhoea, fever
53%
33%
7%
7%
CD4 COUNT VS DISEASE
FREQUENCY
There is a relationship between CD4 count and frequency of disease but the influence is small
(r=-0.291)
MUAC
MUAC BEFORE
80,00%
70,00%
60,00%
50,00%
40,00%
30,00%
20,00%
10,00%
0,00%
11.1-12.5
12.6-13
MUAC Cut offs
>13
Percent
MUAC AFTER
60,00%
50,00%
40,00%
30,00%
20,00%
10,00%
0,00%
11.1-12.5 12.6-13
MUAC cut offs
>13
Percent
W EIGHT FOR HEIGHT Z SCORES
Baseline WHZ Intervention WHZ
CONCLUSION
From the study it was evident that majority of the clients were complying to the specifications of the programme, but a few who did not, was as a result of external and internal factors that influenced their intake of the food supplement given and thus their nutritional status
This factors negatively influence the effectiveness of such food based intervention programs.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The program should introduce an aspect of economic empowerment into it objectives so as to address the problem of poor economic status at the household level which affects the household food security.
The Lea Toto management should stress the appropriate usage of FBP in terms of adherence to FBP guidelines to ensure maximum benefits from the program.
REFERENCES
UNAIDS/WHO/UNICEF,2009/2010
.Global HIV/AIDS Statistics vol. 6, pg 2
Kenya Demographic Health Survey 2008-
2009, pg213-214
Child survival and Development Strategy
Ministry of Health and Sanitation 2008-
2015, pg 1-24
Kenya National Guidelines on Nutrition and HIV/AIDS, 2007, pg 54-64
C ONT .
UNAIDS, Report on the global AIDS epidemic ,
Geneva, 2010.
FANTA 2/USAID, “A Review of Kenya’s Food by prescription Program” 2009
THANK YOU!