IV - MMMIG.nl
advertisement
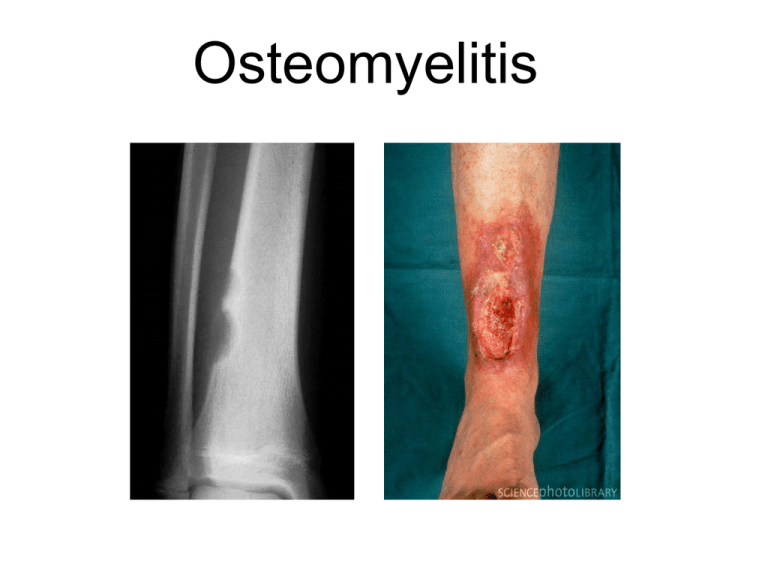
Osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis • Hematogene verspreiding • Verspreiding per continuitatum vanuit wekedelen of gewrichten • Directe inoculatie t.g.v. trauma of chirurgie Anatomic Classification II: (Cierny-Mader) 1985 III: IV: Hematogene osteomyelitis Acute osteomyelitis • Meestal in metaphyse • Doorbraak in gewricht septische artritis • Metaphyse in gewricht bij knie, heup en schouder Chronische osteomyelitis • De aanwezigheid van een drainerende sinus is pathognomisch voor chronische osteomyelitis • Niet helende fracturen en Brodie’s abces • Diabetes mellitus – Ulcera onderliggende osteomyelitis – Als ulcer groter is dan 2 x 2 cm of bot is palpabel is de diagnose osteomyelitis zeer waarschijnlijk Microbiology of osteomyelitis Common (>50%) Occasionally (>25%) Rare (<5%) Staphylococcus aureus Streptococci Mycobacterium tuberculosis CNS Enterococci Mycobacterium avium compl. Pseudomonas spp. Atypical mycobacteria Enterobacter spp. Fungi Proteus spp. Candida spp. Escherichia coli Aspergillus spp. Serratia spp. Mycoplasma spp. Anaerobes Tropheryma whipplei Brucella spp. Salmonella spp. Actinomyces spp. Mandell, Douglas and Bennett’s, Principles and practice of infectious diseases, seventh edition Diagnostiek • Een accurate diagnose van osteomyelitis is cruciaal gezien de langdurige behandeling met antibiotica en de eventuele “aggressieve” chirurgische debridement. Diagnostiek • Microbiologie Open chirurgisch biopt of naaldbiopsie • Pathologie • Beeldvorming: – – – – Gewone röntgenfoto MRI Bot scan PET CT Beeldvorming • Op gewone x-foto zijn afwijkingen te zien 10 tot 14 dagen na de start van infectie X-foto Figure 1. Plain film radiograph of spinal discitis / osteomyelitis. Lateral view of the lumbar spine demonstrates L 3-4 disc space narrowing (arrow) and end-plate irregularity. MRI Figure 2. MRI of lumbar spine discitis/osteomyelitis. A. Sagittal T1-weighted images of the lumbar spine in the same patient as figure 1 demonstrate T1-hypointense signal (solid arrows) centered around the L3-4 interspace. B. Post gadolinium sagittal fat-suppressed T1-weighted images shows marrow (dashed arrows) and disc enhancement with endplate erosions. PET-CT An 11-y-old boy with history of Xlinked chronic granulomatous disease who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT as part of his work-up. Coronal PET image demonstrates several areas of osteomyelitis (both feet and distal right femur) (O), several soft-tissue sites of inflammation (left forearm, left femur, and both shins) (I), pneumonia (P), and paratracheal and hilar adenopathy (A). FDG = Fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose Microbiologie • Afname materiaal voor kweek – Open chirurgische biopsie – Naald biopsie • Bloedkweken Speciale kweken • Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Schimmels en gisten • Brucella Therapie • Chirurgische debridement Plus eventueel: – Verwijderen van “hardware” – Revascularisatie – Complete sluiting wond (spierflap) – Stabiliteit waarborgen bij evt. fracturen • Antibiotica (langdurig) – Iv of oraal? Duur? ZGV • Acute hematogene osteomyelitis: verwekker onbekend flucloxacilline, clindamycine verwekker bekend S aureus: flucloxacilline, clindamycine Streptokokken: peni, clindamycine Pseudomonas: cefta + genta, cipro ZGV • Na trauma of per continuitatem verwekker onbekend geen perifere vaataandoening Flucloxacilline, clindamycine wel perifere vaataandoening clindamycine + /- cipro Casus • • • • • Dhr R 52 jr. Charcot osteoarthropathie voet Ulcus met osteomyelitis Bloedkweken: Streptococcus agalactiae Wondkweek: Stapylococcus aureus HSC • Amoxicilline/ clavulaanzuur iv. Kweken Bloedkweek Wondkweek Vervolg casus • Allergie clindamycine Vragen: • Is oraal behandelen mogelijk? • Welke orale opties zijn er? • Is er bewijs voor toegevoegde waarde van rifampicine? Review CID CID 2012:54 (1 february) Problemen chronische osteomyelitis 1. Geen goede representatieve kweken 2. Vaak “Delay” in behandeling 3. Therapiefalen Parenterale antibiotica • Botpenetratie beta-lactams 5-20% serumspiegels • IV betalactam botspiegels > MIC • Orale dosering beta-lactam AB < 10% iv serumspiegels botspiegels < MIC Parenterale antibiotica • Vancomycine lage penetratie in bot • Hoge serumspiegels botspiegels > MIC • Daptomycine idem. Orale antibiotica • AB met goede penetratie in botweefsel: – Fluoroquinolonen – Linezolid – Trimethoprim – Sulfamethoxazol – Doxycycline – Clindamycine – Metronidazol – Rifampicine – Fusidinezuur – Fosfomycine ± 30-60% van serumspiegels ± 50% ± 50% ± 10-20% ± 2-86% afhankelijk welk bot ± 40-70% ± 80-100% > 100% ± 40-90% ± 25% Gerandomiseerde studies AB behandeling chronische osteomyelitis • 8 kleine studies totaal N=228 • 5 studies vergelijken iv met oraal • Geen significante verschillen in uitkomst na 12 maanden • Bijwerkingen iv vs oraal 15,5% vs 4,8% Rifampicine • 2 studies met toevoeging rifampicine bij chronische osteomyelitis S. aureus • Uitkomst beter in rifampicine groep • Genezing17 van 20 vs 12 van 21 • Zimmerli: geïnfecteerde prothesen • Cipro + rifamp vs cipro mono 3-6 mnd • Genezing 100% vs 58% • 4 van 5 pt met therapiefalen ontw. cipro R Gerandomiseerde studies co-trimoxazol • • • • • • Cloxacillin vs co-trim + rifamp bij S. aureus N=50 8 weken 20 patiënten met prothese “Cure rate” 91% vs 89% Follow-up 10 jr. “relaps rate” 10% vs 11% Opmerkingen • Weinig hard bewijs bij AB behandeling chronische osteomyelitis • Studies met lage aantallen en heterogene groepen • Minder studies voor iv dan orale AB Conclusies 1. Orale behandeling met oraal AB met goede penetratie bot lijkt acceptabel • • • Ciprofloxacine 2dd750mg Co-trimoxazol 7-10 mg/kg/dg (trimethoprim) Clindamycine, doxycycline, Linezolid 2. Toevoeging rifampicine alleen bewezen effect bij S. aureus 3. Geen evidence voor duur therapie (na chirurgische debridement) Vervolg casus Bloedkweek Wondkweek Behandeling? • Chirurgische debridement met sluiten defect mogelijk? • Beste orale optie co-trimoxazol? • Rifampicine toevoegen? • In 25% gevallen DM en osteomyelitis) toch amputatie… Vragen en discussie