Interrelationships of Medicine and Dentistry
advertisement

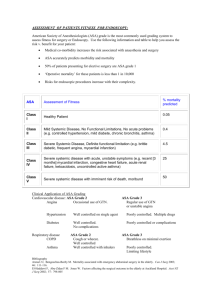
SENIOR ORAL MEDICINE Chapter 1: Physical Evaluation & Risk Assessment Susan Settle, D.D.S. August 26, 2010 Interrelationships Of Medicine And Dentistry Physical Evaluation & Risk Assessment Practice Goals Deliver The Best Care Possible For The Patient Be Aware What Impact The Systemic Status And Medications May Have On Delivery Of Treatment To Feel Comfortable Treating A Variety Of Patients Value Of The Health History Questionnaire & Medical History It Is The Cornerstone Of Patient Evaluation & Risk Assessment Identifies Systemic Disease Identifies Medications Establishes Rapport Medicolegal Protection For The Practitioner Risk Assessment Involves Identification Of: Nature, Severity, & Stability Of The Patient’s Medical Condition Functional Capacity Of The Patient Emotional State Of The Patient Type & Magnitude Of The Dental Procedure American Society Of Anesthesiologists Classification Of Patients Based On Medical Assessment Of Patient ASA Classification Groups ASA I Normal, Healthy Patient ASA II Mild Disease Does Not Interfere With Daily Activities May Need Some Alteration Of Dental Treatment Examples: Mild HTN Or COPD,Type II Diabetes, Allergy, Well-Controlled Epilepsy Or Asthma ASA Classification Groups ASA III Moderate To Severe Systemic Disease May Alter Daily Activities Generally Requires Alteration Of Dental Treatment Medications Type I Diabetes, Moderate To Severe HTN, Angina, CHF, AIDS, COPD, Hemophilia, MI In Last 6 Months ASA Classification Groups ASA IV Severe Systemic Disease Life-Threatening Conditions Requires Alteration Of Dental Management ESRD, Liver Failure, Advanced AIDS ASA Physical Status P1 A normal healthy patient P2 A patient with mild systemic disease P3 A patient with severe systemic disease P4 A patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life P5 A moribund patient who is not expected to survive without the operation P6 A declared brain-dead patient whose organs are being removed for donor purposes Patients Requiring Further Evaluation By The Anesthesiologist For General Surgery Morbid Obesity (BMI>38) MI Within 6 Months Angioplasty Within 3 Months History Of Heart Transplant History Of Unstable Angina Patients Requiring Further Evaluation By The Anesthesiologist For General Surgery History Of Carotid Surgery Within 6 Months History Of Steroid-Dependent Asthma Or COPD Particularly With URI In Last 4 Weeks (Upper Respiratory Infection) Seizure Within 3 Months While Taking Anticonvulsants Patients Requiring Further Evaluation By The Anesthesiologist For General Surgery History Of Allergy To Local Anesthetics History Of Dialysis Or Renal Transplant History Of CVA/TIA Within 6 Months (Cerebrovascular Accident/Transient Ischemic Attack) Systolic BP>200 And/Or Diastolic BP>100 History Of Cirrhosis (Need Recent CBC, INR, LFT) Risk Assessment ABCs Of Risk Assessment Are More Helpful Than The ASA Physical Classification System ASA System Does Not Provide Information About Modification Of Treatment Risk Assessment A: Antibiotics Anesthesia Anxiety Allergy B: Bleeding C: Chair Position D: Drugs Devices E: Equipment Emergencies Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases Heart Failure (CHF) A Clinical Syndrome Complex No Routine Treatment If Not Controlled Consider Chair Position Cardiac Glycosides (Digoxin, Lanoxin) + Vasoconstrictors Arrhythmias (Avoid Vasoconstrictors If Possible) Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Myocardial Infarction No Routine Treatment If In Last 1-6 Months (Refer To Your Text!) Increased Risk Of Reinfarction, CHF Arrhythmias & Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Angina Pectoris Stable Unstable: Chest Pain At Rest Increased Incidence Of Arrhythmias, MI’s, Sudden Death Elective Treatment Contraindicated Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Hypertension Non-Selective Beta-Blockers (Propranolol, Inderal) +Vasoconstrictors Possible Hypertensive Crisis Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Murmur Functional Organic Regurgitation Associated With MVP Diagnosed By Echocardiogram No Recommendation For Endocarditis Prophylaxis From AHA Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Rheumatic Heart Disease From Rheumatic Fever Following A Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal Infection Valve Damage? No Recommendation For Endocarditis Prophylaxis Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Congenital Heart Disease Prosthetic Heart Valves Arrhythmias: Frequently Related To Heart Failure Or Ischemic Disease Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Cardiac Surgery CABG (Coronary Artery Bypass Graft) Transplant: Immunosuppression Considerations Medical History Overview Cardiovascular Diseases (Cont.) Stroke Or CVA: Anticoagulation Possibilities Aneurysm: If Repaired, No Prophylaxis Required After 6 Months Medical History Overview Hematologic Disorders Transfusion: Why Was It Done? Risks Anemia Leukemia “Bleeds Longer Than Normal” Genetic (Hemophilias) Acquired (Pharmacotherapy) Medical History Overview Neural/Sensory Disorders Headache, Dizziness, Syncope Glaucoma: Avoid Anticholinergic Drugs If Patient Has Closed-Angle Glaucoma (Banthine, Pro-Banthine) Given To “Dry Up” Saliva Epilepsy, Seizures, Convulsions Psychiatric Treatment Medical History Overview GI Diseases Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn’s, Ulcerative Colitis - IBD) Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Hepatitis, Cirrhosis Medical History Overview Respiratory Diseases Allergic History COPD-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Emphysema, Chronic Bronchitis) Asthma Tuberculosis Sleep Apnea/Snoring Medical History Overview Musculoskeletal, Mucocutaneous, Dermal Prosthetic Joints Arthritis (Osteo & Rheumatoid) Medical History Overview Autoimmune Disorders Rheumatoid Arthritis SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) Sjögren’s Syndrome Medical History Overview Autoimmune Disorders Scleroderma RAS (Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis) Or “Major” Aphthous Medical History Overview Endocrine Diseases Diabetes Thyroid (Hypo, Hyper) Urinary Tract Kidney Disease Bladder Disease Medical History Overview Sexually-Transmitted Diseases Gonorrhea Syphilis HIV Positive AIDS Medical History Overview Social History Tobacco Alcohol Recreational Drugs Medical History Overview Cancer History Or Treatment Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Surgery Medical History Overview Operations/Hospitalizations & Sequelae Anesthesia Complications Medical History Overview Medications Use Appropriate References When Looking Up Something Steroids, Anticoagulants, Immunosuppressives Allergies, Adverse Reactions Stress Importance Of OTC (Over The Counter) Drugs Medical History Overview Dental History Vital Signs: Initial Exam, Recalls, Whenever Indicated Pulse Rate & Rhythm (60-100 bpm) BP: S <120; D <80 Respiration (12-16 bpm) Medical History Overview General Physical Assessment Gait, Speech, Skin, Nails, Eyes, Nose, Ears, Neck Medical History Overview Laboratory Tests (Indicated?) Hematocrit, Hemoglobin Platelet Count, PT (INR) Fasting Blood Glucose Biopsy Culture & Sensitivity Who Orders The Tests? Communication With Physician HIPAA Forms Must Be Filled Out By Patient At Physician’s Office HIPAA Forms Must Be Filled Out By Patient At Dentist’s Office Communication With Physician Phone & “Sidewalk” Consults Should Be Documented In Progress Notes Formal Documentation Preferred And Now For Some Relatively New Stuff: 2007 AHA Guidelines for Endocarditis Prophylaxis History Of Bisphosphonate Use 2009 American Association of Orthopaedic Surgeons Information Statement Regarding Prosthetic Joint Prophylaxis Risk Is Always Increased When You Treat A Medically Compromised Patient Your Goal Is To Reduce The Risk As Much As Possible