Marijuana, Pills, and Bath Salts, Oh My!
advertisement

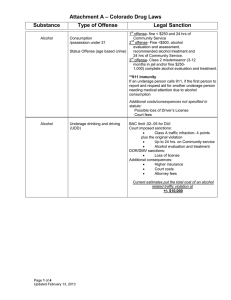
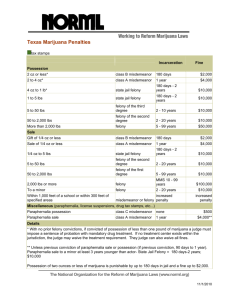
Questions We Will Consider: What are the trends in use, abuse, attitudes and laws on MJ? Historically how have MJ attitudes, use, and laws changed? What short and long term effects does it have on the body? What treatments appear to be effective? What reforms might happen and what might impact be? A couple of disclaimers The information presented here is not intended as direct medical advice or specific treatment information Information is for general educational purposes only and the presentation should not be disseminated or cited without my express permission My email is: tstucky@iupui.edu Trends in Use (see Caulkins et al) Many people have tried MJ Use patterns skewed- a few use a lot Price and potency vary a lot Consumption varies w/ price not enforcement Potency higher in recent years A note about Spice/ K2: Synthetic, similar to MJ, chemical makeup varies, use increasing, may be more potent Not much research yet on effects reporthttp://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/k2spicesynthetic-marijuana How MJ gets distributed Young people most likely to use and get arrested Most arrests for possession Avg user has a 30% chance of arrest in a 10 year using career. Lots of people get it for free Distributed through social networks unlike other drugs Grows just about anywhere Violence NOT common in MJ markets Trends in Attitudes Effects on the Body (see Room et al ch.2) Reminder on disclaimer Not intended as medical advice or to influence treatment directly Short versus long term effects Effects depend on dosage mode of consumption Potency THC/ CBD ratio Some positive, some negative Short term effects Euphoric effects/ duration Effect on heart rate/BP Reduces cognitive performance Some argue enhances creativity Can induce anxiety and paranoia Risk of overdose low, but…. Decreases reaction time so affects driving (DWI) Appears to reduce immune function Some research suggests can harm fetal development Long term effects Cognitive functioning- mixed findings Risks specific to smoking MJ Respiratory and Cardiovascular effects Secondhand smoke Educational outcomes for youth Correlation or cause? Can become dependent Mental health risk Psychosis, schizophrenia, depression Especially for youth? Co-occuring disorders Some open questions Does MJ have medicinal value? Why not just make the THC part legal and prescribe it? How much “medicinal” use is actually recreational use? Is it a gateway drug? Do people just use MJ? Adverse effects compared to other drugs (Room et al, p.42) Effect Traffic accidents MJ Tobacco * Heroin Alcohol * ** Violence/suicide ** Overdose ** * HIV/liver infections ** * Cirrhosis ** Heart disease ** * Respiratory disease * ** Cancers * ** Mental illness * Dependence ** ** ** ** Effects on fetus * * * ** * ** History of Drug Use (see Abadinsky) Around since dawn of civilization Attitudes & laws vary dramatically over time Often seen positively initially Use spreads Dependence (addiction) problems Associated with problem populations Stigma attaches to drug Prohibition creates black markets History of Drug Use (see Abadinsky) Alcohol Tobacco Opium/Morphine/Heroin Coca/Cocaine/Crack Patent medicines E.g. laudenum Amphetamines Barbiturates/ tranquilizers/sedatives Hallucinogens History of MJ (see Abadinsky) Around for thousands of years Used as medicine and for recreational use Commonly used in India and China Hemp used for rope, clothes, & medicinally In U.S. in early 1900s associated with Mexican immigrants and Blacks History of Laws (see Abadinsky) Mistakenly treated as a narcotic despite reports (1890s/1930) not dangerous Harrison Act of 1914 (focused on opium, cocaine) Propaganda such as Reefer Madness Many states banned MJ Marijuana Tax Act of 1937 Never much of an issue until use rose in 1960s Comprehensive Drug Use Prevention and Control Act of 1970 (Schedule I drug) A Brief look at Laws Federal law: MJ is a schedule I drug High potential for abuse No accepted medical use in U.S. Lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision http://norml.org/laws/ Comparing Indiana and Ohio Offense Less than 100 g 100 - 200 g 200 - 1000 g 1000 - 5000 g 5000 - 20,000 g 20,000 - 40,000 g More than 40,000 g Ohio Penalty jail/ prison Possession misdemeanor N/A M 30 days felony 6-12 mos felony felony felony felony 1 - 5 yrs 1 - 5 yrs 5* - 8 yrs 8 years* Max. Fine $150 $250 $2,500 Offense Indiana Penalty jail/prison Max. Fine Possession 30 g or less misdemeanor 1 year More than 30 g felony 6 - 36 mos $5,000 $10,000 Conditional discharge may be available for first-time offenders. $10,000 $10,000 $15,000 $15,000 * Mandatory minimum sentence Sale/Distribution/Trafficking A gift of 20 g or less misdemeanor N/A (first offense) A gift of 20 g or less misdemeanor 60 days (2nd offense) Sale or Cultivation misdemeanor 1 year $150 30 g or less $5,000 $500 30 g - 10 lbs felony 6 - 36 mos $10,000 Less than 200 g 200 - 1000 g felony felony 1 year 6-18 mos $2,500 $2,500 10 lbs+ W/in 1000 ft of school felony felony 2 - 8 yrs 2 - 8 yrs $10,000 $10,000 1000 - 5000 g felony $2,500 To a minor felony 6 - 36 mos $10,000 5000 - 20,000 g felony 20,000 - 40,000 g More than 40,000 g felony felony 1-5 years 1-5 years 5* - 8 yrs 8 years* $2,500 $2,500 $2,500 Correctional Populations by Offense Type 1980-2001 Policy If the goal is to reduce drug use, two options: Supply reduction Primarily legal Demand reduction Prevention, treatment Not an either or situation current policy is to do both Prevention programs (see Mosher and Akins) DARE PSA’s Abstinence only doesn’t work well What does work? Harm reduction, focus on facts, talking with instead of talking at SA Treatments Office of National Drug Control Policy, U.S. National Drug Control Strategy: Addiction a disease of the brain Can be treated and recovery is possible Also focus on prevention Approaches vary widely No current medication for MJ 13 principles of effective treatment… See handout See NIDA report or Crime Solutions.gov for more Reforms (see Caulkins et al or Room et al) What are the range of options for reform? Some terms Depenalization Decriminalization Legalization De facto v. De jure Current policies vary widely Reforms What are the pros and cons of legalization? Can we treat MJ like alcohol? How is legalization of MJ like and unlike legalization for other drugs? Middle ground? Discussion What are the options that are available and what are the likely outcomes one might expect? Other questions? Sources used in presentation Caulkins, Jonathan P., Angela Hawken, Beau Kilmer, and Mark A. R. Kleiman. 2012. Marijuana legalization: What everyone needs to know. Oxford University Press. Room, Robin, Benedict Fischer, Wayne Hall, Simon Lenton, and Peter Reuter. 2010. Cannabis Policy: Moving Beyond Stalemate. Oxford University Press. Abadinsky, Howard. 2010. Drug use and abuse: A comprehensive introduction. Cengage Learning. Faupel, Charles E., Greg S.Weaver, and Jay Corzine (3rd ed.) 2013. The sociology of American drug use. Oxford Press. Mosher, Clayton J., and Scott Akins, eds. 2007. Drugs and drug policy: The control of consciousness alteration. Sage. More sources used in presentation Link to Pew Research Center study on attitudes regarding marijuana legalization. http://www.people-press.org/files/legacypdf/4-4-13%20Marijuana%20Release.pdf This is the National Drug Control Strategy http://www.whitehouse.gov/ondcp/2013national-drug-control-strategy Additional recommended readings and resources Bostwick, J. Michael. "Blurred boundaries: the therapeutics and politics of medical marijuana." Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Vol. 87. No. 2. Elsevier, 2012. Crime Solutions.gov http://crimesolutions.gov/ National Institute on Drug Abuse http://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/marijuana http://www.drugabuse.gov/sites/default/files/podat_1.pdf Principles of effective drug treatment