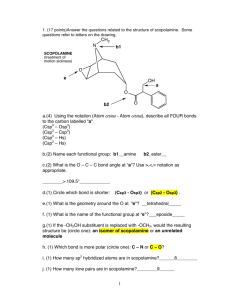
Scopolamine
advertisement
Scopolamine Julia Bedell Laci Click Meredith Barr Where does it come from? Scopolamine is an alkaloid drug found as a secondary metabolite of plants in the Solanaceae family. Solanaceaes are nightshade plants Examples of plants in the family that produce scopolamine are henbane and jimson weed Jimson Weed Chemical make up Alkaloid drugs In the tropane group Alkaloid drugs are defined as naturally occurring amines that are produced by a plant Many have anesthetic or analgesic effects Chemical formula C17H21NO4 A drug with a sorted history! Project MKULTRA In the 1950’s the CIA investigated the use of Scopolamine as a “truth serum” Due to hallucinogenic side effects the drug was determined to be an unreliable interrogation drug So what do we use it for? Scopolamine is used as an anti-nausea medication It is given in patch (transdermal) form to treat nausea associated with motion sickness and chemotherapy. Marketed as Scopoderm and Transderm-V Mechanism of Action Scopolamine is an antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1) Blocking acetylcholine from binding to the receptor blocks Acetylcholine mediated nerve impulses from traveling through the body Mechanism of Action In motion sickness a person feels ill because of conflicting sensory information from the visual senses and balance center in the inner ear. To treat motion sickness this antagonist blocks the acetylcholine mediated nerve impulses to the inner ear where balance is controlled. Other Medical Uses Scopolamine is sometimes used for other medical purposes such as: CNS depressant for pain management Pupil Dilator Paralysis of eye muscles Antispasmodic At one point, Scopolamine was mixed with morphine to produce a state known as “twilight sleep”. “Twilight sleep” was induced to yield an insensibility to pain without loss of consciousness The negative side of Scopolamine use Acetylcholine is the major neurotransmitter found in autonomic ganglia, and is the chemical that allows neurons to communicate for sensory input and muscle control. Muscarinic receptors are important for control of: Central Nervous System Parasympathetic control of heart, lungs, and gastrointestinal functioning Negative side of Scopolamine cont’ By blocking Ach- M1 functioning, you could inhibit the Central and Peripheral Nervous System functioning. Acetylcholine antagonists also cause heart rate to increase which can lead to myocardial infarction or angina. Remember! This drug is highly toxic! It must be used in small doses. An overdose of Scopolamine can cause delirium, paralysis, stupor, heart failure, and death. Other Side Effects Anisocoria Dry mouth Blurred vision Constipation Drowsiness Poor Memory Unequal dilation of pupils (also known as anisocoria) Negative uses of Scopolamine In recent years the use of Scopolamine for criminal purposes has increased dramatically. Scopolamine is often used as a date rape drug because it causes delirium, hallucinations, and has sedative effects on the victim. For more information http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/medmaster/a682509.html http://www.drugs.com/mtm/scopolamine.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scopolamine http://www.transdermscop.com/ (commercial site) http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1641616