Power Point for TCVM lecture
advertisement

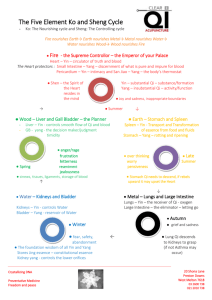
Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine Introduction to Chinese Medicine Theory TCM as a Metaphor Evidence of Acupuncture tools as early as 8,000 years ago 1st definitive evidence of Veterinary Acupuncture ~450 B.C. Taboo to look in body What we say organ does in TCM may be different then what know in western medicine. Western vs. Eastern Goals Western Medicine – treat underlying insult Particularly apt at treating acute illness, emergencies or surgical presentation Eastern Medicine – Treat the whole and try to bring body back to balance Particularly helpful in chronic disease processes Qi Energy, Vital Force, Life Source, Vital Breath All essential life activities involved Spirtual, emotional, mental & physical Obi Wan & the Force If flow of Qi insufficient, unbalanced or interrupted results in illness Different type of Qi including Source, Food, air Qi Travels through meridans or energy pathways 14 main meridians: 12 organ pairs and 2 unpaired Extraordinary meridians Acupuncture (AP) points – where meridians come to surface Includes free nerve endings, arterioles, veins, lymphatics, mast cells Activation results in increased blood flow, change in immune response, relaxes muscles and tissue, alter pain pathway, nerve transmission, hormones, neuro transmitters. Zang Fu/Yang Yin Organ Pairs 12 meridians paired as Husband/Wife or Yang/Yin Yang: male, summer, light, day, external, dry, hot, acute, hollow Yin: female, winter, dark, night, internal, wet, cold, chornic, solid Everything has opposite Opposites control each other Mutually create each other Can transform into each other Zang Fu organ pairs ZANG: Yin Interior Wife Solid Manufacture and store essential substances Qi, Blood, Body Fluid FU: Yang Exterior Husband Hollow Receive and Digest Food Waste transport and excretion Zang Fu Organ Pairs Lung Spleen Heart Pericardium Liver Kidney Large Intestine Stomach Small Intestine Triple Heater/San Jiao Gall Bladder Bladder (Urinary) Lung: Governs Qi & Respiration Dominates Ascending & Descending Control the Body Surface Opens in the Nose Large Intestine: -Receive waste from SI -Reabsorb fluids -Excrete waste Stomach: -Receive Food -Rot and Ripen -Origin of Qi and Blood with Spleen via Food energy Spleen: Governs Transportation & Transformation Controls Blood Dominates the Muscles Opens in Mouth •Lips & Gums (ST) Heart: Dominates the Blood & Vessels Houses the Mind Controls Sweating Opens in the Tongue Small Intestine: -receive from stomach -absorb essentials -seperate clean from turbid - Spleen & Lung then transmit clean to body - Small Intestine transport turbid to LI or Bladder Pericardium: Protects the Heart In Practice, considered the same as the Heart Treat the same May be more related to shen Triple Heater: -Sanjiao – General pathway for distribution of Source Qi and Body fluids -Divided into Upper, Middle, Lower jiao Gall Bladder: --Store/Excrete bile -Assist Digestion -Decision making if Qi deficient Liver: Stores the Blood Maintains the Smooth Flow of Qi & Blood Controls the Sinews Opens in the Eyes Bladder: -Store & Excrete Urine -Association Points Kidney: Stores Essence Governs Water Controls Reception of Qi Dominates the Bones & Marrow Opens in the Ears Controls the 2 Extraordinary Fu Organs Hollow shape of Fu Organs but store essential substances like Zang organs Brain – Sea of Marrow, House of mind, connects with Spinal Marrow Marrow – brain , spinal cord, bone marrow Related to Kidney and Heart Origin =Kidney essence, Nourish brain and bone Bone – controlled by Kidney, form marrow & skeleton Extraordinary Fu Organs, Con’t Vessels – House of blood Circulate Qi and Blood within *Gall Bladder* - Because Hollow, one of regular Fu organ but functions like Zang organ because it stores bile Uterus – Nourishes fetus, controls estrus and pregnancy Closely related to Kidney and extraordinary vessels Diagnostic Systems Systems used to develop a Chinese Medicine pattern 2 main: 8 Principle 5 Element Eight Principle Determine type of Disease process Superficial/Exterior Hot Excess Yang Deep/Internal Cold Deficient Yin Five Element 5 categories in Natural World Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, Water Describe nature of Zang Fu organs, inter-relationship between organs, relationship between body and world With 8 principle can guide diagnosis and treatment Individuals tend to have characteristics, diseases explained by their elemental constitutions 5 Element Wood – leaders, Alpha, Loud, Angers, Quick, Skilled runners, Alert, Diplomat, High BP, Allergy, Depression, Neurosis, Tend to Stagnation Fire – exuberant, always on go, life of party, Extrovert, Center of Attention, Inventor, Persuasive, Arrogant, Exaggerates, separation anxiety, Cardiovascular Disease Earth – Laid back, easy going, Motherly, seek companionship, seek to please, worry, GI issues, Obesity Metal – aloof, confident, love order, Broad minded, Righteous, Vain, Resp problems, Diabetes, Constipation Water – Introverted, Fearful, quiet-observer, planner, advisor, deep thinker, ok alone, consistent but slow, sinister, fear biter, infertility, back pain, UTI Wood Fire Earth Metal water Season Spring Summer Late Summer Fall Winter Climate Wind Heat Damp Dryness Cold Direction East South Center West North Flavor Sour Bitter Sweet Pungent Salty Emotions Anger Irritation Joy Fright Preoccupation Worry Grief Sadness Fear Terror Orifice Eyes Tongue Mouth Nose Ears Sense Vision Speech Taste Smell Hearing Tissue Tendons Ligaments Vascular System Muscles Skin Hair Coat Bones Body Action Spasms Tantrums Mania Depresion Spitting Vomiting Coughing Wheezing Trembling Shivering Additional Diagnostics Tongue – Areas for each element Color Red – Heat, Yin deficiency Pale – Qi or Blood Deficiency Purple – Qi or Blood Stagnation Lavender – Cold, Yang deficiency Yellow – Heat/Damp Coat White –cold, damp, phlegm Yellow – Heat Dry-Yin/Blood Deficiency Wet – Qi/Yang Deficiency, Damp Additional Diagnostics Pulse Dog/Cat – Femoral Equine – Carotid 3 locations on each side and 3 depths In beginning: deep, superficial, thin, broad, fast, slow Work up to wiry and slippery Left<Right – Yin/Blood Deficiency Right<Left – Yang/Qi deficiency