presentation
advertisement

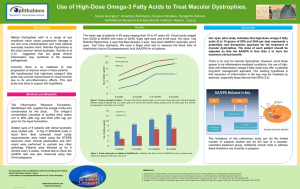
Complimentary and alternative medications (CAMs) in RA Brad Butt Managing partner Cooleman Court Pharmacy WESTON Objectives • Which CAMs are our patients seeking information on • What evidence is there for their use • Possible interactions – disease state/medication CAMs in RA • Fish oils – Trend towards Krill oil • Tumeric/curcumin • Others… Fish Oils • EPH/DHA is the key – polyunsaturated 3 fatty acids. • Flaxseed oil – ALA 5-10% EPA and 1-5% DHA only1&2 • Quality – TGA v GOED (global organisation for EPA and DHA 3) Inflammatory cascade TGA v GOED table Fish oils benefits • Anti-inflammatory effect – complex! – PG/TXA/LT – signalling molecules in inflammation • Arachidonic acid (AA) is the major substrate for their synthesis3-5 – EPA/DHA leads to reduced conversion of AA – Decreases leukocyte chemotaxis reduced proinflammatory cytokines (TNF and IL subtypes) 6-7 – 3.8g EPA + 2g DHA 10 capsules daily Fish oil benefits • Anti depressant effect – Evidence for EPA/DHA in major depressive episodes • Meta analysis – 15 randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trials (916 patients) at doses up to 2200mg EPA/DHA per day concluded effective against primary depression8 Fish oil precautions • Recent clinical studies show no increase in bleed risk; even in patients on aspirin and warfarin with doses up to 7g/day of EPA/DHA9 – Should be done under medical supervision1 • Doses <12g/day need medical supervision1 • Hypomania can occur with fish oil in bipolar patients10 • Seafood allergy theoretically problematic Krill oil – fad or not? • Krill oil has been hugely popular – Comprehensively out sells fish oil – There is a lack of good clinical evidence – Doses need to be in excess of 1500mg daily • 1500mg krill oil 226mg EPA 122mg DHA – General feel is that evidence is for fish oils so recommend fish oil at appropriate dose first for best results Curcumin/Tumeric • May assist with the down regulation of inflammatory mediators • Reduces joint inflammation in RA • Symptomatically works quickly • Lack of large clinical trials – COX2 inhibition believed to be MOA – Less GIT/BP issues associated with curcumin (v NSAID) Curcumin pathway Curcumin precautions • • • • Bile duct obstruction Anti coagulants Can reduce BGL – hypoglycaema risk May increase stomach acid secretion Others • Glucosaime – Minimum 4 week time to effect – Shell fish allergy precaution – 1500mg daily required – +/- condroitin/MSN • Green lipped muscle extract – Anti-inflammatory effect – Small evidence for use Others • St Johns Wart – Used for depression – Effect similar to a SSRI – Variability between brands/batches as plant derived – numerous environmental factors may affect outcome of dose – Many interactions with other Rx medications – Reasonable evidence for its use/effect References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. McCusker MM, Grant-Kels JM. Healing fats of the skin: the structural and immunologic roles of the omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Clin Dermatol 2010;28(4):440-451. Braun L, Cohen M. Herbs and natural supplements: an evidence-based guide, 3rd ed. Sydney: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, 2010. Silva V, Barazzoni R, Singer P. Biomarkers of fsh oil omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids intake in humans. Nutr Clin Pract 2014;29(1):63-72. Calviello G, Su HM, Weylandt KH, et al. Experimental evidence of w-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid modulation of infammatory cytokines and bioactive lipid mediators: their potential role in infammatory, neurodegenerative, and neoplastic diseases. Biomed Res Int 2013;2013:743171. Calder PC. n-3 fatty acids, infammation and immunity: new mechanisms to explain old actions. Proc Nutr Soc 2013;72(3):326-336 Calder PC. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, infammation, and infammatory diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;83(Suppl):1505S-1519S Galarraga B, Ho M, Youssef HM, et al. Cod liver oil (n-3 fatty acids) as an non-steroidal antiinfammatory drug sparing agent in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2008;47(5):665-669. Sublette ME, Ellis SP, Geant AL, et al. Meta-analysis of the effects of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in clinical trials in depression. J Clin Psychiatry 2011;72(12):1577-1584. Harris WS. Expert opinion: omega-3 fatty acids and bleeding-cause for concern? Am J Cardiol 2007;99(6A):44C-46C. Bays HE. Safety considerations with omega-3 fatty acid therapy. Am J Cardiol 2007;99(6A):35C43C.