Upwellings and El Nino
advertisement

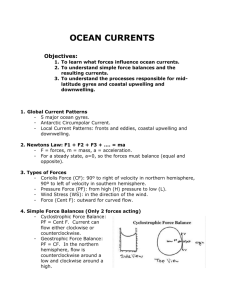
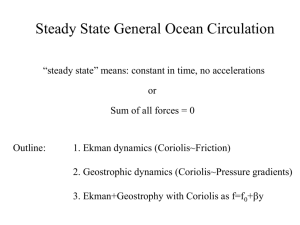
Upwelling, Down welling, and Current Types I. Ekman Transport A. Definition – term given for the 90 degree net transport of the surface layer due to wind forces and Coriolis Effect. B. First investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman C. Ekman motion theory 1. In the northern hemisphere this transport is at a 90 degree angle to the right of the direction of the wind. 2. In the southern hemisphere it occurs at a 90 degree angle to the left of the direction of the wind. D. Ekman Spiral – Model plotting the water layers at various directions, speed and depth Ekman Spiral Model II. Upwelling A. Definition – upward movement of the deeper, cooler waters toward the surface pushing surface waters away from the shore due to the Ekman Transport. B. Description 1. Coriolis Effect moves water at right angles slightly right of the direction the wind is blowing resulting in surface currents pushing the surface waters offshore. 2. When surface waters are pushed offshore, water from below is drawn upward to replace them. C. Caused by Waters Diverging away from a region. D. Effects 1. Brings nutrient –rich waters to the surface encouraging seaweed and phytoplankton growth. 2. Moves drifting larvae long distances from their natural habitat affecting population stability. III. Downwelling A. Definition – Surface waters move toward the shore due to Ekman Transport and sink to the bottom. B. Remember: water is a fluid in constant motion; a change in the distribution of water in one area is accompanied by a compensating change in another area. C. Caused by a Waters Converging toward a region. Upwelling and Downwelling Diagram IV. Types of Currents 1. Gravitational Currents- the vertical pull of gravity and the buoyant force on a mass of fluid 2. Surface Currents- caused by movement of a fluid due to a transfer of energy from another source such as wind 3. Thermohaline Circulation- the movement of a fluid due to differences in salinity or temperature B. Types of Currents (continued) 4. Haline Currents- the movement of a fluid due to differences in salinity. 5. Convection Currents- the movement of a fluid due to differences in temperature