“Fuzzy Logic Speed Controllers Using FPGA Technique
advertisement

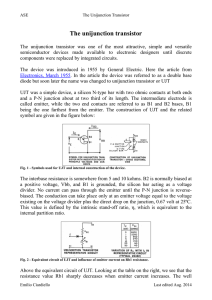
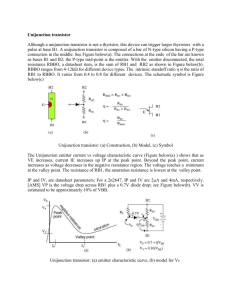
The five layers, n1,p1,n2,p2,n3 can be combined into a single Triacs and Diacs structure to form a new device. A power with four one direction When T1device is positive with layers respectconducts to T2 byinvoltage greateronly. than Bidirectional device may be obtained byon. connecting two of VBO (p2,n2,p1,n1) thyristor will be these back-to-back. If Reverse polarity (p1,n2,p2,n3) will be on. A five-layer diac is a device without used to agate trigger canother be designed semiconductor for various power breakdown switches. Current voltagesand andvoltage currentratings ratings.are A diac determined is a five-layer by the gateless type of device. device. A five-layer device with gate is called triac.( four stages) Unijunction Transistor (UJT) Complementary unijunction transistor (CUJT) Programmable unijunction transistor (PUT) The UJT has one pn junction and is used mainly as a triggering device in thyristor circuits and can also be used in oscillator circuits. The symbol is similar to a JFET. Note the angle of the emitter. The other terminals are called base 1 and base 2. The characteristics are quite different than any other transistor. The resistive equivalent circuit of a UJT shown makes it easier to understand its operation. The emitter current controls the value of rB1 inversely. The total resistance or interbase resistance (rBB) equals the sum of rB1 and rB2. The standoff ratio () is the ratio rB1/ rBB. UJT Operation: Unijunction transistor can trigger larger thyristors with a pulse at base B1.With the emitter disconnected, the total resistance RBB, a datasheet item, is the sum of RB1 and RB2 . RBBO ranges from 412kΩ for different device types. The intrinsic standoff ratio η is the ratio of RB1 to RBBO. It varies from 0.4 to 0.8 for different devices. As VE increases, current IE increases up IP at the peak point. Beyond the peak point, current increases as voltage decreases in the negative resistance region. The voltage reaches a minimum at the valley point. The resistance of RB1, the saturation resistance is lowest at the valley point. IP and IV, are datasheet parameters; For a 2n2647, IP and IV are 2µA and 4mA, respectively. VP is the voltage drop across RB1 plus a 0.7V diode drop; VV is estimated to be approximately 10% of VBB. Peak votage of UJT Vp Vp=ηVbb +Vd Complementary unijunction Transistor (CUJT) Like standard UJT except that the currents and voltages applied to it are of opposite polarity. Ideal for stable oscillators, timers, frequency dividers. Programmable unijunction Transistor (CUJT) Although it has the same name as a UJT the programmable unijunction transistor’s structure is not the same. It is actually more similar to an SCR. Programmable unijunction Transistor (CUJT) The PUT can be “programmed” to turn on at a certain voltage by an external voltage divider. This yields a curve similar to a UJT. Programmable unijunction Transistor (PUT) External PUT resistors R1 and R2 replace unijunction transistor internal resistors RB1 and RB2, respectively. These resistors allow the calculation of the intrinsic standoff ratio η. Programmable unijunction Transistor (PUT) VR is voltage divider (R1 and R2 can be specified) Vc capacitor voltage When Vc > VR the PUT will conduct Programmable unijunction Transistor (PUT) unijunction Transistor trigger circuits LASCR (Light Activated SCR) End of Lecture