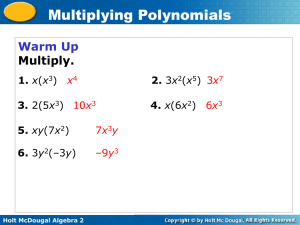
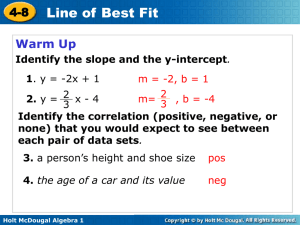
Lesson 2
advertisement

Graphs GraphsofofOther OtherTrigonometric Trigonometric 11-2Functions 11-2 Functions Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz HoltMcDougal Algebra 2Algebra 2 Holt Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Warm Up If sin A = , evaluate. 1. cos A 2. tan A 3. cot A 4. sec A 5. csc A Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Objective Recognize and graph trigonometric functions. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions The tangent and cotangent functions can be graphed on the coordinate plane. The tangent function is undefined when θ = + n, where n is an integer. The cotangent function is undefined when θ = n. These values are excluded from the domain and are represented by vertical asymptotes on the graph. Because tangent and cotangent have no maximum or minimum values, amplitude is undefined. To graph tangent and cotangent, let the variable x represent the angle θ in standard position. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Like sine and cosine, you can transform the tangent function. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Example 1: Transforming Tangent Functions Using f(x) = tan x as a guide, graph g(x) = Identify the period, x-intercepts, and asymptotes. Step 1 Identify the period. Because b = the period is Step 2 Identify the x-intercepts. The first x-intercept occurs at x = 0. Because the period is 3, the x-intercepts occurs at 3n where n is an integer. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Example 1 Continued Step 3 Identify the asymptotes. Because b = , the asymptotes occur at Step 4 Graph using all of the information about the function. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Check It Out! Example 1 Using f(x) = tan x as a guide, graph . Identify the period, x-intercepts, and asymptotes. Step 1 Identify the period. Because b = the period is Step 2 Identify the x-intercepts. The first x-intercept occurs at x = 0. Because the period is 2, the x-intercepts occur at 2n where n is an integer. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Check It Out! Example 1 Continued Step 3 Identify the asymptotes. Step 4 Graph using all of the information about the function. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Example 2: Graphing the Cotangent Function Using f(x) = cot x as a guide, graph . Identify the period, x-intercepts, and asymptotes. Step 1 Identify the period. Because b = 3 the period is Step 2 Identify the x-intercepts. The first x-intercept occurs at x = . Because the period is , the x-intercepts occurs at , where n is an integer. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Example 2: Graphing the Cotangent Function Step 3 Identify the asymptotes. Because b = 3, the asymptotes occur at Step 4 Graph using all of the information about the function. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Check It Out! Example 2 Using f(x) = cot x as a guide, graph g(x) = –cot2x. Identify the period, x-intercepts, and asymptotes. Step 1 Identify the period. Because b = 2 the period is . Step 2 Identify the x-intercepts. The first x-intercept occurs at x = . Because the period is , the x-intercepts occurs at , where n is an integer. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Check It Out! Example 2 Continued Step 3 Identify the asymptotes. Because b = 2, the asymptotes occur at x= Step 4 Graph using all of the information about the function. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Recall that sec θ = . So, secant is undefined where cosine equals zero and the graph will have vertical asymptotes at those locations. Secant will also have the same period as cosine. Sine and cosecant have a similar relationship. Because secant and cosecant have no absolute maxima, no minima, amplitude is undefined. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions You can graph transformations of secant and cosecant by using what you learned in Lesson 11-1 about transformations of graphs of cosine and sine. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Example 3: Graphing Secant and Cosecant Functions Using f(x) = cos x = as a guide, graph g(x) = Identify the period and asymptotes. Step 1 Identify the period. Because sec is the reciprocal of cos the graphs will have the same period. Because b = 2 Holt McDougal Algebra 2 for cos the period is Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Example 3 Continued Step 2 Identify the asymptotes. Because the period is 4, the asymptotes occur at where n is an integer. Step 3 Graph using all of the information about the function. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Check It Out! Example 3 Using f(x) = sin x as a guide, graph g(x) = 2csc x. Identify the period and asymptotes. Step 1 Identify the period. Because csc x is the reciprocal of sin x the graphs will have the same period. Because b = 1 for csc x the period is 2 Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Check It Out! Example 3 Continued Step 2 Identify the asymptotes. Step 3 Graph using all of the information about the function. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Lesson Quiz: Part I 1. Using f(x) = tan x as a guide, graph g(x) = Identify the period, x-intercepts, and asymptotes. period: 2; x-intercepts: 2n; asymptotes: x = + 2n Holt McDougal Algebra 2 Graphs of Other Trigonometric 11-2 Functions Lesson Quiz: Part II 2. Using f(x) = sin(x) as a guide, graph g(x) = Identify the period, and asymptotes. period: 6; asymptotes: x = 3n Holt McDougal Algebra 2