L11_statics
advertisement

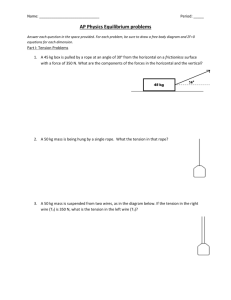
Statics Forces in equilibrium § 5.1 What’s the point? • How do forces balance? • What forces must structures withstand? • What is the result of non-balancing forces? Poll Question weight 1m T 8m T A hammock slung between trees 8 m apart sags 1 m when a person lies in it. The tension in each rope holding the hammock is A. B. C. D. Equal to the weight of the person. Half the weight of the person. More than the weight of the person. Less than the weight of the person, but more than half. Whiteboard Problem weight 1m T T 8m • Identify the forces acting on the hammock. • Draw a free-body diagram for the hammock. • Find the components of all the forces. Free-body Diagram tension tension weight Acceleration = 0, so forces add to zero Observe the magnitudes! So, for the hammock… • Tension is the same direction as rope stretch: 4 horizontal: 1 vertical • Add up the vectors! 4 1 2 1 Here, tension is over twice the weight! Dynamics acceleration § 5.2 Example Problem 4.1001 A person pulls on a rope attached to an initially motionless 25-kg box on a frictionless plane inclined 30° to the horizontal. She pulls with a force of 20 N parallel to the plane of the ramp. Find the speed and position of the box after 5 s. 30° Example Problem A cart of mass M is attached to a free-hanging weight of mass m over a frictionless pulley by a massless string. Find the acceleration of the cart and the tension in the rope. M m