Kinematics
advertisement

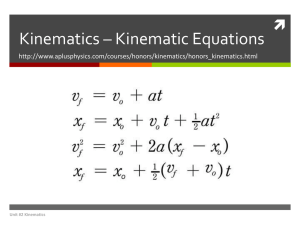
Topic 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Displacement Vectors Kinematics Graphs Energy Power Springs Shadows Field of Vision Colors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors Refraction Lenses Optical Power Slides Minutes 9 27 13 39 13 39 10 30 10 30 5 15 4 12 3 9 7 21 3 9 7 21 4 12 5 15 10 30 6 18 Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects without regard to the forces that produce the motion. There are six important formulas used in kinematics, four are defined and two are derived (from the defined ones). Using the following six formulas, all the problems in kinematics can be solved: Defined Derived s = v = vi = vf = va = t = a = distance velocity initial velocity final velocity average velocity time acceleration Click Kinematics Slide: 3. 1 Remember When calculating the average velocity of an entire trip, use the total time of the trip, even the time while not moving. Click 3. 2 Find the velocity of an object after falling freely for 3 m. Kinematics Slide: 3. 3 ti = 2 s to tf = 3 s Use g = 9.8 m/s2 if you want to be more accurate! Click Kinematics Slide: 3. 4 A stone is thrown straight up with a velocity of 32 m/s towards a tree branch that is 25 m high. With what velocity does the stone hit the branch? A) 15 m/s B) 23 m/s C) 39 m/s D) 534 m/s Click Kinematics Slide: 3. 5 Click Kinematics Slide: 3. 6 June dropped a stone and measured the time it took to fall a certain distance. After collecting her data, she plotted the acceleration versus the time of the falling stone. Which of the following graphs represents this situation? REMEMBER Falling objects have a constant acceleration. Click Kinematics Slide: 3. 7 Jack and Jill ride their bikes in an empty parking lot. The graph below represents the paths of the two cyclists during a 10 second period. Note that the slope represents speed. At t = 2 s, Jack’s speed is 1 m/s but Jill’s speed is 0. Speed = 0 Which of the following statements is false? A) B) C) D) E) At time t = 0, Jill is two meters ahead of Jack. Jill's speed is always zero. Between the times t=0 and t=6 s, Jack has a constant speed. At time t = 8 s, Jack and Jill have the same speed. At time t = 2 s, Jack and Jill have the same speed. Click Kinematics Slide: 3. 8 An automobile is traveling at a constant speed along a highway. Which set of graphs best illustrates the motion of the automobile? This means zero acceleration Constant speed Zero acceleration Kinematics Slide: 3. 9 Sitting on a bench, Stefania sees a cyclist ride by in front of her traveling at constant speed in a straight line. She observed the trajectory of the reflector that is fastened to a spoke on the front wheel of the bike. Direction of bicycle Reflector Which of the following represents the trajectory that Stefania observes? Click Kinematics Slide: 3. 10 A ball is thrown vertically into the air with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. How high does it go? 20 m Kinematics Slide: A ball travels horizontally with an average velocity of 35 m/s. How far does it go? 35 m 35 m 35 m 140 m 35 m 3. 11 Projectiles The horizontal component of the velocity is constant (always the same) The vertical component of the velocity is the same as free fall Free fall Free fall VV = 0 VV VV VV VV VV V V VH VV V VVH V VV Height VH VH V VV VV VH VV V V VV Range The actual (or instantaneous) velocity is the vectorial sum of the horizontal and the vertical component velocities. Click Projectiles Slide: 3. 12 A ball is thrown into the air with a velocity of 40 m/s at an angle of 30o. Determine its: a) Height b) Range Height Range Projectiles Slide: 3. 12 A ball is thrown into the air with a velocity of 40 m/s at an angle of 30o. Determine its: a) Height b) Range Projectiles Slide: 3. 12 A ball is thrown into the air with a velocity of 40 m/s at an angle of 30o. Determine its: a) Height b) Range Height 2 s going up + 2 s coming down Range Projectiles Slide: 3. 13 Mike shoots a ball up to his friend Dave who is standing on a balcony 4.0 m high. Dave misses the ball on its way up but catches it on its way down as illustrated below. For how may seconds was the ball in the air? NOTE For simplicity, you may use 10 m/s2 instead of 9.8 m/s2 for a. Units are not shown to keep the formula simple. Quadratic equation If he would have caught the ball Click … and good luck!