Sequencing
advertisement

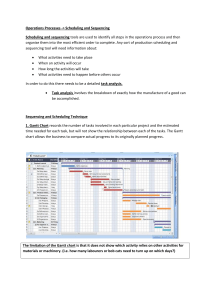
Scheduling Introduction to Operations Management 1 What is scheduling In a production system, it is the timing and sequencing of the use of specific resources in the system and is the final step in the decision making process of an organization before the actual transformation processes begin. Introduction to Operations Management 2 Scheduling Manufacturing Operations JAN High-volume FEB MAR APR MAY JUN Build A Intermediate- A Done volume Low-volume Service operations Build B B Done Build C C Done Build D On time! Ship Introduction to Operations Management 3 High-Volume Systems Flow system: High-volume system with Standardized equipment and activities Flow-shop scheduling: Scheduling for high-volume flow system Work Center #1 Work Center #2 Output Introduction to Operations Management 4 High-Volume Success Factors Process and product design Preventive maintenance Rapid repair when breakdown occurs Optimal product mixes Minimization of quality problems Reliability and timing of supplies Introduction to Operations Management 5 Intermediate-Volume Systems Outputs are between standardized highvolume systems and made-to-order job shops Economic run size: 2DS p Q0 H p u Introduction to Operations Management 6 Scheduling Low-Volume Systems Loading - assignment of jobs to process centers Sequencing - determining the order in which jobs will be processed Introduction to Operations Management 7 Loading Gantt chart - used as a visual aid for loading and scheduling Work Mon. Tues. Center 1 Job 3 2 Job 3 3 Job 1 4 Job 10 Wed. Thurs. Fri. Job 4 Job 7 Job 6 Job 7 Introduction to Operations Management 8 Assignment Problem Assigning jobs to workers. There is a cost associated with a worker completing a certain job. The objective is to finish all the jobs by the workers so that the total cost is minimized. Jobs Workers An optimal solution can be found by the Hungarian Method. Introduction to Operations Management 9 Sequencing Sequencing: Determine the order in which jobs at a work center will be processed. Workstation: An area where one person works, usually with special equipment, on a specialized job. Introduction to Operations Management 10 Sequencing Priority rules: Simple heuristics Everything is used to select the order in #1 Priority which jobs will be processed. Job time: Time needed for setup and processing of a job. Introduction to Operations Management 11 Priority Rules FCFS SPT DD CR S/O Rush - first come, first served - shortest processing time - due date - critical ratio - slack per operation Top Priority - emergency Introduction to Operations Management 12 Two Work Center Sequencing Johnson’s Rule: technique for minimizing completion time for a group of jobs to be processed on two machines or at two work centers. Minimizes total idle time Several conditions must be satisfied Introduction to Operations Management 13 Johnson’s Rule Conditions Job time must be known and constant Job times must be independent of sequence Jobs must follow same two-step sequence Job priorities cannot be used All units must be completed at the first work center before moving to second Introduction to Operations Management 14 Scheduling Service Operations Appointment systems – Controls customer arrivals for service Reservation systems – Estimates demand for service Scheduling the workforce – Manages capacity for service Scheduling multiple resources – Coordinates use of more than one resource Introduction to Operations Management 15 Service Operation Problems Cannot store or inventory services Customer service requests are random Scheduling service involves – Customers – Workforce – Equipment Introduction to Operations Management 16