Progressive Mesh in DirectX
advertisement

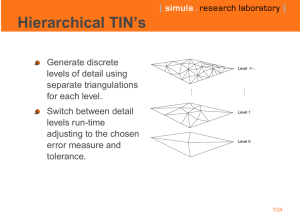
Progressive Mesh in DirectX 2000160114 Seung ho Lee 2000160207 Hyun taek Kwon What is Progressive Mesh? Level of Detail (LOD) Progressive simplification or detail Mesh Overview of Progressive Mesh Edge collapse or Vertex Split Selective Refinement Edge collapse or Vertex Split Selective Refinement Use Vertex History The Pipeline of DirectX Mesh ID3DXMesh interface ID3DXPMesh interface ID3DXMesh interface General Mesh interface Buffers – – – Vertex Buffer Index Buffer Attribute Buffer Functions – DrawSubset(DWORD n); ID3DXPMesh Progressive Mesh interface Make from ID3DXMesh Using Progressive Mesh interface Implementation Implement from ID3DXMesh Using Vertex Buffer and Index Buffer Class Gmesh Vertex Node Tree, History Rendering Pipeline Read PM File Make GMesh Write in Mesh Buffer Draw Mesh Result Rabbit View-Dependent Refinement 1. Definitions 2. Refinement Criteria 3. Implementation 1. Definitions (1) - Active vertex, Active face A vertex or face is active if it exists in the selectively refined mesh Ms. 1. Definitions (2) - Vertex hierarchy 1. Definitions (3) - Legal 2. Refinement Criteria (1) View frustum Coarsen regions outsize the view frustum (2) Surface orientation Coarsen regions oriented away from viewer (3) Screen-space geometric error Makes the difference between approximate surface M and the original M^ small 2. Refinement Criteria (1) - Bounding Sphere 2. Refinement Criteria (1) - Out of View frustum Red lines show distance 2. Refinement Criteria (2) - Cone of normals Unnecessary to split if 2. Refinement Criteria (3) - Distance The distance between the approximate surface M and the original M^, when projected on the screen, is every where less than a screen-space tolerance r. 3. Implementation - ListNode *ActiveVertexHead double linked list of active vertex - ListNode *RootVertexHead Double linked list of root vertex 3. Implementation Active Vertex v1 v2 v3 Qrefine() v1 v3 v4 v5 v6 v6 v21 Split v4 v5 v22