SIMPLE CFD Algorithm: Residuals & Relaxation Techniques
advertisement

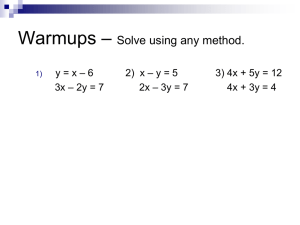
Lecture Objectives • Review • Define Residual and Relaxation • SIMPLE CFD Algorithm SIMPLE Semi-Implicit Method for Pressure-Linked Equations Review • • • • • Conservation equations Turbulent flow and turbulence modeling RANS Equation Discretization System of equation and solution methods – Accuracy – Numerical stability of solution procedure (new) • Solution algorithm (new today) Residual Example: x-exp(1/x)-2=0 Find x using iteration Explicit form 1: Explicit form 2: x=exp(1/x)+2 x=1/(ln(x)-ln(2)) Solution process: Guess x0 Not all iteration process converge! Iteration : x1=exp(1/x0)+2 , X2=exp(1/x1)+2 , …….. ……. R1=x1-x0 R2=x2-x1 See the example for the same equation Convergence example Explicit form 2: x=1/(ln(x)-ln(2) Residual calculation for CFD • Residual for the cell RFijk=Fkijk-Fk-1ijk Variable: p,V,T,… iteration cell position • Total residual for the simulation domain RFtotal=S|RFijk| For all cells • Scaled (normalized) residual RF=S|RFijk|/FF Flux of variable F used for normalization Vary for different CFD software Relaxation Relaxation with iterative solvers: divergence variable When the equations are nonlinear it can happen that you get divergency in iterative procedure for solving considered time step solution convergence Solution is Under-Relaxation: iteration Y*=f·Y(n)+(1-f)·Y(n-1) Y – considered parameter , n –iteration , f – relaxation factor Value which is should be used for the next iteration For our example Y*in iteration 101=f·Y(100)+(1-f) ·Y(99) f = [0-1] – under-relaxation -stabilize the iteration f = [1-2] – over-relaxation - speed-up the convergence Under-Relaxation is often required when you have nonlinear equations! Example of relaxation (example from homework 3 assignment) Example: Advection diffusion equation, 1-D, steady-state, 4 nodes a NTN-1 b NTN c NTN1 f N 1) Explicit format: TN 1/ b Nf N a N /b NTN-1 c N /b NTN1 1 2 3 4 2) Guess initial values: T10 ..., T20 .., T30 .., T40 .. 3) Substitute and calculate: T11 1/ b1f1 c1/b1T0 2 T12 1/ b 2 f 2 a 2 /b 2 T11 c 2 /b 2 T 0 3 T13 1/ b3f 3 a 3 /b3T12 c3 /b3T 0 4 T14 1/ b 4 f 4 a 4 /b 4 T13 4) Substitute and calculate: Substitute and calculate: …………………………. T11 ..., T21 .., T31 .., T41 .. T11r fT11 (1- f)T10 , T21r fT21 (1- f)T20 , .... T12 ..., T22 .., T32 .., T42 .. T12r fT12 (1- f)T11 , T22r fT22 (1- f)T21 , .... Navier Stokes Equations Continuity equation v x v y v z 0 x y z This velocities that constitute advection coefficients: F=rV Momentum x v x v x v x v x p 2vx 2vx 2vx ρ( vx vy vz ) μ 2 μ 2 μ 2 SM x τ x y z x x y z Momentum y v y v y v y v y 2vy 2vy 2vy p ρ( vx vy vz ) μ 2 μ 2 μ 2 SM y ρ g (T T ) τ x y z y x y z Momentum z v z v z v z v z p 2 vz 2 vz 2 vz ρ( vx vy vz ) μ 2 μ 2 μ 2 SM z τ x y z z x y z Pressure is in momentum equations which already has one unknown In order to use linear equation solver we need to solve two problems: 1) find velocities that constitute in advection coefficients 2) link pressure field with continuity equation Pressure and velocities in NS equations How to find velocities that constitute in advection coefficients? v x v x v x v x p 2vx 2vx 2vx ρ( vx vy vz ) μ 2 μ 2 μ 2 SM x τ x y z x x y z a P Vx,P a E Vx, E a WVx, W aSVx,S a NVx, N a HVx, H a LVx,P L f aP 6 x 2 x Vx , a W x 2 x x 2 ................................ aE r Vx Vy Vz r For the first step use Initial guess And for next iterative steps use the values from previous iteration Pressure and velocities in NS equations How to link pressure field with continuity equation? SIMPLE (Semi-Implicit Method for Pressure-Linked Equations ) algorithm v x v x v x v x p 2vx 2vx 2vx ρ( vx vy vz ) μ μ 2 μ 2 SM x τ x y z x x 2 y z x W p Pw – Pe (PW PP )/2 – (PP PE )/2 (PW – PE )/2 x x x x a P Vx P a E Vx E a W Vx W a S Vx S a N Vx N a H Vx H a L Vx L f Aw x P x Ae Aw=Ae=Aside (PW – PE )/2 Aside x We have two additional equations for y and x directions The momentum equations can be solved only when the pressure field is given or is somehow estimated. Use * for estimated pressure and the corresponding velocities E SIMPLE algorithm Guess pressure field: P*W, P*P, P*E, P*N , P*S, P*H, P*L 1) For this pressure field solve system of equations: x: a P Vx P a E Vx E a W Vx W a S Vx S a N Vx N a H Vx H a L Vx L f y: ……………….. ……………….. z: Solution is: (PW – PE )/2 Aside x V *x P , V *x E , V *x W , V *x S , V *x N , V *x H , V *x L 2) The pressure and velocity correction P = P* + P’ V = V* + V’ P’ – pressure correction V’ – velocity correction For all nodes E,W,N,S,… Substitute P=P* + P’ into momentum equations (simplify equation) and obtain V’=f(P’) V = V* + f(P’) 3) Substitute V = V* + f(P’) into continuity equation solve P’ and then V 4) Solve T , k , e equations SIMPLE algorithm start p=p* Guess p* Step1: solve V* from momentum equations Step2: introduce correction P’ and express V = V* + f(P’) Step3: substitute V into continuity equation solve P’ and then V Step4: Solve T , k , e equations no Converged (residual check) yes end Other methods SIMPLER SIMPLEC PISO variation of SIMPLE COUPLED - use Jacobeans of nonlinear velocity functions to form linear matrix ( and avoid iteration )