IE_F10_lecture8
advertisement

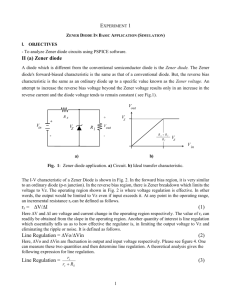
Lecture 8 Diode Applications and small signal models 1 Agenda -Diode Regulator -Zener Diode -Design of regulator circuits -Clamping circuits (DC-restoration) -Diode Small Signal Models 2 Application 2: Voltage Regulators: Introduction to Reverse Breakdown Increased reverse bias eventually results in the diode entering the breakdown region, resulting in a sharp increase in the diode current. The voltage at which this occurs is the breakdown voltage, VZ. 2 V < VZ < 2000 V 3 Reverse Breakdown Mechanisms • Zener Breakdown Zener breakdown occurs in heavily doped diodes. The heavy doping results in a very narrow depletion region at the diode junction. Reverse bias leads to carriers with sufficient energy to tunnel directly between conduction and valence bands moving across the junction. Once the tunneling threshold is reached, additional reverse bias leads to a rapidly increasing reverse current. 4 Zener Diode I Z iD VZ vD Knee Current Valid iff IZ > IZK 5 Zener Diode Model In breakdown, the diode is modeled with a voltage source, VZ, and a series resistance, RZ. RZ models the slope of the i-v characteristic. Diodes designed to operate in reverse breakdown are called Zener diodes and use the indicated symbol. 6 Analysis of Zener Diodes Choose 2 points (0V, -4 mA) and (-5 V, -3 mA) to draw the load line.It intersects with i-v characteristic at Q-point (-2.9 mA, -5.2 V). 2.Using piecewise linear model: I I 0 Z D 1.Using load-line analysis: 20 V 5000I D D 20 5100I 5 0 Z (20 5)V I 2.94mA Z 5100 Since IZ >0 (ID <0), solution is consistent with Zener breakdown assumption. 7 Regulator design Rectifier 120 Vrms vr Filter R C vp fRC Less ripple larger C We can get less ripple without using a larger C with a Zener regulator Unregulated supply RL 8 Voltage Regulator using Zener Diode constant voltage model V V (20 5)V I S Z 3mA S R 5k V 5V I Z 1mA L R 5k L I I I 2mA Z S L For proper regulation, Zener current must be positive. If Zener current <0, Zener diode no longer controls voltage across load resistor and voltage regulator is said to have Zener diode keeps voltage “dropped out of regulation”. across load resistor constant. R R V R For Zener breakdown I S V 1 1 0 L VS min Z R ZR R 1 operation, IZ >0. L V Z 9 Voltage Regulator using Zener Diode: Example (Including Zener Resistance) V 20V VL 5V VL 0 5000 100 5000 L V 5.19V L Problem: Find output voltage and Zener diode current for Zener diode regulator. Given data: VS=20 V, R=5 k, RZ= 0.1 k, VZ=5 V Analysis: Output voltage is a function of current through Zener diode. V 5V 5.19V 5V I L 1.9mA 0 Z 100 100 10 Regulator Characteristics Rth R + Thevenin rZ Equivalent VOC IL + VZo Vth (VOC ) Vs rZ R Vzo rZ R rZ R Rth rZ // R For best regulation rZ <<<< limitation on the value of Iz VL VOC I L Rth VL Vs rZ R Vzo I L (rZ // R ) rZ R rZ R VL Vs Line Regulation VL I L Load regulation 11 Line and Load Regulation Line regulation characterizes how sensitive output voltage is to input voltage changes. dV Line Regulation L mV/V dV r S Z For fixed load current, Line regulation = Rr Z Load regulation characterizes how sensitive output voltage is to changes in load current withdrawn from regulator. dV Load Regulation L Ohms dI L For changes in load current, Load regulation = (rZ R) Load regulation is Thevenin equivalent resistance looking back into regulator from load terminals. 12 Selecting R to keep Zener Diode in the Breakdown Region R + IZ IL rZ VZo I Z I Z min , when vs vs min I Z I Z max , when vs vs max vs min [VZo I Z minrZ ] R I Z min I L max 13 Application 3: Peak Detector Circuit (Clamping circuit) As input voltage rises, diode is on and capacitor (initially discharged) charges up to input voltage minus the diode voltage drop. At peak of input, diode current tries to reverse, diode cuts off, capacitor has no discharge path and retains constant voltage providing constant output voltage Vdc = VP – Vd,on. 14 Application 4: Clipping or Limiting Circuits Clipping circuits have dc path between input and output, whereas clamping circuits use capacitive coupling between input and output. The voltage transfer characteristic shows that gain is unity for vI < VC, and gain is zero for vI > VC. A second clipping level can also be set or diodes can be used to control circuit gain by switching resistors in and out of circuits. 15 Clamping or DC-Restoring Circuit After the initial transient lasting less than one cycle in both circuits, output waveform is an undistorted replica of input. Both waveforms are clamped to zero. Their dc levels are said to be restored by the clamping circuit. Clamping level can also be shifted away from zero by adding a voltage source in series with diode. 16 Clamping or DC-Restoring Circuit 17 Voltage Doubler 18 Diode Small Signal Model Diode Small Signal Model Diode Small Signal Model (Example) Example