Trigonometric Functions of Acute Angles Presentation
advertisement

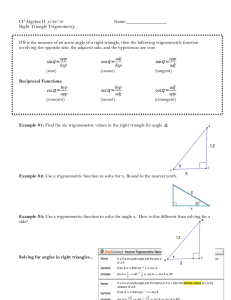
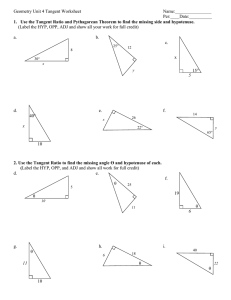
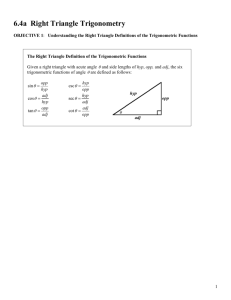
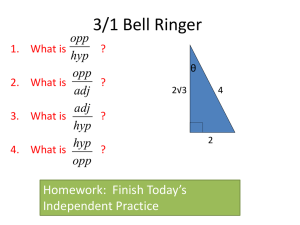
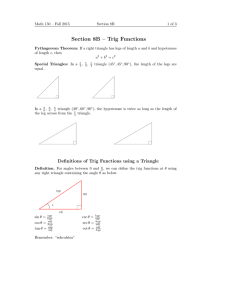
Chapter 4.2 Trigonometric Functions of Acute Angles. Learning Targets: I can define the six trigonometric functions using lengths of the sides of a right triangle. Trig Functions Let θ be an acute angle in the right Δ, then • • • • • • • Sine (θ) = sin θ = opp/hyp Cosine (θ) = cos θ = adj/hyp Tangent (θ) = tan θ = opp/adj (Remember Soh Cah Toa) Cosecant (θ) = csc θ = hyp/opp Secant (θ) = sec θ = hyp/adj Cotangent (θ) = cot θ = adj/opp Recall from Geometry • 30-60-90 triangle and 45-45-90 triangle • Do you remember their side ratios? Quick Note • On your calculators, the tan-1, sin-1, and cos-1 are not the same as cot, csc, and sec. -1 represents the inverse, not the reciprocal. Example • Solve the right triangle. 11 b 28° a Example • A right triangle with a hypotenuse of 8 includes a 37° angle. Find the measure of the other two angles and the lengths of the other two sides. Example • Find the value of all six trig functions of angle θ. 17 8 15 Example • Assume that θ is an acute angle in a right triangle satisfying the given conditions. Evaluate the remaining 5 trig functions. • Sin θ = 2/3 Example • Evaluate using a calculator. • Tan (8°) = • Sin (Π/15) = Example • Solve for the variable shown. 14 x 43° Homework Pg. 366 # 1 – 17 odd, 29 – 39 odd, 49 – 57 odd