quizzes answers
advertisement
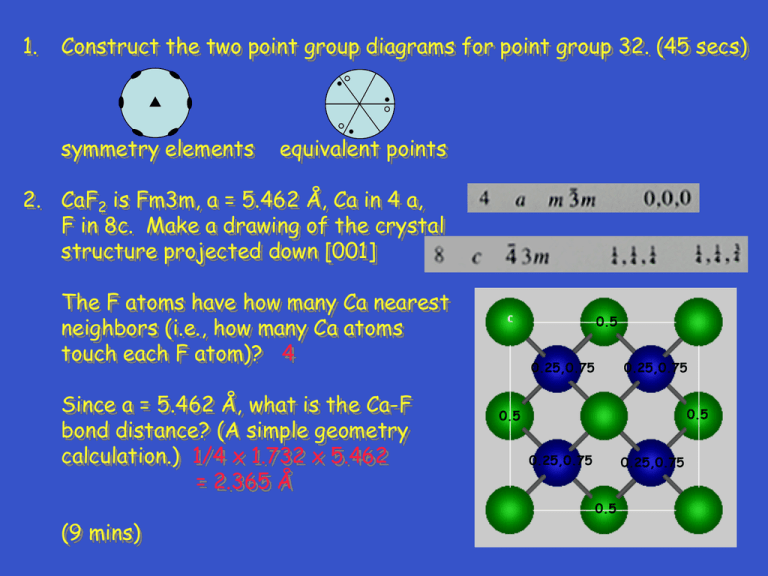
1. Construct the two point group diagrams for point group 32. (45 secs) symmetry elements equivalent points 2. CaF2 is Fm3m, a = 5.462 Å, Ca in 4 a, F in 8c. Make a drawing of the crystal structure projected down [001] The F atoms have how many Ca nearest neighbors (i.e., how many Ca atoms touch each F atom)? 4 Since a = 5.462 Å, what is the Ca-F bond distance? (A simple geometry calculation.) 1/4 x 1.732 x 5.462 = 2.365 Å (9 mins) 0.5 0.25,0.75 0.25,0.75 0.5 0.5 0.25,0.75 0.25,0.75 0.5 3. Metals with the ccp and hcp structures are both close packed. How are they different? Explain; you must use drawings in your discussion. (2 mins) layer sequence is different ccp - ABCABC hcp - ABAB C B A B A 4. For characteristic x-radiation, why is K > K? (1 min) 4. For characteristic x-radiation, why is K > K? (1 min) electron transition for is greater in energy; thus, is smaller 1. Construct the two point group diagrams for point group 6mm. (45 secs) symmetry elements equivalent points 2. PtO2 is Pnnm, a = 4.533, b = 4.488, c = 3.138 Å, Pt in 2a, O in 4g, x = 0.652, y = 0.281. Make a drawing of the crystal structure projected down [001]. See list of equipoints on next slide. What is the coordination number for the Pt atoms (i.e., how many O atoms touch each Pt atom)? 6 What is the shape of the Pt coordination polyhedron. octahedron 2. 3. a. Are rutile and anatase polytypes?__no__ b. Are rutile and anatase polymorphs?__yes__ c. Discuss how (in what way) the crystal structures of rutile and anatase are different. TiO6 octahedron in rutile is regular; in anatase, TiO6 octahedron is distorted 4. A monoclinic crystal has a = 6, b = 4, c = 10 Å, = 110°. Draw the k = 0 level of the reciprocal lattice. You will have to estimate (guess) what the distances and angles are on your drawing. Show (mark) the reciprocal lattice vectors and angle for the reciprocal lattice unit cell. c c* * a a*