N-bit plane Frame buffer
advertisement

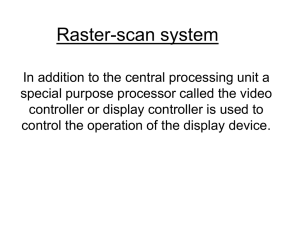
Input & Output Devices Display Devices Kocaeli University Computer Engineering Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2012 Input Devices • Alphanumeric Input – Keyboards • 2D Inputs – (Joystick, Mouse, etc) • 3D Inputs – Glove, Space, ball • Image Inputs – Camera, Scanner Output Graphic Devices • Color Raster CRT • Calligraphic (vector) CRT • Flat-panel displays: – Color LCD (Liquid Crystal) – Plasma Display • Hardcopy Devices – Printers CRT • Cathode Ray Tube • Enclosed vacuum tube; electron beam is focused toward front surface of the tube, which is coated in phosphor • Single gun for monochrome and three guns for color • High voltage reduces the electron density and thus brightness Vertical and horizantal reflection plates CRT -Cont • Technology relatively old; has disadvantages – Physical size and weight – Power consumption • Random scan display (Vector Display) & Rater scan display Vector Displays • Random scan display • Also called – vector, – stroke-writing, – or calligraphic displays. • The electron beam directly draws the picture in any specified order. • A pen plotter is an example of such a system Raster Displays • The image is stored in a frame buffer containing the total screen area and where each memory location corresponds to a pixel. • In a monochrome system, each bit is 1 or 0 for the corresponding pixel to be on or off (bitmap). • Image is represented as a bitmap (1 bit/pixel) or as a pixmap (8 or 24 bits/pixel) (a) (b) (c) (d) A raster-scan system displays an object as a set of points across each screen scan line Raster Displays Buffers in Raster Display • Image description is stored in a memory area called refresh buffer or frame buffer • The video controller sweeps the beam across the screen, one row at a time, from top to bottom and back to the top again. • Three beams are controlled (red, green, blue) and the intensity of each color is stored in the frame buffer • To give an idea: refreshing is carried out at the rate of 60 to 80 frames/second Buffers in Raster Display Buffers in Raster Display N-bit plane Frame buffer • Choice of the number of gray scales and colors depend on the value of N (bit plane size) –N=1 • two colors (B&W) –N=3 • 8 gray scales or colors –N=8 • 256 gray scales or colors – N = 24 • 16 million colours A single bit-plane frame Buffer • For colored displays (raster-scan), three separate color guns must be used. • Each bit plane drives a color gun An N-bit plane gray level frame buffer Simple color frame buffer N-bit plane gray level Frame buffer • In case of one-bit for each color frame buffer, we get 8 colors LCD • Contains matrix of liquid crystals sandwiched between two polarizing filter panels • Active and passive matrix displays • Manufactured with thin film transistor (TFT) technology • Compared with CRTs – – – – Less contrast Reduced size, weight, and power consumption Higher cost energy-efficient, have sharp picture – Contrast: how big the difference between "white" and "black" Plasma Display • Combine elements of CRT and LCD technology • Flat panel, active matrix devices • Actively generate colored light near surface of the display; good brightness and viewing • Require more power than LCDs, less than CRTs • Shortcomings – Limited operational lifetime – Larger pixel size reduces comparative image quality when viewed from short distances How Plasma Display Works • Plasma displays have no backlight and no color filters; each pixel contains a gas that emits ultraviolet light when electricity is applied. Plasma • Plasma technology consists of hundreds of thousands of individual pixel cells, which allow electric pulses to excite rare natural gases-usually xenon and neon-causing them to glow and produce light. • This light illuminates the proper balance of red, green, or blue phosphors contained in each cell to display the proper color sequence from the light. • Each pixel cell is essentially an individual microscopic florescent light bulb, receiving instruction from software contained on the rear electrostatic silicon board. Look very closely at a plasma TV and you can actually see the individual pixel cell coloration of red, green, and blue bars. You can also see the black ribs which separate each. LED TV • LED (light emitting diode) • LED TVs are a new form of LCD Television. The panel on an LED TV is still an LCD TV panel and operates with the same twisting crystals matrix. • The backlight is the difference - changing from fluorescent to LED based backlighting • Have better contrast and more accurate colors than LCD Digital Images from Scanners and Cameras • The color and brightness of each tiny area seen by a sensor is "sampled", meaning the color value of each area is measured and recorded as a numeric value which represents the color there • Each one of these sampled numeric color data values is called a pixel • A 6 inch photograph scanned at 100 dpi will produce 600 pixels across that dimension of the image. • The scanner scanning resolution (pixels per inch) and the size of the area being scanned (inches) determine the image size (pixels) created from the inches scanned. – If we scan 8x10 inch paper at 300 dpi, we will create (8 inches x 300 ppi) x (10 inches x 300 ppi) = 2400x3000 pixels