Velocity and Acceleration
advertisement

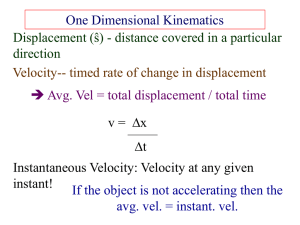
Objectives: 1. Be able to distinguish between distance and displacement 2. Explain the difference between speed and velocity 3. Be able to interpret motion graphs Vocabulary Distance Displacement Speed Average speed Instantaneous speed velocity Distance and Displacement Distance: How far an object has moved. Measure in Meters (M) Displacement: the distance and direction of an object’s change in position from the starting point. Speed • Speed: The distance an object travels per unit of time. Speed = Distance (m) Time (s) • Average Speed: the total distance traveled divided by the total time travel, even if the speed was changing. Instantaneous Speed • Instantaneous Speed: the speed at a given point in time. Plotting a Distance vs. Time Graph • • • • Distance is plotted on the vertical axis (y-axis) Time is plotted on the horizontal axis (X-axis) A horizontal line is a speed of 0 m/s (stopped) The slope of the line is equal to the speed of the object Velocity • Velocity: includes the speed of an object and the direction of its motion. Objectives: 1. Identify how acceleration, time, and velocity are related 2. Explain how positive and negative acceleration affect motion 3. Describe how to calculate the acceleration of an object Acceleration Acceleration: is the rate of change of velocity. It’s how fast an object is getting faster Acceleration = Change in Velocity (m/s) time (s) Calculating Acceleration 1. First calculate the change in velocity. Final Velocity - Initial Velocity (Vf - Vi) 2. Divide the change in Velocity by the Time of the measurements. Final Velocity - Initial Velocity (Vf - Vi) Time t Practice Problem What is the acceleration the Fastest Car in the World Sport: 0 to 60 mph in 3.7 seconds Initial speed = 0 m/h Final speed = 60 m/h Time = 3.7 seconds = 0.00103 hours 60 m/h - 0 m/h = 58,252 m/h2 0.00103 hours • For every hour this car drives it’s speed will increase by 58,252 m/h Practice Problem for Positive Acceleration A jet airliner starts from rest at the end of a runway and reaches a speed of 80m/s in 20 seconds. What is its acceleration? Initial speed = 0 m/s Final speed = 80 m/s t= 20 seconds 80 m/s - 0 m/s = 4 m/s2 20 s For every second the plane went down the runway it’s speed will increase by 4 m/s Practice Problem for Negative Acceleration A skateboarder is moving a constant velocity of 3 m/s and comes to a stop in 2 seconds. What is its acceleration? Initial speed= 3 m/h Final speed= 0 m/s t= 2 sec 0 m/s - 3 m/s = - 1.5 m/s2 2s For every second the skateboarder slows down he will decrease his speed by 1.5 m/s