点击下载
advertisement

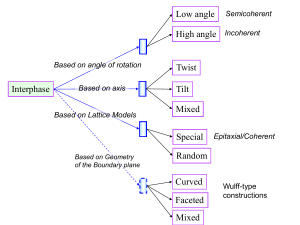
Chapter 4 Imperfections in Crystal 4.1 Point defects and Equilibrium concentration 4.2 Impurity atoms 4.3 Origin and Concept of dislocations ~ Linear defects 4.4 Burgers vectors and movement of dislocation 4.5 Elastics properties of dislocation 4.6 Formation and proliferations of dislocation 4.7 Dislocations in real crystal 4.8 Dislocation reaction 4.9 Outer surface 4.10 Grain boundaries and sub-grain boundaries 4.11 Phase boundaries Lan Yu 4.1 点缺陷的形成和平衡浓度 4.2 杂质原子 4.3 位错理论的提出和基本概念 4.4 伯氏矢量 位错的运动 位错的基本性质 4.5 位错的弹性性质 4.6 位错的起源与增殖 4.7 实际晶体中的位错 4.8 位错反应 4.9 外表面 晶体外形与表面微观形貌 表面驰豫与重构 4.10 晶界、亚晶界、孪晶界 4.11 相界 Lan Yu Imperfections in Crystal Ideal or perfect crystal:the arrangements of atoms that can regularly and repetitively fill space Real or defective crystal: A very tiny fraction of the atom sites, often less than one in a million, the atoms arrangement is not perfect.~ discrepancy structure According to dimension, types: Lan Yu point defect: vacancies, interstitial atoms, impurity atoms line defect: dislocation planar defect: stacking fault volume defect: mosaic structure 晶体缺陷:实际晶体中存在原子排列偏离理想状态的 不完整区域。 按晶体缺陷的几何特征,分为:点缺陷、线缺陷(位 错)、面缺陷和体缺陷。 即按照晶体缺陷在空间所占的维度,分为 零维、一维、二维和三维缺陷。 晶体缺陷赋予材料丰富内容 Lan Yu 晶体缺陷(晶格的不完整性):晶体中任何对完整周期性 结构的偏离就是晶体的缺陷。 结构缺陷: 没有杂质的具有理想的化学配比的晶体 中的缺陷,如空位,填隙原子,位错。 晶体的缺陷 化学缺陷: 由于掺入杂质或同位素,或者化学配比偏 离理想情况的化合物晶体中的缺陷,如杂 质,色心等。 Lan Yu 4.3 Origin and Concept of dislocations ~ Linear defects 位错~线缺陷 Dislocation is a long tubular transition zone from slipped to unslipped zones. Within this zone, atoms on opposite sides of the slip plane do not fit,which is called atoms misfit. So dislocation is a linear imperfection. 在三维空间的一个方向上的尺寸很大(晶粒数量级101nm~102um), 另外两个方向上的尺寸很小(原子尺寸大小~Å)的晶体缺陷。周期性遭 受破坏的区域形成一条线。 晶体中的位错: 刃型位错 螺型位错 混合型位错 Lan Yu Dislocation edge dislocation screw dislocation mixed dislocation The dislocation can’t be seen by eyes. How did people originally realise the dislocation? What is dislocation? Ⅰ. Origin of dislocation theory 位错学说的产生 Clue 1905, Vito Volterra originally developed the theory about dislocation. The crystal plastic deformations had been experimentally studied. 1926, Professor Sir Frederick Charles Frank calculated theoretical shearing strength of crystal according the crystal sliding mode Theoretical shearing strength of crystal: m G 2 估算一般金属: τm=103~105MPa 实际金属单晶: 1~10MPa 理论剪切强度与实际值相差3-4个量级 b S.P. a x ’ ’ x =b Lan Yu m sin 2x Assuming b x: displacement of atoms 原子位移 For small x: 2x m b x Gr G ( ) a G G b ~ m ( ) 2 2 a .m ~ 103 104 MPa C ~ 1MPa Development of dislocation theory The shearing force required to deform a crystal solidcan be a facter of about 103-104 smaller than the theoretical shearing force. The dramatic discrepancy was solved by assumed presence of lattice defects called Dislocation. 1934,Orowam,Taylor and Polanyi independently applied the concept of edge dislocations. 1939, Burgers described the lattice distortion associated with a dislocation by the so-called Burgers vector. 1947, Cottrell suggested the interaction between the dislocation and solute Atoms~ Cottrell atmosphere. 1950, mechanism of Frank-Read Source has been applied. 1956, the first observations of edge dislocation by TEM (transmission electron microscope) were published. 1934年,泰勒、波朗依、奥罗万几乎同时提出位错的概念。 1939年,柏格斯提出用柏氏矢量表征位错。 1947年,柯垂耳提出溶质原子与位错的交互作用。 1950年,弗兰克和瑞德同时提出位错增殖机制。 之后,用TEM直接观察到了晶体中的位错。 蠕虫蠕动机制 A extra half-plane has been inserted from the crystal top and terminated in crystal. EF is called the dislocation line. Regions of compression and tensionaround an edge dislocation EF:位错线 Lan Yu Ⅱ. Edge dislocation 刃位错 Lan Yu () Lan Yu ( ) G H D A E Extra half-plane:EFGH Dislocation line: EF Sliding plane: ABCD F B C Characters of edge dislocation 刃型位错的特征: 1) 刃型位错是由一个多余半原子面所组成的线缺陷; 2) 位错滑移矢量(柏氏向量)垂直于位错线,而且滑移面是位错线和滑移 矢量所构成的唯一平面; 3) 位错的滑移运动是通过滑移面上方的原子面相对于下方的原子面移 动一个滑移矢量来实现的; 4) 刃型位错线的形状可以是直线、折线和曲线; 5) 晶体中产生刃型位错时,其周围的点阵发生弹性畸变,使晶体处于 受力状态,既有正应变,又有切应变。 Ⅲ. Screw dislocation 错 螺位 The upper front region of the crystal is shifted one atomic distance to the back relative to the bottom portion.~ distortion Dislocation line BC (a) (b) 右螺位错 b L 左螺位错 L Characters of screw dislocation 螺型位错的特征: 1) 螺型位错是由原子错排呈轴线对称的一种线缺陷 ; 2) 螺型位错线与滑移矢量平行,因此,位错线只能是直线; 3) 螺型位错线的滑移方向与晶体滑移方向、应力矢量方向互相垂直; 4) 位错线与滑移矢量同方向的为右螺型位错;为此系与滑移矢量异向 的为左螺型位错。 Ⅳ. Mixed dislocation 混合型位错 混合位错 a) 晶体的局部滑移; b) 混合位错的原子组态 Ⅴ. Burgers vectors 柏氏矢量 1. Burgers loops Edge dislocation 柏氏回路 先确定位错的方向(一般规定位错线垂直纸面时,由纸面向外为正),按右手 法则做柏氏回路,右手大拇指指位错正方向,回路方向按右手螺旋方向确定。 Burgers loops: MNOPQ 2. Burgers vector 柏氏矢量:b N O N O Q Q P b=QM,终点-起点 M P M 刃型位错柏氏矢量的确定 柏氏矢量b=QM (a) 有位错的晶体 (b) 完整晶体 位错线⊥b Screw dislocation 柏氏矢量b=QM 螺型位错柏氏矢量的确定 (a) 有位错的晶体 (b) 完整晶体 位错线∥b 4.守恒性 若干位错线交于一点, 流入节点的位错线的柏氏矢量和=流出节点的位错线的柏氏矢量和 Ⅵ. Dislocation density 位错密度 Total dislocation length per unit volume-Number of dislocations intersecting unit area of a random section. 单位体积中位错的总长度: L , cm / cm 3 V 将位错线看作于垂直某一平面的直位错线 nL n AL A Examples: Carefully solidified metal: 103 mm-2. Heavy deformed metals: 109 – 1010 mm-2. Heat treated metals: 105 – 106 mm-2. Ceramic materials: 102 – 104 mm-2. Examples and Discussions 1. 位错线从晶体表面入出,封闭环。 2. 一个圆形位错环,柏氏矢量垂直于表面。讨论 3. 晶体中的环代表什么 4. 单晶体中的位错环运动到表面。晶体外形发生什 么变化。