presentation source
advertisement

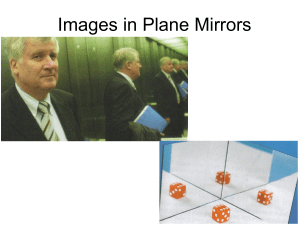
Essential Question: How do images form by reflection? Reflection Two types of reflection 1. Regular or Specular 2. Diffuse Law of Reflection –the angle of incidence = the angle of reflection Characteristics of Images in Plane Mirror Characteristics of Images in Plane Mirror 1. Image located as far into the mirror as object is in front of mirror. 2. Virtual Image 3. Erect Image 4. Same Size 5. Reverse left to right 6. Image form directly in front of object Steps in drawing ray diagrams to locate image in plane mirror. 1. Measure distance of object in front of mirror. 5 cm object mirror 2. Draw in position of image directly in line with object;same distance behind mirror. image object Can a person a position X see the image? image X object Draw a line from X to the image. image X object If the line of sight crosses the mirror then the image can be seen. image X object The red arrows show the actual path of the light. image X object Reflection from Parabolic Mirror Images formed by curved mirrors have different characteristics than those formed from flat mirrors. Terminology of Curved Mirrors Center of curvature (C)– the center of the circle the mirror is a part of;twice the distance as F Principal axis C F Terminology of Curved Mirrors Center of curvature (C)– the center of the circle the mirror is a part of;twice the distance as F/ Principal axis C F Focus(F) – the point where all rays parallel to axis reflect to; half the distance to C Terminology of Curved Mirrors Center of curvature (C)– the center of the circle the mirror is a part of;twice the distance as F/ Principal axis C F Focus(F) – the point where all rays parallel to axis reflect to; half the distance to C Principal axis- the line passing through C, and F and the center of mirror Locating an image in a parabolic mirror – must draw at least two rays. 1ST -Draw a ray parallel to the axis C F Locating an image in a parabolic mirror – must draw at least two rays. 1st-Draw a ray parallel to the axis C F Locating an image in a parabolic mirror – must draw at least two rays. 1st-Draw a ray parallel to the axis;it must reflect though F C F 2nd – Draw a ray through the focus C F 2nd – Draw a ray through the focus; it will reflect parallel to the axis C F Where the two rays cross is where the image will form. C F The light rays cross in front of mirror so the image is real – it could be projected! C F The light rays cross in front of mirror so the image is real – it could be projected! C F The image is inverted. The light rays cross in front of mirror so the image is real – it could be projected! C F The image is inverted. The image is smaller than the object. Will the Image always have these same characteristics? Lets move the object to a new position closer to C. C F Lets move the object to a new position closer to C. C F Now lets draw in the two rays. C F Now lets draw in the two rays. C F Now lets draw in the two rays. C F Now lets draw in the two rays. C F Now lets draw in the two rays. C F Now lets draw in the two rays. C F How are the images different? C C F F What do you think will happen if the object is placed at C? C F What do you think will happen if the object is placed at C? C F Lets draw in the rays to see the formation of the image C F Lets draw in the rays to see the formation of the image C F Lets draw in the rays to see the formation of the image C F Lets draw in the rays to see the formation of the image C F Lets draw in the rays to see the formation of the image C F The size and type of image varies with the object’s distance (do) from the mirror. If the object is so far away that the rays come in parallel, the image will just be a point a the focus. If the object is beyond f the image will always be real and inverted. The size will vary If the object is right at f an image will not form. If the object is less than f away, the image will be enlarged, erect and virtual. The mirror equation: 1 1 1 f do di do di Magnification Equation: h ' di M h do h’ is image height h is object height Images formed in Convex Mirrors: Images formed in Convex Mirrors: Images formed in Convex Mirrors: Images are always virtual, erect and smaller. Large spherical mirrors have spherical aberration which causes the blurred images Making the mirror parabolic instead of spherical reduces the spherical aberration