Midship Section
advertisement

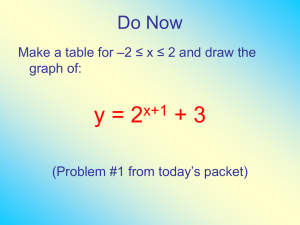
Funnel Navigation Bridge Superstructure Hatch Deck Crane Superstructure Stern Port Side Deck Bow Starboard Side Poop Deck Main Deck Forecastle Deck THREE DIMENSIONAL HULL FORM Transverse Section Transverse Section Stations Body Plan Horizontal Section Waterline Waterlines Plan View Vettical Sections Buttocks Buttocks Profile View Lines Plan Offset Table Cross Sectional Areas GEOMETRIC DEFINITIONS SHIP GEOMETRY 4.1 GEOMETRIC DEFINITIONS LOA LWL LBP f LWL D T BL FP AP B f LWL D T BL Deck Deck Loaded waterline B/2 Loaded waterline Figure 4.1. General geometric definitions STANDARD DEFINITIONS OF LENGTH STANDARD DEFINITIONS OF LENGTH Fore Perpendiculars (FP) : A line drawn perpendicular to the waterline at the point where the forward edge of the stem intersects the summer load line. Aft Perpendiculars (AP) : A line perpendicular to the waterline either (1) where aft edge of the rudder post meets the summer load line or (2) in cases where no rudder post is fitted, the centerline of the rudder pintles is taken . Midships The point midway between the forward and after perpendiculars . Centreplane (CL) : It is a referance plan that divide the ship in longitudinal direction in the mid point of beam between port and starboard sides. Baseline (BL) : A fore-and-aft reference line at the upper surface of the flat plate keel at the centerline for flush shell-plated. Vertical dimensions are measured from a horizontal plane through the baseline, often called the molded baseline. Midship Section : The section of the ship at this point by a plane normal to both the summer waterplane and the centreline plane of the ship is called the midship section. It may not be the largest section of the ship. Unless otherwise defined the beam is usually quoted at amidships. Sheer Line the curvature of the deck in a longitudinal direction. It is measured between the deck height at midships and the particular point along the deck. Deck Camber : The rise or crown of a deck, athlwartship; also called round of beam. It can be 1/50 times of beam as a standard value. Parallel Body (LP) : The amidship portion of a ship with in which the contour of the under water hull form is unchanged. Siyer Kıç Baş LWL BL LWL BL Şekil 4.2. Trimsiz ve trimli durum CL tumblehome güverte sehimi f LWL levha omurga sintine dönümü radius T kalkıntı Şekil 4.3. Enine kesit karakteristikleri BL Şekil 4.4. Section lines Bulbous bow area (ABL) : Bulbous area at center plane. Bulbous bow section area (ABT) : Bulbous bow area at fore perpendicular. ABT ABL FP Figure 4.5Bulbousbow area definition figure Z Su hatları En kesitler X Y Batoklar Şekil4.6. Üç boyutlu tekne formu ve kesit düzlemleri Table 4.1. Typical offset table Yarı Genişlikler İst Küpeşte Main Deck 5700 Yarı Genişlik 7350 7710 5700 7540 9450 7170 7820 5700 7700 9450 5120 7400 7880 5700 7810 9450 4630 6440 7730 7900 5700 7900 9450 3830 6170 7280 7870 7900 5700 7900 9450 3200 5500 7120 7730 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 3140 4700 6620 7620 7870 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 2120 4730 5920 7270 7820 7900 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 7 3780 5900 6720 7580 7880 7900 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 8 4900 6390 7100 7710 7895 7900 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 9 5070 6400 7080 7720 7890 7900 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 10 4700 6170 6880 7570 7840 7900 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 11 4000 5680 6450 7240 7860 7830 7900 7900 5700 7900 9450 12 3130 4990 5820 6700 7250 7540 7800 7900 5700 7850 9450 13 2230 4230 5040 6000 6620 7000 7480 7750 5700 7670 9450 14 1400 3500 4220 5120 5770 6250 6950 7430 5724 7300 9474 15 750 2730 3380 4180 4800 5320 6180 6950 5753 6730 9503 7900 16 330 1990 2530 3220 3780 4280 5250 6225 5783 6000 9536 7890 17 130 1380 1830 2400 2850 3260 4150 5320 5812 5100 9575 7730 18 60 920 1320 1730 1960 2170 2930 4190 5841 3970 9623 7270 19 40 550 900 1290 1250 1140 1650 2790 5870 2650 9682 6410 19 ½ 40 380 700 1090 1050 610 970 2000 5885 1920 9715 5810 20 40 280 530 900 1000 - 320 1220 5900 1140 9748 5090 BL 0m WL1/2 0.5 m Ayna - - WL 1 1m - WL 2 2m - WL 3 3m - WL 4 3.8 m 2140 WL 5 5m 6650 WL 6 6m 7550 0 - - - - - 3260 6900 ½ - - - - 600 4250 1 300 - - - 2280 2 300 - 1620 1620 3 300 1580 3820 4 370 1740 5 860 6 Yükseklik Yükseklik Yarı Genişlik 9450 Figure 4.7. A typical lines plan Form Coefficients Midship Section Coefficient B AM T CM AM B T Waterplane Area Coefficient B AW P L CWP AW P LB Block Coefficient B L*B*T L CB L B T Prismatic Coefficient B L CP AW P CP L AM B T L B T AM CB CM -Displacement /Length Ratio 3 L C B LBT 3 L CB B T L L BLOCK COEFICIENT CB L WL L WL A ( x ) dx CB 0 L WL B WL T L WL B WL T xA ( x ) dx LCB 0 L WL A ( x ) dx 0 WATERPLANE AREA COEFICIENT (CWP) A WL L WL B WL ( x ) dx 0 . LWL CWP B WL ( x ) dx 0 LW L B W L LWL xB LCF WL ( x ) dx 0 LWL B 0 WL ( x ) dx AW L LW L B W L MIDSHIPS SECTION COEFFICIENT (CM) CM AM B WL T PRISMATIC COEFICIENT (CP) CP LW L A M LW L B W L TC M CB CM VERTICAL PRISMATIC COEFFICIENT (CVP) C VP A WL T L WL B WL TC WP CB C WL Example 4.6. Find the form coefficients of a 100 m long barge with corss section as given below. 10m 1m 1.5 m Midship cross section Area : A M 10 1 Midship cross section area coefficient : CM Displacement Volume : AM B WL T 1 10 0 . 5 12 . 5 m 2 2 12 . 5 10 1 . 5 0 . 833 A M L WL 100 12 . 5 1250 m 3 Block coefficient Prizmatic coefficient Waterplane area coefficient: : CB L WL B WL T C P : CB CM C WL 1250 100 10 1 . 5 0 . 833 0 . 833 1 0 . 833 A WL L WL B WL 100 10 100 10 1 Örnek 4.3. Find the form coefficients of a a barge with cross section as given below. 5m 1 Blok coefficient : CB AML L WL B WL T 5 2 L B WL T 5 3 5 5 3 2 1 Midship section coefficient : CM AM B WL T 5 2 5 5 3 2 5 3 2 L 2 0 .5 0 .5 L Prizmatic coefficient Waterplane area coefficient: C P : CB CM C WL Vertical prizmatic coefficient: 1 A WP L WL B WL C VP CB C WL LB 1 LB 0 .5 1 0 .5 Example 4.1. Find the form coefficients of a cylinderical barge with length of L and radius of R with cross section as given below R R Block Coefficent C: B AML L WL B WL T L B WL T Midship Section coefficient : CM Prizmatic coefficient : CP CB CM B WL T /4 /4 *L 2 2R * R * L 4 R AM 2 2 2 2 RR 4 1 Waterplane area coefficient: C WL Vertical prizmatic coefficient C VP A WL L WL B WL CB C WL /4 1 L 2R L 2R 4 1 Example 4.2 Calculate form coeffcients of the barge with length L with cross section as below. R R 4R Block coefficient : CB ( Prizmatic coefficient: 2 4 RR ) L 8 4 0 . 928 L WL B WL T L B WL T ( 4 R R R ) RL 12 AML 2 R Midship section coefficient 2 R : CM CP AM B WL T CB CM 1 2 4 RR 8 4 0 . 928 (4R R R )R 12 Waterplane area coefficient Vertical prizmatic coefficent C WL C VP A WP L WL B WL CB C WL 6 RL 1 6 RL 0 . 928 1 0 . 928 Example 4.5. Calculate the form coefficients for a ship with the following characteristics. Waterline length LWL 200 m Waterline breadth BWL 22 m Draught T 7m Prizmatic coefficient CP 0.75 Loaded waterplane area AWL 3500 m2 Displacement tonnage 23000 t Sea water density 1.025 t/m3 CB CM L WL B WL T CB CP C WP 0 . 729 L WL B WL T 23000 200 22 7 1 . 025 0 . 972 0 . 75 A WP L WL B WL 3500 200 22 0 . 795 0 . 729