activities
advertisement

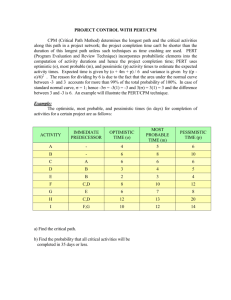
Project Scheduling: PERT/CPM Managers are often responsible for planning, scheduling and controlling projects that consist of numerous separate jobs or tasks performed by a variety of individuals or departments. Project managers must schedule and coordinate the activities that make up the project to ensure the project is completed on time. A complicating factor is the interdependence of the activities • Some activities must be completed before others can be started. PERT/CPM PERT • Program Evaluation and Review Technique • Developed by U.S. Navy for Polaris missile project • Developed to handle uncertain activity times CPM • Critical Path Method • Developed by Du Pont & Remington Rand • Developed for industrial projects for which activity times generally were known Today’s project management software packages have combined the best features of both approaches. PERT/CPM PERT and CPM have been used to plan, schedule, and control a wide variety of projects: • R&D of new products and processes • Construction of buildings and highways • Maintenance of large and complex equipment • Design and installation of new systems PERT/CPM PERT/CPM is used to plan the scheduling of individual activities that make up a project. Projects may have as many as several thousand activities. A complicating factor in carrying out the activities is that some activities depend on the completion of other activities before they can be started. PERT/CPM Project managers rely on PERT/CPM to help them answer questions such as: • What is the total time to complete the project? • What are the scheduled start and finish dates for each specific activity? • Which activities are critical and must be completed exactly as scheduled to keep the project on schedule? • How long can noncritical activities be delayed before they cause an increase in the project completion time? PERT/CPM First step: develop a list of the activities that make up the project. Then identify the immediate predecessor- the activities that must be completed immediately prior to the start of that activity. Estimate the activity time for each activity Shopping Center Project Activity Activity Description Immediate Predecessor Activity Time A Prepare architectural drawings -- 5 B Identify potential new tenants -- 6 C Develop prospectus for new tenants A 4 D Select contractor A 3 E Prepare building permits A 1 F Obtain approval for building permits E 4 G Perform construction D,F 14 H Finalize contracts with tenants B,C 12 I Tenants move in G,H 2 Total 51 Draw Project Network E A Start G D C B F H I Finish Determining the Critical Path (forward pass) Find the earliest start time and a latest start time for all activities in the network • ES – earliest start time for an activity • EF = earliest finish time for an activity • T = activity time EF = ES + t • Activity A: ES = 0, t = 5, EF = 5 An activity cannot be started until all immediately preceding activities have been finished. ES = the largest of the earliest finish times for all its immediate predecessors. Determining the Critical Path Activity B: ES = 0, EF = ES + t = 0 + 6 = 6 Activity C: earliest finish time for activity A is 5, so the earliest start time for activity C must be 5 • ES = 5, t = 4 • EF = ES + t = 5 + 4 = 9 Activity H: Both B and C are predecessors. • ES = the largest of the earliest finish times for activities B and C • EF = 6 for activity B, and EF = 9 for activity C, t = 12 • Thus ES for H is 9 • EF (for H): ES + t = 9 + 12 = 21 Critical Path (forward pass) A 0 5 5 START C 5 4 9 H 12 9 21 Forward pass Activity ES EF A 0 5 B 0 6 C 5 9 D 5 8 E 5 6 F 6 10 G 10 24 H 9 21 I 24 26 Forward pass Thus, the project can be completed in 26 weeks. Backward Pass Begin the backward pass with a latest finish time of 26 for activity I Once the latest finish time is known, the latest start time can be computed: • LS = latest start time for an activity • LF = latest finish time for an activity Beginning with activity I, LF = 26, t = 2 LS = LF – t = 26 – 2 = 24 I 24(ES) 26(EF) 2 (t) 24(LS) 26(LF) Backward Pass Activity Time (t) ES EF LS LF A 5 0 5 0 5 B 6 0 6 6 12 C 4 5 9 8 12 D 3 5 8 7 10 E 1 5 6 5 6 F 4 6 10 6 10 G 14 10 24 10 24 H 12 9 21 12 24 I 2 24 26 24 26 SLACK Slack is the length of time an activity can be delayed without increasing the project completion time. Slack = LS – ES = LF = EF Activity C: LS – ES = 8 – 5 = 3 weeks • Thus activity C can be delayed up to 3 weeks and the entire project can still be completed in 26 weeks Activity E: LS – ES = 5 – 5 = 0 • Activity E has no slack. This activity cannot be delayed without increasing the completion time for the entire project. • Activity E is a critical activity, and on the “critical path.” Critical Path Critical activities are those with zero slack Activities with zero slack are on the critical path. Critical Path Activity ES LS EF LF Slack LS-ES Critical Path? A 0 0 5 5 0 Yes B 0 6 6 12 6 No C 5 8 9 12 3 No D 5 7 8 10 2 No E 5 5 6 6 0 Yes F 6 6 10 10 0 Yes G 10 10 24 24 0 Yes H 9 12 21 24 3 No I 24 24 26 26 0 Yes Project Network A project network can be constructed to model the precedence of the activities. The nodes of the network represent the activities. The arcs of the network reflect the precedence relationships of the activities. A critical path for the network is a path consisting of activities with zero slack. Example: Frank’s Fine Floats Frank’s Fine Floats is in the business of building elaborate parade floats. Frank and his crew have a new float to build and want to use PERT/CPM to help them manage the project . The table on the next slide shows the activities that comprise the project. Each activity’s estimated completion time (in days) and immediate predecessors are listed as well. Frank wants to know the total time to complete the project, which activities are critical, and the earliest and latest start and finish dates for each activity. Example: Frank’s Fine Floats Immediate Activity Description Predecessors A Initial Paperwork --B Build Body A C Build Frame A D Finish Body B E Finish Frame C F Final Paperwork B,C G Mount Body to Frame D,E H Install Skirt on Frame C Completion Time (days) 3 3 2 3 7 3 6 2