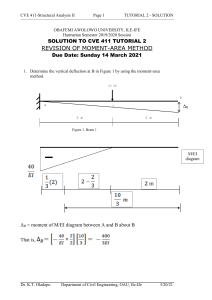
Conjugate-Beam
advertisement

Chapter 8: Deflections CIVL3310 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS Professor CC Chang Deflection- Displacement & Rotation Deflections maybe due to loads, temperature, fabrication errors or settlement Linear elastic behavior: linear stress-strain relationship and small deflection Need to: Plot qualitative deflection shapes before/after the analysis Calculate deflections at any location of a structure Deflection Diagrams/Shapes M curvature EI +M tensile side tensile side -M Example 8.1 Draw the deflected shape of each of the beams. Need to show 1st order (slope) and 2nd order (curvature) information tensile side tensile side Inflection point Straight line (why?) Straight line (why?) Example 8.2 negligible M=0 No curvature M≠0 All members are axially inextensible! Calculation of Deflections Direct integration Moment-area method Conjugate-beam method Energy methods (in Chapter 9) Calculation of Deflections Note: Superposition can be used for linear structures = y( x ) y1 ( x ) y 2 ( x ) y1 ( x ) y2( x ) Direct Integration + disp Bernoulli-Euler beam 2 d y dx 2 y M EI M dθ EI dx dx dx θ M EI M dx EI apply boundary conditions Example 8.3 The cantilevered beam is subjected to a couple moment Mo at its end. Determine the eqn of the elastic curve. EI is constant. x 2 EI d v dx EI 2 dv dx EI v Mo M o x C1 M ox 2 at x = 0 dv/dx = 0 & v = 0 C1 = C2 =0. 2 C1 x C 2 Max M ox v ; EI A M oL EI M ox 2 2 EI ; vA M oL 2 EI 2 Direct Integration 5 kN/m 3 kN/m A 0 50 V F B C 20m 20m 241 50 kN 91 D 50m E 20m 20m 30 149 90 -150 y M dx dx -30 -59 EI M M1 + y M2 _ M3 + Moment-Area Theorems 2 d y dx 2 M dθ EI dx M EI M d dx EI B B A A B / A M dx B A EI + 1st moment-area theorem Moment-Area Theorems 2nd moment-area theorem dθ dx M EI d Horizontal dis btw A & centroid of M/EIA-B dt x d x M dx EI tA/ B B x A M EI dx x M/EI area btw A & B B A M EI dx Moment-Area Theorems B t A / B A x M EI B dx x A A M t B / A B x x' dx EI M EI A dx x ' B M EI dx Moment-Area Theorems 1st moment-area theorem 2nd moment-area theorem + B/A B A M EI dx tA/B B x A M EI dx Example 8.5 Determine the slope at points B & C of the beam. Take E = 200GPa, I = 360(106)mm4 B/A B B / A; B B / A 50 kNm EI 375 kNm 1 100 kNm 50 kNm (5 m ) 2 EI EI 2 0 . 00521 rad EI C C / A 0 . 00694 rad (5 m ) C C / A B A M EI dx Conjugate-Beam Method Mathematical analogy M EI -slope-deflection dθ M dV EI dx θ dM dx dy dx dx 2 w V dx 2 d y Load-shear-moment 2 M d M EI 2 dx w Conjugate-Beam Method M EI Mathematical equivalence -slope-deflection M Load-shear-moment w EI θ V y M Actual beam Conjugate beam Conjugate-Beam Method Conjugate beam Actual beam θ0 θ0 y0 y0 P PL PL EI EI V 0 V 0 M 0 M 0 M EI ? PL x 1 EI L w 2 x PL x EI 2L P V θ y 2 3 PL x x EI 2 6L M Conjugate-Beam Method or Conjugate-Beam Method Conjugate beams are mathematical/imaginative beams No need to worry about their stability Just use EQ concept to obtain V and M from w Example 8.5 Determine the max deflection of the steel beam. The reactions have been computed. Take E = 200GPa, I = 60(106)mm4 Max disp Max M Solution Conjugate beam: Max Moment Note: dM V 0 dx when 45 EI M M max 1 2x x 0 2 EI x 6 . 71 m ( 0 x 9 m ) OK 2 1 2 ( 6 . 71 ) 1 ( 6 . 71 ) 6 . 71 ( 6 . 71 ) M ' 0 EI 2 EI 3 45 x EI max M ' 6.71 6 201 . 2 kNm 3 EI 201 . 2 kNm 2 6 3 4 4 3 4 4 [ 200 (10 ) kN / m ][ 60 (10 ) mm (1m /(10 ) mm )] 0 . 0168 m 16 . 8 mm Conjugate-Beam 5 kN/m 3 kN/m A F B 20m 20m C D 50m E 20m 20m M M EI Conjugate beam B C V = D M =y E F Summary Can you plot a qualitative deflection shape for a structure under loads (need to show 1st & 2nd order information)? Can you calculate structural deformation (displacement & rotation) using Direct integration? Moment-area principle? Conjugate-beam method?