Ac1.3hMorePracticeProblems
advertisement

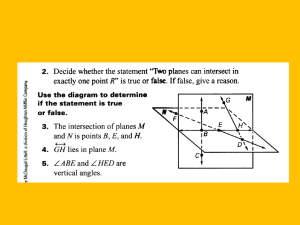
Millenium Park Frank Lloyd Wright Millau Bridge Sir Norman Foster Fallingwaters Frank Lloyd Wright Point, Lines, Planes, Angles 1.3 Segments, Rays, and Distance WE Page 15 1.3 Segments, Rays, and Distance WE Page 15 The numbers given are coordinates of 2 points on a number line. Find the distance between the points. 1. - 6 and 9 9 ( 6) 15 2. - 3 and - 17 17 ( 3) 17 3 14 3. - 1.2 and - 5.7 1.2 ( 5.7 ) 1 .2 5 .7 4 .5 4. - 2.5 and 4.6 4 .6 ( 2 .5) 4.6 2.5 7.1 In the diagram, H L and K T intersect at the midpoint of H L . Classify each statement as true of false. State why the statement is false. 5. LM M H H True. The order of the letters doesn’t matter. T K M L True. It goes through midpoint. In the diagram, H L and K T intersect at the midpoint of H L . Classify each statement as true of false. State why the statement is false. 5. LM M H H True. The order of the letters doesn’t matter. 6. T KM must = MT False. KM < MT K M L In the diagram, H L and K T intersect at the midpoint of H L . Classify each statement as true of false. State why the statement is false. 5. LM M H H True. The order of the letters doesn’t matter. 6. T KM must = MT False. KM < MT K M 7. M T bisects L H True. It goes through midpoint. 8. K T is a bisector of L H True. It goes through midpoint. L In the diagram, H L and K T intersect at the midpoint of H L . Classify each statement as true of false. State why the statement is false. . M T and T M are opposite rays. 9 H False. They do not have the same endpoint. 10. M T and M K T are opposite rays. True. 11. L H is the same as HL K M False. One’s a line & the others a segment. 12. K T is the same as K M True. They have same starting point and direction. L In the diagram, H L and K T intersect at the midpoint of H L . Classify each statement as true of false. State why the statement is false. 13. K T is the same as KM H True. Same line but different points. 14. K T is the same as T KM False. One’s a line & the others a segment. 15. HM + ML = HL K M True. Segment Add. Postulate. L In the diagram, H L and K T intersect at the midpoint of H L . Classify each statement as true of false. State why the statement is false. 13. K T is the same as KM H True. Same line but different points. 14. K T is the same as T KM False. One’s a line & the others a segment. 15. HM + ML = HL K M True. Segment Add. Postulate. 16. TM + MH = TH False. Shortest distance between 2 points is a straight line. L In the diagram, H L and K T intersect at the midpoint of H L . Classify each statement as true of false. State why the statement is false. 17. T is between H and M. H False. T is not on segment HM. 18. T M is between K and T. K M True. M is on segment KT. L Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 19. The point on DA 1 F G 2 3 whose distance from D is 2. B Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 19. The point on DA 1 F G 2 3 whose distance from D is 2. B 20. The point on D G whose distance from D is 2. F Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 21. 1 Two points whose distance from E is 2. C and G F G 2 3 Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 21. Two points whose distance from E is 2. C and G 22. 1 The ray opposite to BE BA F G 2 3 Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 23. The midpoint of 1 F G 2 3 BF D seen visually. Average the coordinates. or 2 2 0 2 Note that the name of the midpoint is a letter while the coordinate is a number. D Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 24. The coordinate of the midpoint of 1 F G 2 3 BD Average the coordinates. -1 seen visually. or 2 0 2 1 Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 25. The coordinate of the midpoint of -1 AE 1 F G 2 3 Name each of the following. A B C D E -3 -2 -1 0 25. The coordinate of the midpoint of -1 26. A segment congruent to A F BG AE 1 F G 2 3 In Exercises 27-30 draw C D and R S so that the conditions are satisfied. D 27. Segments CD and RS intersect, but neither segment bisects to other. R R OR D There are an infinite possibilities. S C S C S 28. Segment CD and RS bisect each other. D OR C R S C R There are an D infinite possibilities. In Exercises 27-30 draw C D and R S so that the conditions are satisfied. 29. C D bisects R S but R S doesn’t bisect C D D C R There are an infinite possibilities. S OR R S C D In Exercises 27-30 draw C D and R S so that the conditions are satisfied. 30. C D and R S do not intersect. But C D and RS do intersect. There are an infinite possibilities. R C C D D S R OR S 31. In the diagram, PR RT QR = 4 and ST = 5. Label Diagram First !! , S is midpoint of RT . Complete. P Q 6 R 4 10 S 5 T 5 10 5 a] RS = _____ 10 b] RT = _____ 10 c] PR = _____ 6 d] PQ = _____ Note that once the diagram was labeled, everything was easier. 32. In the diagram, X is the midpoint of VZ VW = 5, and VY = 20. Find the coordinates of W, X, & Y. Label Diagram 22 (12) 34 V W - 12 X Y 5 Z 22 17 34 17 20 W = -12+ 5 = -7 X = -12+17 = 5 Y = -12+20 = 8 E is the midpoint of 33. DF . Find the value of x. F DE = 5x + 3 , EF = 33 G E 33 Label the diagram first 5x + 3 D 5x + 3 = 33 5x = 30 x=6 H E is the midpoint of 34. DF . Find the value of x. F DE = 45 , EF = 5x - 10 G E 5x - 10 Label the diagram first DE = 45 D 45 = 5x - 10 55 = 5x 11 = x H E is the midpoint of 35. DF . Find the value of x. F DE = 3x , EF = x + 6 G E H EF = x + 6 Label the diagram first DE = 3x D 3x = x + 6 2x = 6 X=3 E is the midpoint of 36. DF . Find the value of x. F DE = 2x - 3 , EF = 5x - 24 Label the diagram firstCC G E 5x - 24 H 2x – 3 2x – 3 = 5x - 24 -3x -3 = -24 - 3x = - 21 x=7 D Find the value of y. 37. GE = y , EH = y – 1 , GH = 11 Label the diagram first F G y Segment Addition Postulate Sum of the parts = the whole. y + y - 1 = 11 2y - 1 = 11 2y = 12 x=6 E y–1 GH = 11 D H Find the value of y. 38. F GE = 3y , EH = 24 , GH = 7y - 4 Label the diagram first G 3y Segment Addition Postulate Sum of the parts = the whole. 3y + 24 = 7y - 4 24 = 4y - 4 28 = 4y 7=y E 24 GH = 7y - 4 D H Find the value of z. Then find GE and EH and state whether E is the midpoint. 39. GE = z + 2 , EH = 2z - 6 , GH = 20 Label the diagram first F G z+2 E Segment Addition Postulate Sum of the parts = the whole. z + 2 + 2z - 6 = 20 3z - 4 = 20 3z = 24 z=8 2z - 6 H GH = 20 D Not done yet. Find segments. GE = z + 2 = 10 EH = 2z – 6 = 10 E is a midpoint. Find the value of z. Then find GE and EH and state whether E is the midpoint. 40. F GE = z , EH = 2z - 4 , GH = z + 6 Label the diagram first G z E 2z - 4 Segment Addition Postulate Sum of the parts = the whole. z + 2z - 4 = z + 6 3z - 4 = z + 6 2z - 4 = 6 2z = 10 z=5 GH = z + 6 D GE = z = 5 EH = 2z – 4 = 6 E is not a midpoint. H Name the graph of the given equation or inequality. 41. 2 x 2 HN 42. G H M N T -4 -2 0 x0 M H or M G 43. x 4 4 x4 GT 2 4 Y Z 6 8 Name the graph of the given equation or inequality. 44. x 0 GH The whole line. G H M N T -4 -2 0 2 4 Y Z 6 8 The absolute value of negative numbers are greater than 0; the absolute value of 0 = 0 ; and the absolute value of positive numbers are greater than zero. 45. x 0 Point M Draw the diagram and illustrate your answer. 46a. On AB , how many points are there whose distance from point A is 3 cm. 3 cm 1 46b. On AB A B , how many points are there whose distance from point A is 3 cm. 2 3 cm 3 cm A B C’est fini. Good day and good luck.