Development of Urinary system
and reproductive system
1. Development of kidney and ureter
2. Development of urinary bladder and urethra
3. Abnormality in urinary system
4. Development of gonad
5. Development of reproductive tracts
6. Abnormality in reproductive system
3rd week:
Head segmentation Nephrotome →
Intermediate
Mesoderm
Pronephros
Other migration, proliferation Nephrogenic cord
→ Mesonephros and Metanephros
3rd week
Intermediate
mesoderm
───
─────→
Mesonephric
ridge
Gonadial
ridge
Intermediate
mesoderm
Nephrogenic
cord
───→
Urogenital
ridge
Urinary system,
Genital excurrent ducts
Gonad
Pudendum
Mesonephric
ridge
Urogenital
ridge
Gonadial ridge
Mesonephric
ridge
Gonadial ridge
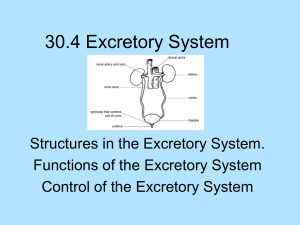
Development of urinary system
Development of kidney and ureter
1. Pronephros
4th week
Nephrotome (7-14th Somite)
Pronephric
Pronephric
tubule
duct
Degeneration
in 1 week
Mesonephric
duct
Pronephric
tubule
Pronephros
Time:4th week
Function:no
Destiny: degeneration
2. Mesonephros
14-18th somite
Middle part of
nephrogenic cord
80 transverse Sshaped tubule
Mesonephric
tubule
Inner end
form renal
capsule
Glomerulus
Outer end bind
to mesonephric
duct
Mesonephric
duct
The end bind
to cloaca
Continus to
pronephric
duct
Time:
end of 4th week
Function:
Mesonephric duct
transient urinary
Mesonephric tubule
Destiny:
Most degeneration,
Small part form male
excurrent duct
3.Metanephros
Time:begin at 5th week,
exist forever
Function:begin at 3th month,
urinary function
Position:rise gradually
Metanephros
End of
(adjacent to cloaca)
mesonephric duct
Origin
Ureteric bud
one
Prolong
Ureter
Embranchment >12
Renal pelvis, renal calyce
(The end branched as T)
Collecting tube
Origin
two
Metanephrogenic
blastema
(Mesoderm of the
mesonephric ridge)
Cap-shaped cell
cluster
S-shaped
tubule
Bind to collecting
tubule
Renal capsule Glomerulus
Renal
tubule
+
Renal
corpuscle
Nephron
Mesonephric
tubule
Ureteric
bud
Metanephrogenic
blastema
Renal Renal
pelvis calyce
Collecting
tubule
Formation and rising of metanephros
Development of urinary bladder and urethra
Male
Upper:
Urogenital
4-7th week
sinus
Middle:
Urinary
bladder
Urinary
Upper part
Urethra
bladder
of urethra
Cloaca
Urorectal
septum
Female
Anorectal
canal
Lower:
Lower part
of urethra
Vestibule
of vagina
Evolvement of male urogenital sinus
A
C
B
D
E
Positional evolvement of
Ureter and Mesonephric duct
Ureter
Mesonephric duct
Abnormality
•
•
•
Polycystic kidney
Horseshoe kidney
Single kidney
•
•
•
Double ureter
Urachal fistula
Exstrophy of bladder
Polycystic kidney
Horseshoe kidney
Single kidney
Right single kidney
Left single kidney
Ectopic kidney
Double ureter
Ureter
Urachal fistula
Exstrophy of bladder
Development of gonad
Gonad differentiation at 7th week
Developmental stage:
Sex undifferentiated stage→ Sex differentiated stage
Reproductive tracts:2 →
Proper current:
1
→ Feamle
Development of gonad
Endoderm cells
of yolk sac
1.Development of
undifferentiated gonad
4th week
Proliferation,
differentiation
Primordial germ cells
6th week
Gonadial ridge
6th week
Superficial epithelium
→cell cords
Migration in one week
Primary sex
cord
Primordial
germ cells
Large and round
endoderm cells
in yolk sac
Migration of
primordial
germ cells
6th week
Histocompatibility Y antigen
H-Y antigen determine the differentiation to testis
The gene of H-Y antigen located at Y chromosome
The cell membrane of the cell which sex chromosome
is XY possesses H-Y antigen
Primary sex cord H-Y antigen proliferation
seminiferous tubule
2. Development of testis
Primary sex cord (H-Y antigen)
7th week
Separated from surface
Mesenchymal
cell
Cells of sex cord Primordial germ cells
Interstitial cell
+
Sustantacular cell
+
Spermatogonium
Testis
3. Development of ovary
Superficial epithelium
Primary sex
(No H-Y antigen)
Mesenchymal cells
Secondary sex cord (cortical cord)
cord
After 10th
16th week
week
Primordial follicle
Degeneration
Cells of sex cord
Stroma
+
Follicular cells
Primordial germ cells
+
Oogonium
Ovary
Cortex
Medulla
Cortical
Cord
Testis
Ovary
Rete testis
Tubule rectus
Follicle
Seminiferous
tubule
Testis
Rete testis
Ovary
Tubule rectus
Follicle
Seminiferous
tubule
Spermatogonium
Primary oocyte
Sustantacular
cell
Follicular cell
Seminiferous tubule
Follicle
4. Descend of testis
and ovary
Embryo →lengthen
Gubernaculum →shorten
7th to 8th month → Scrotum
Development of reproductive tracts
1. Undifferentiated stage:
Mesonephric
tubule
Gonad
Mesonephric
duct
Sinus
tubercle
A. Male
Paramesonephric
tubule
Urogenital
sinus
B. Female
2. Differentiation of female reproductive tract
End of upper segment:Fimbria
Paramesonephric
duct:
Upper and middle segment:oviduct
Lower segment: Uterus
End:
Sinus tubercle: Vaginal plate
Mesonephric
ducts and
tubules
Vaginal fornix
Vagina
Degeneration
3. Differentiation of male reproductive tract
Metanephric Head ── Epididymal duct
Tail ── Spermaduct
duct
Mespnephric
tubules
Most of →degeneration
Some of → Efferent ducts
Paramesonephric
duct
Degeneration
Ovary
Testis
Urogenital
sinus
Urogenital
sinus
Oviduct
Spermaduct
Uterus
Vaginal
plate
Efferent duct
Epididymal duct
Abnormality of reproductive system
1. Cryptorchidism
2. Congenital inguinal hernia
3. Double uterus
4. Vaginal atresia
5. Hypospadias
6. Hermaphroditism
Cryptorchidism
Congenital inguinal hernia
Double uterus
Vaginal atresia
Hypospadias
Hermaphroditism