All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology
and Science Press
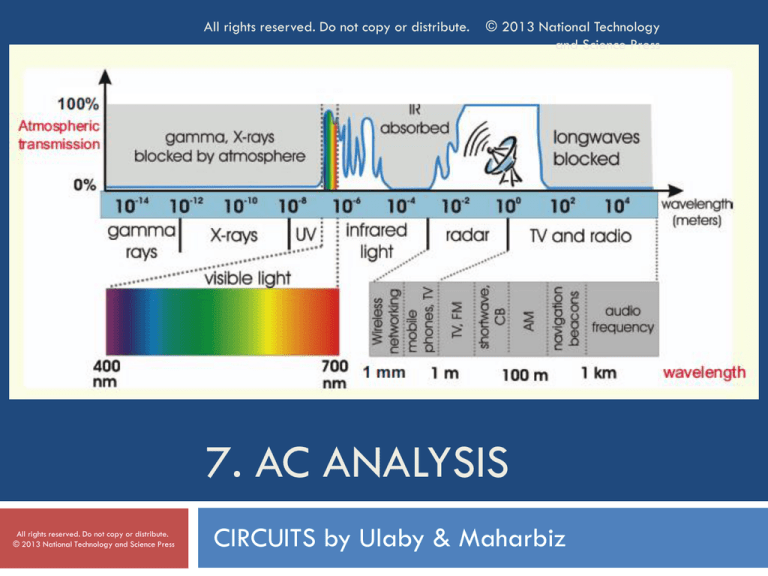
7. AC ANALYSIS
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
CIRCUITS by Ulaby & Maharbiz
Overview
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Linear Circuits at ac
Objective: To determine the steady state response of
a linear circuit to ac signals
Sinusoidal input is common in electronic circuits
Any time-varying periodic signal can be represented
by a series of sinusoids (Fourier Series)
Time-domain solution method can be cumbersome
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Sinusoidal Signals
v t V m cos t
Useful relations
2 f
T
1
f
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
Phase Lead/Lag
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Phasor Domain
1. The phasor-analysis technique transforms equations
from the time domain to the phasor domain.
2. Integro-differential equations get converted into
linear equations with no sinusoidal functions.
3. After solving for the desired variable--such as a particular voltage or
current-- in the phasor domain, conversion back to the time domain
provides the same solution that would have been obtained had
the original integro-differential equations been solved entirely in the
time domain.
Phasor Domain
Phasor counterpart of
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Time and Phasor Domain
All rights reserved. Do not copy or
distribute. © 2013 National
Technology and Science Press
It is much easier to deal
with exponentials in the
phasor domain than
sinusoidal relations in
the time domain.
You just need to track
magnitude/phase,
knowing that everything
is at frequency .
Phasor Relation for Resistors
Current through a resistor
Time Domain
Frequency Domain
Time domain
i I m cos t
v iR RI m cos t
Phasor Domain
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Phasor Relation for Inductors
Current through inductor in time
domain
i I cos t
All rights reserved. Do not copy
or distribute. © 2013 National
Technology and Science Press
Time domain
m
Phasor Domain
Time Domain
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Phasor Relation for Capacitors
Voltage across capacitor in
time domain is v V cos t
m
Time domain
iC
dv
dt
Time Domain
Phasor Domain
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Summary of R, L, C
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
ac Phasor Analysis General Procedure
Using this procedure, we can apply our techniques from
dc analysis
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Example 7-4: RL Circuit
Cont.
Example 7-4: RL Circuit cont.
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Impedance and Admittance
Impedance is
voltage/current
Admittance is
current/voltage
R = resistance = Re(Z)
X = reactance = Im(Z)
G = conductance = Re(Y)
B = susceptance = Im(Y)
Resistor
Z R
Y 1/ R
Inductor
Z j L
Y 1 / j L
Z 1 / j C
Y j C
Capacitor
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Impedance Transformation
Voltage & Current Division
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do
not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National
Technology and Science
Press
Cont.
Example 7-5: Input Impedance (cont.)
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Example 7-8: Thévenin Circuit
Linear Circuit Properties
Thévenin/Norton and Source Transformation Also Valid
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
Phasor Diagrams
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Phase-Shift Circuits
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Example 7-10: Cascaded Phase Shifter
Choose R such that output is 1200 ahead of input
Solution leads to:
All rights reserved. Do not copy or
distribute. © 2013 National
Technology and Science Press
Node 1
Cont.
(cont.)
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Cont.
(cont.)
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Example 7-13: Mesh Analysis by Inspection
Power Supply Circuit
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Ideal Transformer
Half-Wave Rectifier
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Full-Wave Rectifier
Current flow
during first half
of cycle
Current flow
during second
half of cycle
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Smoothing RC Filter
Complete Power Supply
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Example 7-19:
Multisim Measurement of Phase Shift
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Example 7-19 (cont.)
Using Transient Analysis
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Summary
All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute.
© 2013 National Technology and Science Press