Understanding the demand curve - Abernathy
advertisement
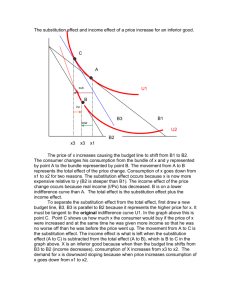
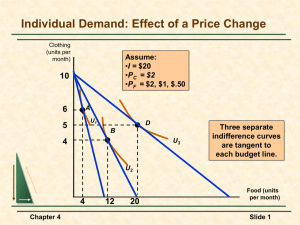
Behind the Demand Curve: Consumer Choice Explaining the law of demand • The Substitution effect ▫ Remember the law of demand, this why the demand curve slopes downward ▫ An alternative way to think about why demand curves slope downward is to focus on opportunity cost ▫ The change in the quantity demanded as the good has become relatively cheaper is substituted for the good that was become relatively more expensive….this is known as the substitution effect When a good absorbs only a small share of the typical consumer’s income, the substitution effect is essentially the sole explanation of why the market demand curve slopes downward. ▫ There are some goods i.e. food and housing, that account for a substantial share of many consumers’ incomes…..this brings in the income effect • The Income effect ▫ Example: half of family income is spent on rental housing Price of housing increases everywhere and will have a substitution effect on the family’s demand All things being equal, the family will have an incentive to consume less housing In a real sense the family will also be made poorer by that higher housing price ▫ Income will by less housing than before When income is adjusted to reflect its true purchasing power it is called real income In contrast money that has not been adjusted is called money income or nominal income • The income effect is the change in quantity of a good demanded that results from a change in the overall purchasing power of the consumer’s income due to a change in the price of that good. Distinction between the two effects ▫ For the majority of goods and services, the income effect is not important and has no significant effect on individual consumption Market demand curves slope downward solely because of substitution effect ▫ When it matters at all, income effect usually reinforces the substitution effect Vast majority of goods are normal goods (goods for which demand decreases when income falls) This reinforces the substitution effect With inferior goods- income effect and substitution effect work in opposite directions Substitution effect decrease the quantity demanded as its price increases, the income effect of a price increase for an inferior good is an increase in quantity demanded Price increase lowers real income , as real income falls demand for an inferior good increases Defining and measuring elasticity ▫ Economist use the concept of elasticity to measure the responsiveness of one variable to change in another ▫ Price elasticity of demand Measures the responsiveness of quantity of demand to changes in price ▫ Calculating the price elasticity of demand • Calculate % change in demand ▫ % change in quantity demand = change in quantity demanded/ initial quantity demanded X 100 • Calculate % change in price ▫ % change in price = change in price/ initial price X 100 • Calculate price elasticity of demand • Find ratio of the % change in Quantity demanded and in % change in price ▫ Price elasticity of demand = %change in quantity demanded/ % change in price