004.00 Geometric Construction - rrhs-engineering
advertisement

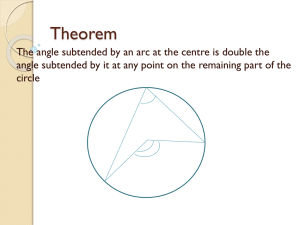
Career & Technical Basic Geometric Terms & Construction 004.00 Explain geometric terms and apply geometric construction techniques Career & Technical Basic Geometric Terms & Construction 004.01 Explain selected geometric terms Geometry The study of the size and shape of things The relationship of straight and curved lines in drawing shapes It is essential to recognize geometry that exists within objects for the purpose of creating solid models or multiview drawings Angles Acute Angle Obtuse Angle Measures more than 90° Right Angle Vertex Measures less than 90° Measures exactly 90° Vertex Point at which two lines of an angle intersect Circle Radius Diameter Distance across a circle through its center Circumference Distance from the center of a circle to its edge Distance around the edge of a circle Chord Line across a circle that does not pass at the circle’s center Circle Has 360° Quadrant One fourth (quarter) of a circle Measures 90° Concentric Two or more circles of different sizes that share the same center point Triangles Equilateral Isosceles All three sides are of equal length and all three angles are equal Two sides are of equal length Scalene Sides of three different lengths and angles with three different values Triangles Right Triangle One of the angles equals 90° Hypotenuse The side of a right triangle that is opposite the 90° angle HYPOTENUSE Quadrilaterals Square Rectangle Four equal sides and all angles equal 90° Two sides equal lengths and all angles equal 90° Trapezoid Only two sides are equal length Quadrilaterals Rhombus All sides are equal length and opposite angles are equal Rhomboid Opposite sides are equal length and opposite angles are equal Regular Polygons Pentagon Hexagon Five sided polygon Six sided polygon Octagon Eight sided polygon Regular Polygons Distance across flats Measurement across the parallel sides of a polygon FLATS Distance across corners Measurement across adjacent corners of a polygon CORNERS Solids Prism Right Rectangular Right Triangular Solids Cylinder Cone Sphere Solids Pyramid Torus Geometric Terms Circumscribe Process of creating a polygon that fully encloses a circle and is tangent to all of the polygons sides Inscribe Process of creating a polygon that is fully enclosed by a circle at its corners Geometric Terms Bisect Divide into two equal parts Tangent A line and arc, or two arcs that touch each other at one point only Geometric Terms Parallel Two or more lines that are always the same distance apart Perpendicular Two lines that are at a 90° angle Geometric Symbols Angle Parallel Triangle Perpendicular R Radius Diameter Square CL Centerline Career & Technical Basic Geometric Terms & Construction 4.02 Demonstrate the procedures for drawing standard geometric constructions Compass Usage LOCATE AND DRAW a center mark MEASURE and mark radius and set compass Compass metal point on center mark, lead at radius mark Hold compass handle between thumb and finger LEAN the compass forward as you rotate it Bisect a Line w/ a Compass Given line AB With points A & B as centers and any radius greater than ½ of AB, draw arcs to intersect, creating points C & D Draw line EF through points C and D Bisect a Line w/ a Triangle Given line AB H F D Draw line CD from endpoint A Draw line EF from endpoint B E B C A Draw line GH through intersection G Bisect an Arc Given arc AB With points A & B as centers and any radius greater than ½ of AB, draw arcs to intersect, creating points C & D Draw line EF through points C and D Bisect an Angle Given angle AOB With point O as the center and any convenient radius R, draw an arc to intersect AO and OB to located points C and D With C and D as centers and any radius R2 greater than ½ the radius of arc CD, draw two arcs to intersect, locating point E Draw a line through points O and E to bisect angle AOB Divide a Line into Equal Parts Given line AB Draw a line from endpoint A perpendicular to line AB Position scale, placing zero on line AC at an angle so that the scale touches point B Keeping zero on line AC, adjust the angle of the scale until any of the desired number of divisions are included between line AC and point B A Mark the divisions Draw lines parallel to AC through the division marks to intersect line AB C B Construct a Hexagon given distance Across Flats (Circumscribed) prefix “circum” – around, outside,… as in circumference” Given distance across the flats of a hexagon, draw centerlines and a circle with a diameter equal to the distance across flats With parallel edge and 30° – 60 ° triangle, draw the tangents Construct a Hexagon given distance Across Corners (Inscribed) Given distance AB across the corners, draw a circle with AB as the diameter With A and B as centers and the same radius, draw arcs to intersect the circle at points C, D, E, and F Connect the points to complete the hexagon C D A B F E Construct an Octagon Across Flats (Circumscribed) Given the distance across the flats, draw centerlines and a circle with a diameter equal to the distance across flats With a parallel edge and 45 triangle, draw lines tangent to the circle in the order shown to complete the octagon 1 5 7 3 4 8 6 2 Construct an Octagon Across Corners (Inscribed) Given the distance across the corners, draw centerlines AB and CD and a circle with a diameter equal to the distance across corners With the T-square and 45° triangle, draw diagonals EF and GH Connect the points to complete the octagon C G E B A H F D Construct an Arc Tangent to Two Lines at an Acute Angle A Given lines AB and CD Construct parallel lines at distance R B O Construct the perpendiculars to locate points of tangency With O as the point, construct the tangent arc using distance R C D Construct an Arc Tangent to Two Lines at an Obtuse Angle A Given lines AB and CD Construct parallel lines at distance R O Construct the perpendiculars to locate points of tangency With O as the point, construct the tangent arc using distance R B C D Construct an Arc Tangent to Two Lines at Right Angles Given angle ABC With B as the point, strike arc R1 equal to given radius A O D With D and E as the points, strike arcs R2 equal to given radius With O as the point, strike arc R equal to given radius B E C Construct an Arc Tangent to a Line and an Arc Given line AB and arc CD Strike arcs R1 (given radius) Draw construction arc parallel to given arc, with center O Draw construction line parallel to given line AB From intersection E, draw EO to get tangent point T1, and drop perpendicular to given line to get point of tangency T2 Draw tangent arc R from T1 to T2 with center E O C E T1 R1 A B D T2 Construct an Arc Tangent to Two Arcs Given arc AB with center O and arc CD A with center S Strike arcs R1 = radius R Draw construction arcs O parallel to given arcs, using centers O and S Join E to O and E to S to get tangent points T Draw tangent arc R from T to T, with center E E T BC S T D