ppt
advertisement
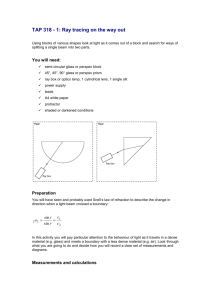
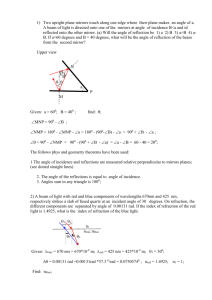
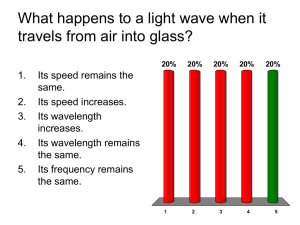
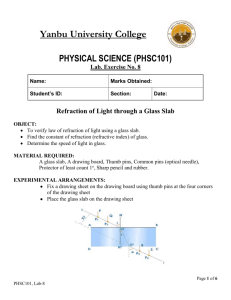
Physics 2112 Unit 25 What happens at boundaries - Reflection - Refraction - Snell’s Law - Critical Angle Polarization - Brewster’s Angle Topic 25, Slide 1 Boundaries Recall from 2111: When wave hits a boundary where speed changes - part is transmitted - part is reflected DEMO Same with E&M: Think of window. Can see through it Can see reflection in it Speed of light is different in vacuum and glass Topoc 25, Slide 2 Speed of Light in media Relative speeds given by index of refraction, n n= speed of light in vacuum speed of light in media Media vacuum air water alcohol glass diamond = V C n 1.0 ~1.0 1.33 1.36 1.5 2.4 Recall: c 1 o o So can think of n as: o o / Topic 25, Slide 3 Reflection Measured from normal Topic 25, Slide 4 CheckPoint 2: Changes at Boundary A ray of light passes from air into water with an angle of incidence of 30 degrees. 30o Which of the following quantities does not change as the light enters the water? A. B. C. D. E. wavelength frequency speed of propagation (A) and (B) (B) and (C) Topic 25, Slide 5 Refraction: Snell’s Law tab=Dxab/v1 tab = tdc a D b c d D sin 2 D sin 1 c / n2 c / n1 n2 sin 2 n1 sin 1 Unit 25, Slide 6 Think of it another (weird) way… Minimum Travel Time What's the fastest path to the ball knowing you can run faster than you can swim? This one is better Not the quickest route… Topic 25, Slide 7 Not on test…. A x1 l1 Same Principle works for Light! y1 D y2 l2 x2 Time from A to B : To find minimum time, differentiate t wrt x1 and set 0 How is x2 related to x1? Setting dt/dx1 0 l l t 1 2 v1 v2 x12 y12 v1 B x22 y22 v2 dt x1 x2 dx2 dx1 v1 x12 y12 v2 x22 y22 dx1 x2 D x1 x1 x 2 0 v1l1 v2l2 dx2 1 dx1 sin 1 sin 2 v1 v2 v c/n n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 Topic 25, Slide 8 REALLY(!) weird (….but not on test) This business of “minimum travel time” is everywhere in nature! Remember from 2111? When you kick a soccer ball up at 30o, where does it land? It lands so that the integral minimum value. “Principle of Least Action” ( KE PE )ds has “Lagranginan” CheckPoint 2: Refraction A ray of light is bent as it passes from medium 1 to medium 2. Compare the indices of refraction in the two mediums. A. n1 > n2 B. n1 = n2 C. n1 < n2 Topic 25, Slide 10 Example 25.1: Cube of Glass 25o A beam of laser light hits a cube of glass that is 4cm on a side with a angle that is 25o to the normal. The index of refraction for glass is n= 1.5. At what angle will it leave the cube? ? ? How much is the beam shifted by the cube? Topic 25, Slide 11 Example 25.2: Fish in the water The light from a fish is incident from below on the boundary between water and air with an incident angle of 30o. 30o At what refracted angle does it leave the boundary? What if the incident angle had been 60o? Topic 25, Slide 12 Phet Demo Click Here for Demo Topic 25, Slide 13 Total Internal Reflection NOTE: n1 > n2 implies 2 > 1 1 > c BUT: 2 has max value = 90o! Total Internal Reflection Unit 25, Slide 14 Example 25.3: Diver’s Ilusion If a scuba diver looks straight up towards the surface from underwater, he see a bright circle of light. Why? What is the size of that circle? Unit 25, Slide 15 Checkpoint 2 A light ray travels in a medium with n1 and completely reflects from the surface of a medium with n2. The critical angle depends on: A. n1 only B. n2 only C. both n1 and n2 Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 25, Slide 16 How much is reflected? When going from n1>n2, some is reflected, some is transmitted (refracted) How much goes into each? Complex. We can do extremes. i 90 i 0 o o R 1 n 2 n1 2 R( ) n2 n1 Unit 25, Slide 17 Example 25.3: Reflection from Window If you looked straight into a window made of regular glass, you would see a reflection of the things behind you. What refraction of the intensity of the original waves would in that reflected image? Topic 25, Slide 18 Polarization Unpolarized Intensity decreased in plane of incidence Partially polarized plane of incidence Topic 25, Slide 19 Polarization Completely polarized when Q1 + Q2 = 90o Brewster’s Angle: QB = tan-1(n2/n1) 1 2 90 sin 2 sin(90 1 ) cos1 Snell’s Law: n2 sin 2 n2 cos1 n1 sin 1 tan1 n2 n1 Unit 25, Slide 20 Example 25.4: Brewster’s Angle A light beam is incident on a piece of glass (n=1.5) at the minimum angle for which to reflected beam is completely polarized. What is Qr for the portion of the beam that is refracted? Q B Qr Topic 25, Slide 21 CheckPoint 4 A ray of light passes from air into water with an angle of incidence of 30 degrees. 30o Some of the light also reflects off the surface of the water. If the incident light is initially unpolarized, the reflected light will be A. Unpolarized B. Somewhat horizontally polarized C. Somewhat vertically polarized Topic 25, Slide 22 CheckPoint 3 A light is shining at the bottom of a swimming pool (shown in yellow in the figure). A person is standing at the edge of the pool as shown. Can the person standing on the edge of the pool be prevented from seeing the light by total internal reflection at the water-air surface? A. yes B. no Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 25, Slide 23 Dispersion Speed of E&M wave in media decreases in media slightly with frequency dispersion n is slight frequency (wavelength) dependent Topic 25, Slide 24 Rainbows Refraction (dispersion) Rain drops Mixed (white) light reflection Refraction (dispersion) 84o Topic 25, Slide 25 Example 25.4: Meter Stick in Tank A meter stick lies at the bottom of a rectangular water tank of height 50cm. You look into the tank at an angle of 45o relative to vertical along a line that skims the top edge of the tank. 45o nwater 1.33 50 cm 0 20 40 60 meter stick 80 100 What is the smallest number on the meter stick that you can see? Unit 25, Slide 26 Summary from n2 to n1 Unit 25, Slide 27