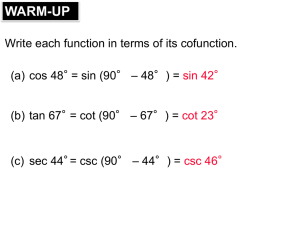
Finding Reference Angles
advertisement

Finding Reference Angles It is necessary to be able to make larger angles smaller. We do this by finding reference angles: Determine the reference angle for 140 degree angle. Step: 1. Start by drawing the given angle 2. Now, we determine how many degrees it is until we get to the x-axis (horizon) 40 140 3. This is your reference angle 4. A reference angle is always positive 40 degrees is the reference angle for 140 degrees 180 140 40 A reference angle must be an ACUTE angle!! Determine the reference angle for a 240 degree angle. Determine the reference angle for a 323 degree angle. 240 323 60 240 180 60 360 323 37 In the first quadrant, the angles are acute, so no need to find a reference angle. 37 Determine the reference angle for a 470 degree angle. Determine the reference angle for a -125 degree angle. 470 70 55 125 470 360 110 180 110 70 180 125 55 Homework Page 8 & 9 #16,28 Applications of reference angles: Express as a function of a positive acute angle: tan 100 80 100 Step: 1. Start by drawing the given angle 2. Find the reference angle 3. Rewrite the function using reference angle 4. Determine SIGN of function in quadrant where it was drawn tan 80 What is tan in quadrant II? tan 80 180 100 80 tan 100 tan 80 S A T C Express as a function of a positive acute angle: Express as a function of a positive acute angle: cos 241 sin 492 492 241 48 61 492 360 132 241 180 61 cos 61 cos 61 180 132 48 sin 48 Applications of reference angles: 1. Start by drawing the given angle Find the exact value of each expression: Reference angle 2. Find the reference angle 3. Rewrite the function using reference angle cos 120 60 Step: 4. Determine SIGN of function in quadrant where it was drawn 120 5. Now find exact value using exact value chart 180 120 60 cos 60 1 cos 60 2 Cos in quad II is negative 0 1 2 Since cos is negative in 3 1 2 quadrant II, then the exact value is negative as well 0 3 3 2 2 3 2 1 2 2 1 2 0 1 3 undefined Find the exact value of each expression: tan 315 0 1 2 2 2 3 2 1 1 3 2 2 2 1 2 0 0 3 3 1 45 315 360 315 45 tan 45 tan 45 1 3 undefined Find the exact value of each expression: sin 120 60 cos 210 120 210 30 180 120 60 3 sin 60 2 210 180 30 cos 30 3 cos 30 2 Find the exact value of each expression: sin 600 tan 30 600 30 60 600 360 240 240 180 60 sin 60 3 sin 60 2 tan 30 3 tan 30 3 30 Exact Values of quadrantal angles: We are going to graph four points and use our knowledge of the unit circle to help us! Pcos , sin sin 0,1 cos y-value is sin 1,0 1,0 0,1 Just use these points to find the sin or cos of any angle falling on that line. sin 90 1 cos 180 1 sin 360 0 Exact Values of quadrantal angles: How do we find tan of these angles? 0,1 1,0 Remember: tan 180 0 sin 180 0 cos 180 1 tan 270 0,1 sin cos 1 sin 90 undefined 0 cos 90 tan 90 1,0 tan tan 360 undefined 0 Homework •Page 8 & 9 #8-14,21,24