5.1 Radian and Degree Measure Measuring Angles
advertisement

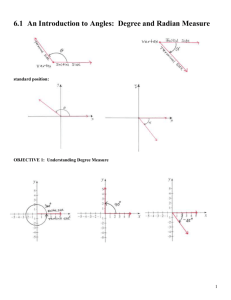
Angles and Arcs in the Unit Circle 1 In this section, we will study the following topics: Terminology used to describe angles Degree measure of an angle Radian measure of an angle Converting between radian and degree measure Finding coterminal angles 2 Angles Trigonometry: measurement of triangles Angle S e c tio n 4 .1 , F ig u re 4 .1 , T e rm in a l a n d Measure In itia l S id e o f a n A n g le , p g . 2 4 8 C o p yrig ht © H o ug hto n M ifflin C o m p a n y. A ll rig hts re se rve d . D ig ita l F ig u re s , 4 – 2 3 Standard Position S e c tio n 4 .1 , F ig u re 4 .2 , S ta n d a rd P o s itio n o f a n A n g le , p g . 2 4 8 Vertex at origin C o p yrig ht © H o ug hto n M ifflin C o m p a n y. A ll rig hts re se rve d . The initial side of an angle in standard position is always located on the positive x-axis. D ig ita l F ig u re s , 4 – 3 4 Positive and S negative angles Figure 4.3, P ositive and ection 4.1, N egative A ngles, pg. 248 When sketching angles, always use an arrow to show direction. C opyrig ht © H o ug hto n M ifflin C om pany. A ll rig hts re serve d. D igital F ig ures, 4–4 5 Measuring Angles The measure of an angle is determined by the amount of rotation from the initial side to the terminal side. There are two common ways to measure angles, in degrees and in radians. We’ll start with degrees, denoted by the symbol º. One degree (1º) is equivalent to a rotation of 1 of one 360 revolution. 6 S e c tio n 4 .1 , F ig u re 4 .1 3 , C o m m o n D e g re e Measuring Angles M e a s u re s o n th e U n it C irc le , p g . 2 5 1 1 360 C o p yrig ht © H o ug hto n M ifflin C o m p a n y. A ll rig hts re se rve d . D ig ita l F ig u re s , 4 – 9 7 Classifying Angles Angles are often classified according to the quadrant in which their terminal sides lie. Ex1: Name the quadrant in which each angle lies. 50º Quadrant 1 208º Quadrant 3 II I -75º Quadrant 4 III IV 8 Classifying Angles Standard position angles that have their terminal side on one of the axes are called quadrantal angles. For example, 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º, … are quadrantal angles. 9 Coterminal Angles e c tio n same 4 .1 , Finitial ig u re 4 .4 , C o tesides rm inare al Angles thatShave the and terminal A n g le s , p g . 2 4 8 coterminal. Angles and are coterminal. C o p yrig ht © H o ug hto n M ifflin C o m p a n y. A ll rig hts re se rve d . D ig ita l F ig u re s , 4 – 5 10 Example of Finding Coterminal Angles You can find an angle that is coterminal to a given angle by adding or subtracting multiples of 360º. Ex 2: Find one positive and one negative angle that are coterminal to 112º. For a positive coterminal angle, add 360º : 112º + 360º = 472º For a negative coterminal angle, subtract 360º: 112º - 360º = -248º 11 Ex. 3: Find one positive and one negative angle that is coterminal with the angle = 30 o in standard position. Ex. 4: Find one positive and one negative angle that is coterminal with the angle = 272 in standard position. Radian Measure A second way to measure angles is in radians. Definition of Radian: e c tio n 4 .1 , F igof u rea 4central .5 , Illu s tra tio n o fthat intercepts One radian isSthe measure angle e n g th , p g . 2 4 9 arc s equal in lengthA rc to Lthe radius r of the circle. In general, s r C op yrig h t © H ou gh ton M ifflin C om p any. All righ ts reserved . D ig ita l F ig u re s , 4 –6 13 Radian Measure 2 radians corresponds to 360 2 6.28 radians corresponds to 180 3.14 2 radians corresponds S e c tio n 4 .1 ,to F ig90 u re4 .6 , Illu s tra tio n o f S ix R a d ia n L e n g th s , p g . 2 4 9 C o p yrig ht © H o ug hto n M ifflin C o m p a n y. A ll rig hts re se rve d . 1.57 2 D ig ita l F ig u re s , 4 – 7 14 S e c tio n 4 .1 , F ig u re 4 .7 , C o m m o n Radian Measure R a d ia n A n g le s , p g . 2 4 9 15 Conversions Between Degrees and Radians 1. To convert degrees to radians, multiply degrees by 2. To convert radians to degrees, multiply radians by 180 180 16 a) 60 b) 30 c) -54 d) -118 e) 45 a) b) 6 c) d) 2 11 18 e) 9 3 Ex 8: Find one positive and one negative angle that is coterminal with the angle = 7 in standard position. 5 Degree and Radian Form of “Special” Angles 90 ° 120 ° 60 ° 135 ° 45 ° 150 ° 30 ° 0° 180 ° 360 ° 210 ° 330 ° 225 ° 315 ° 240 ° 300 ° 270 ° 20 Convert from degrees to radians. 1. 54 2. -300 Convert from radians to degrees. 3. 11 4. 3 1 3 12 Find one postive angle and one negative angle in standard position that are coterminal with the given angle. 5. 135 6. 11 6